Comprehensive Guide to Spotting and Managing Skin Rashes for Healthy Skin
This comprehensive guide provides detailed information on recognizing and managing skin rashes, emphasizing the importance of accurate diagnosis and professional treatment. It covers infectious and non-infectious causes, treatment options, and preventive strategies to maintain healthy skin. Whether dealing with mild irritation or complex skin conditions, understanding the different types of rashes and their management helps in achieving healthier skin and reducing discomfort effectively.
Comprehensive Guide to Spotting and Managing Skin Rashes for Healthy Skin
What Are Skin Rashes and Why Do They Occur?
Skin rashes are visible changes on the outer layer of the skin, often appearing as redness, bumps, swelling, blisters, or other irregularities. They can affect anyone regardless of age, from infants and young children to adults and seniors. The occurrence of skin rashes is a common dermatological concern and can result from a multitude of causes, including allergic reactions, infections, environmental factors, and underlying health conditions. Understanding the different types of rashes, their underlying causes, and appropriate management strategies is essential for maintaining healthy skin and preventing complications.
The Role of a Dermatologist in Skin Rash Management
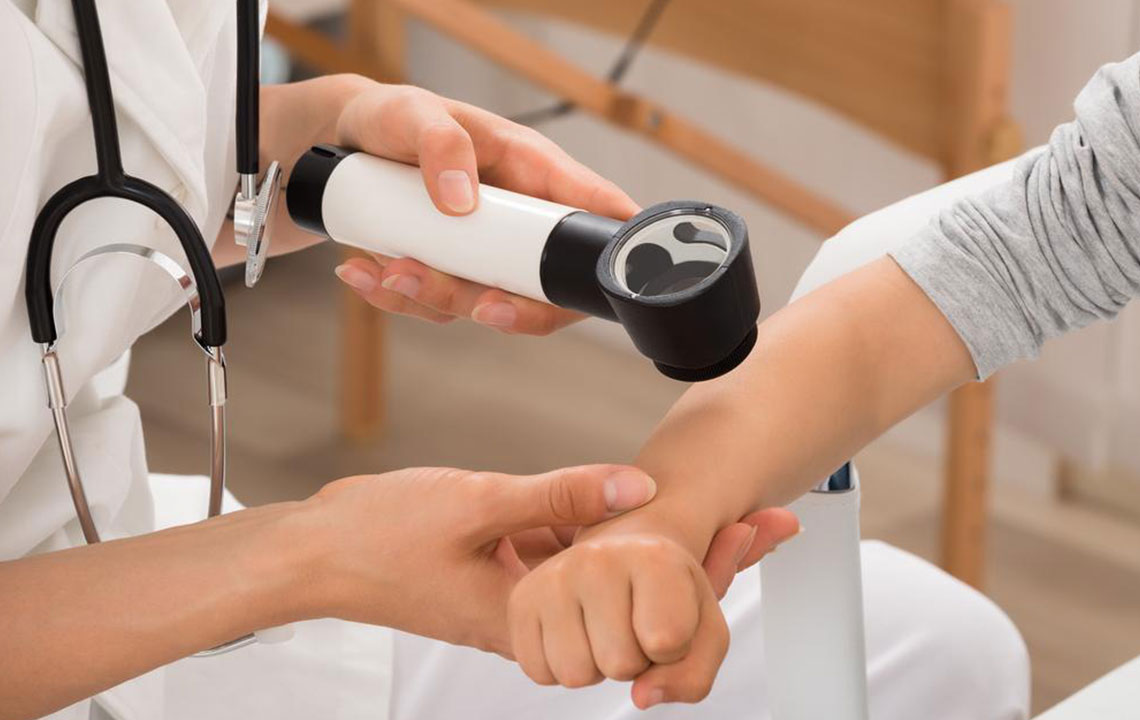
A dermatologist is a medical specialist trained in diagnosing and treating a wide array of skin conditions, including various types of rashes. When skin irritations are persistent, worsening, or difficult to identify, consulting a dermatologist is crucial. They utilize advanced diagnostic tools, such as skin biopsies or allergy tests, to pinpoint the exact cause of a rash and prescribe targeted treatments. Dermatologists' expertise ensures that skin conditions are managed effectively, reducing discomfort and preventing long-term skin damage.
Skin rashes are generally categorized into infectious and non-infectious types, each requiring specific diagnostic and treatment approaches. Recognizing the differences is vital for effective management.
Infectious Rashes and Their CausesInfectious rashes are caused by microorganisms, including viruses, fungi, bacteria, or parasites. These rashes are often contagious and can spread from person to person if not properly treated. Common infectious skin rashes include chickenpox, shingles, ringworm, impetigo, herpes simplex, and scabies. Managing these rashes involves addressing the underlying infection with appropriate medications, such as antiviral drugs, antifungal creams, antibiotics, or antiparasitic treatments. Isolation and hygiene measures are also important to prevent spreading the infection to others.
Non-Infectious Skin Rashes and Their Common Causes
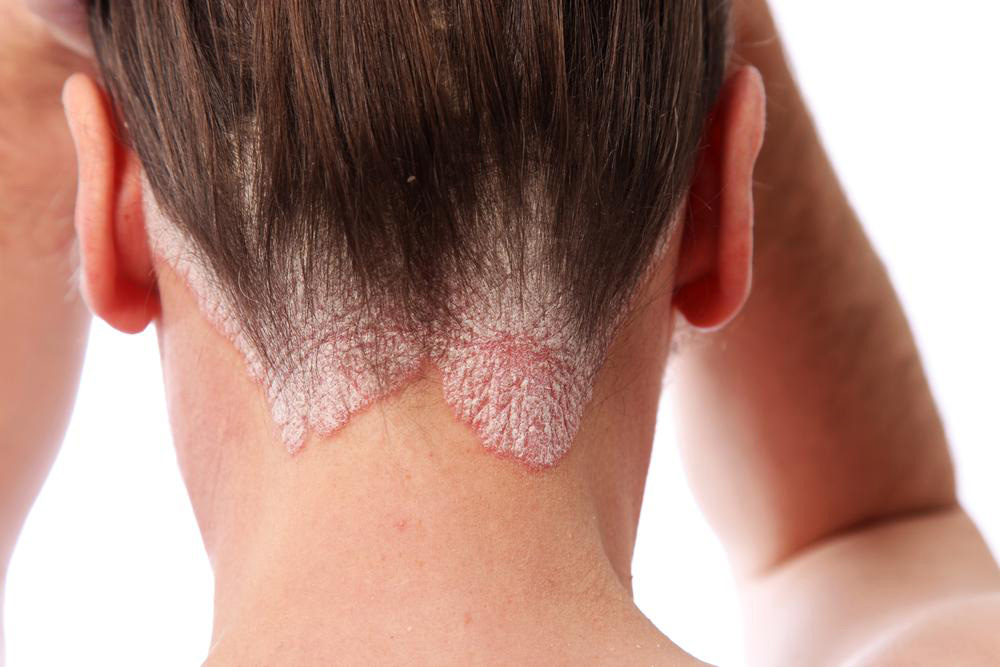
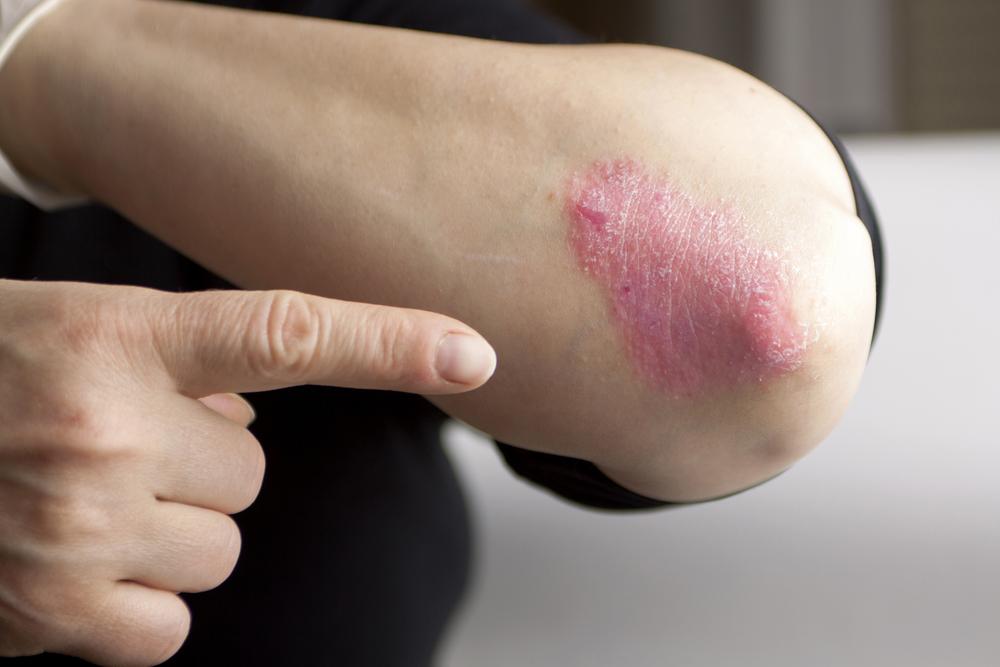
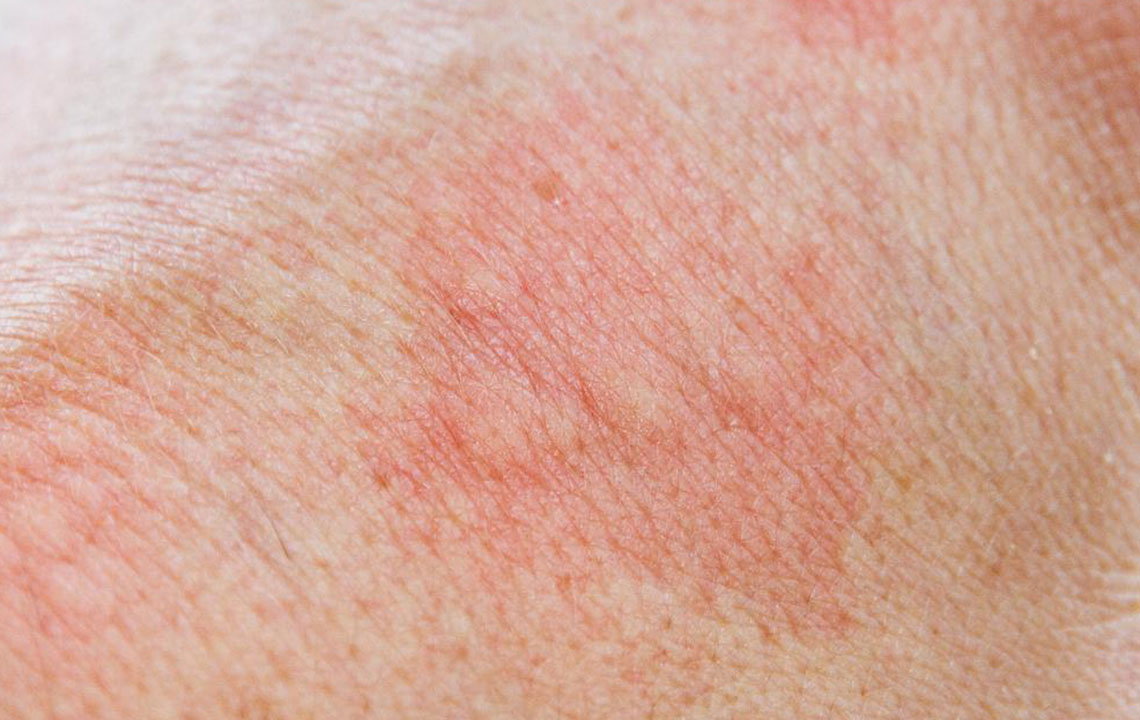
Non-infectious rashes are unrelated to infectious agents and often stem from allergic reactions, autoimmune disorders, or skin sensitivities. Conditions such as psoriasis, eczema (atopic dermatitis), contact dermatitis, hives (urticaria), dry skin dermatitis, and allergic reactions to food or environmental factors fall into this category. These rashes are typically non-contagious but can cause significant discomfort, itching, and inflammation. Managing non-infectious rashes often involves topical medications, oral antihistamines, immune-modulating therapies, and lifestyle modifications.
Effective Treatment and Management Strategies
Managing skin rashes effectively requires accurate diagnosis and an appropriate treatment plan. Basic self-care measures include regular gentle skin cleansing, avoiding harsh soaps, and using cold water baths to soothe irritation. Wearing loose, soft, and breathable clothing, especially made from natural fibers like cotton, helps prevent further irritation and allows the skin to heal. It is crucial to avoid scratching, which can aggravate the rash, cause secondary infections, and prolong recovery.
Dietary adjustments can also support treatment, especially if food allergies are identified as a cause of rashes. Common dietary allergens such as eggs, nuts, shellfish, and certain fish should be avoided if associated with skin reactions. An allergist or dermatologist can help identify trigger foods through allergy tests and recommend suitable elimination diets.
Consulting a healthcare professional ensures proper diagnosis, personalized treatment, and management guidance. In some cases, topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, moisturizers, or immunosuppressants may be prescribed to control symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Additionally, monitoring environmental factors, such as exposure to allergens or irritants, can help reduce rash occurrences.