Comprehensive Guide to Itchy Skin: Causes, Symptoms, and Proven Remedies
This comprehensive article explores the many causes of itchy skin, symptoms to watch for, and proven remedies to achieve relief. From dry skin and allergies to underlying health conditions, the guide offers practical advice on managing persistent itching. Learn how proper skincare, avoiding irritants, and seeking medical advice can help alleviate discomfort and prevent complications. Whether you’re dealing with Seasonal dryness, skin conditions like eczema, or internal medical issues, this detailed overview provides essential insights for effective skin health management.

Comprehensive Guide to Itchy Skin: Causes, Symptoms, and Proven Remedies
Persistent itching of the skin, whether on the arms, legs, or across the entire body, can be both frustrating and alarming. Many individuals experience bouts of itchy skin at some point, but understanding the underlying causes is crucial for effective treatment and relief. Itchy skin, medically known as pruritus, can manifest without apparent skin changes, making diagnosis a bit tricky. However, in some cases, symptoms such as redness, dryness, flaking, spots, or blisters accompany the itching, providing clues to underlying health issues.
Addressing itchy skin effectively requires a comprehensive understanding of its potential causes. These causes range from common skin conditions and allergies to internal health disorders. Recognizing triggers and symptoms can help in managing and preventing persistent discomfort. In this guide, we delve into the various reasons behind itchy skin, symptom identification, and effective, scientifically-supported remedies for relief.
Common Causes of Itchy Skin
Dry Skin: One of the most prevalent causes of itchiness, especially during winter months or in dry climates. Dry skin, or xerosis, results from lack of moisture, leading to rough, flaky, and itchy skin.
Skin Conditions: Conditions such as eczema (atopic dermatitis), psoriasis, and dermatitis cause inflammation, dryness, and irritation, all contributing to persistent itching.
Allergic Reactions: Allergies to soaps, detergents, skincare products, cosmetics, or foods can trigger immune responses manifesting as itchy patches on the skin.
Irritants and Environmental Factors: Exposure to chemicals, harsh cleaning agents, or environmental pollutants can irritate the skin, leading to itchiness.
Medications: Certain drugs may cause allergic or side-effect related skin reactions, resulting in itching.
Internal Medical Conditions: Systemic illnesses such as liver disease, thyroid disorders, anemia, or nerve-related issues can cause widespread or localized itching, often without skin lesions.
Symptoms Associated with Itchy Skin
Redness and inflammation on areas of itching
Dryness and flakiness of the skin
Scaling or thickening of skin in chronic cases
Appearance of spots, hives, or blisters
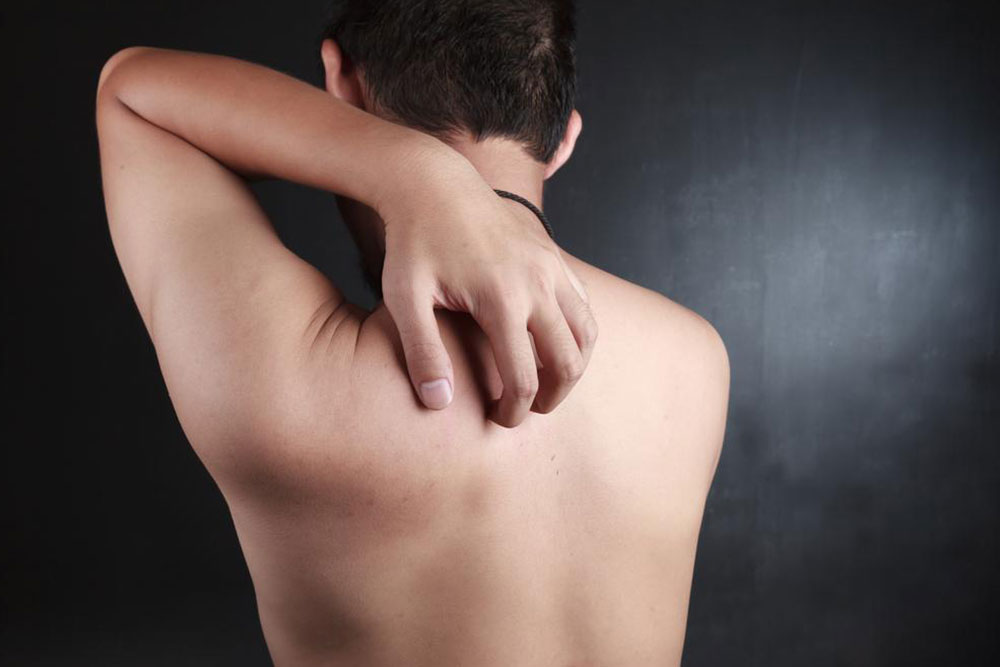
Persistent urge to scratch, which may lead to skin damage and secondary infections
Effective Remedies and Preventive Measures
Managing itchy skin involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, topical treatments, and medical interventions. The key is to identify and address the root cause and prevent exacerbation through proper skin care.
1. Maintain Proper Skin Hygiene and Hydration
Regular cleansing with mild, fragrance-free soaps helps remove irritants without stripping the skin's natural oils. Applying moisturizers immediately after bathing helps lock in moisture, especially those containing ceramides, glycerin, or hyaluronic acid.
2. Avoid Irritants and Allergens
Switch to hypoallergenic skincare products, wear breathable fabrics like cotton, and avoid exposure to known allergens or harsh chemicals. Keeping a diary of allergen exposure can help identify triggers.
3. Use Medicated Treatments
For inflammatory or allergic skin reactions, topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors may be prescribed by a healthcare provider. These help reduce inflammation and itching effectively. In severe cases, light therapy or phototherapy may be considered.
4. Address Underlying Internal Conditions
If systemic diseases are suspected, clinicians may recommend blood tests and further investigations. Managing conditions like liver dysfunction, thyroid imbalances, or anemia can significantly reduce associated itching.
5. Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day
Use cool compresses on itchy areas to soothe discomfort
Avoid hot showers and harsh scrubbing of the skin
Use gentle laundry detergents and avoid fabric softeners with strong fragrances
Having a consistent skincare routine and avoiding known triggers can greatly alleviate persistent itching. However, if relief is not achieved with home remedies, consulting a dermatologist or healthcare professional is essential for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment.
When to See a Doctor
Persistent itching accompanied by severe redness, swelling, oozing, or signs of infection requires prompt medical attention. Additionally, if the itching spreads across large areas of the body, worsens despite treatment, or is associated with other symptoms like weight loss, fatigue, or fever, an underlying systemic illness should be evaluated. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can prevent complications and improve quality of life.
In summary, itchy skin is a common condition with many potential causes. Recognizing symptoms and understanding preventive and treatment options can help manage this discomfort effectively. With proper skin care, lifestyle changes, and medical support when needed, individuals can find relief from persistent skin itchiness and enjoy healthier, more comfortable skin.