Comprehensive Guide to Adult Acne Treatments and Their Top Benefits
Adult acne is a common skin concern that extends beyond teenage years. Effective management involves understanding its causes—like hormonal fluctuations, diet, and environmental factors—and applying targeted treatments. This comprehensive guide explores over-the-counter remedies, prescription options, and lifestyle tips to control adult acne, helping you achieve clearer, healthier skin while reducing the risk of future breakouts. The article emphasizes a personalized approach, combining skincare routines with medical interventions when necessary, to restore your confidence and skin health.

Comprehensive Guide to Adult Acne Treatments and Their Top Benefits
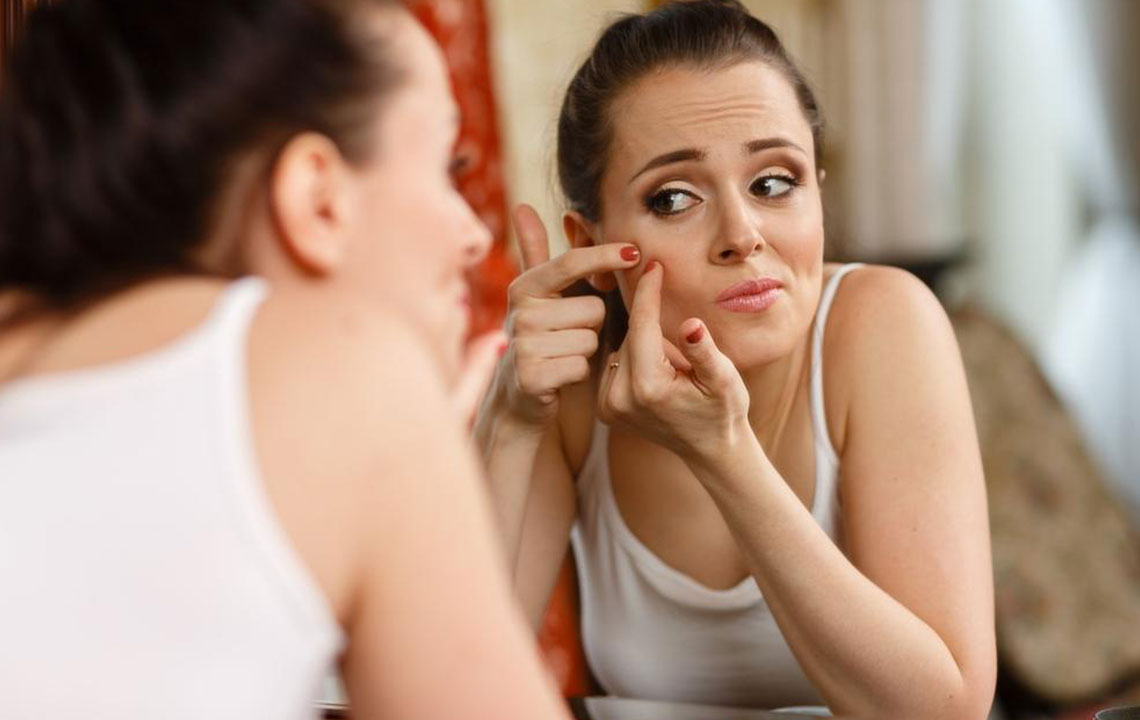
Acne is often associated with teenagers, but for many adults, skin problems like breakouts and blemishes continue to be a persistent issue well into their 30s, 40s, and beyond. Managing adult acne requires a nuanced approach, tailored to the unique skin conditions and triggers that affect mature skin. Unlike teenage acne, which is primarily driven by hormonal fluctuations during puberty, adult acne can be caused by a complex mix of hormonal imbalances, lifestyle factors, environmental influences, and pre-existing skin conditions. Understanding these underlying causes helps in selecting the most effective treatments to restore clear and healthy skin.
Adult acne can significantly impact confidence and emotional well-being. Therefore, it is essential to adopt a comprehensive treatment plan that combines the right skincare products, lifestyle modifications, and, if necessary, medical interventions. This detailed guide discusses the causes of adult acne, the common triggers, and the most effective over-the-counter and prescription treatments available today, highlighting their benefits and risks.
Understanding the Causes of Adult Acne
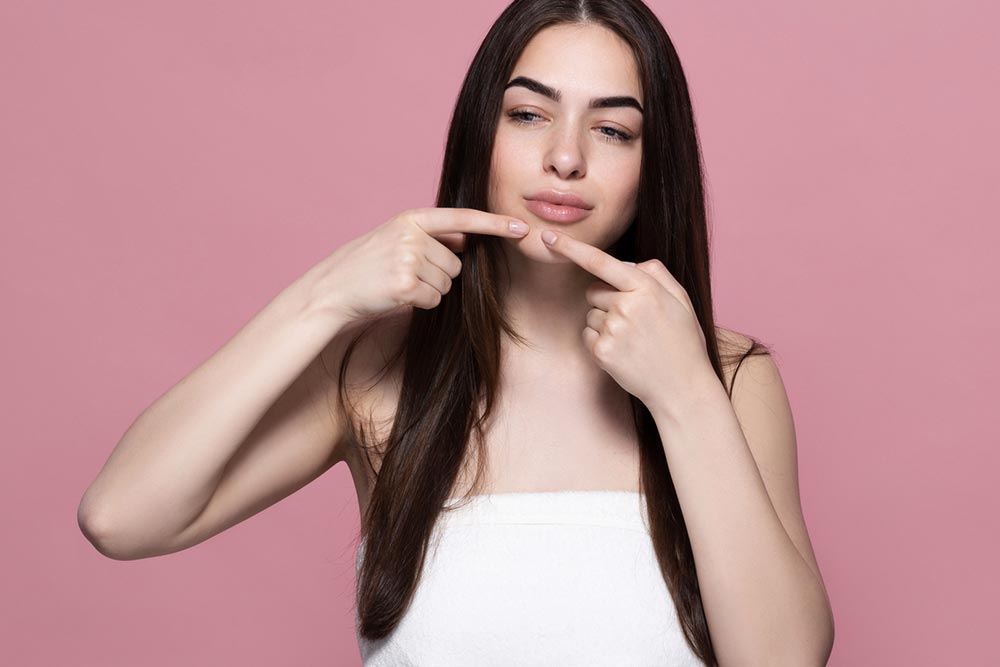
Identifying the root causes of adult acne is crucial for effective management. These causes include hormonal fluctuations, dietary habits, stress levels, environmental pollutants, and skincare routines. For instance, high sugar or dairy intake may stimulate excess oil production, leading to clogged pores and breakouts. Hormonal imbalances, such as increased testosterone or fluctuations throughout the menstrual cycle, can also elevate sebum levels, resulting in acne. Stress is another significant factor; elevated cortisol levels can trigger excess oil secretion that clogs pores. Additionally, exposure to environmental pollutants, such as smog or cigarette smoke, can introduce dirt and toxins onto the skin, aggravating existing skin conditions. Over-washing or using harsh skincare products can strip the skin's natural barrier, making it more prone to irritation and breakouts.
Managing adult acne effectively involves understanding its triggers. Stress, hormonal variations, pollution, and skincare routines all contribute to skin health. Elevated stress levels increase cortisol, leading to more oil production and clogged pores. Hormonal disturbances, such as ovarian cysts or menopause, can also cause breakouts, which might require medical management. Environmental pollutants clog pores and inflame the skin, making acne worse. Daily skincare routines with overly harsh products or excessive washing can damage the skin's natural defenses, exacerbating blemishes. Recognizing these factors aids in designing an effective treatment strategy that targets the root causes.
There are numerous over-the-counter treatments formulated specifically for adult acne, suitable for different severity levels. The most common options include:
Salicylic Acid
A beta hydroxy acid that exfoliates dead skin cells inside the pores, preventing clogging and reducing inflammation. It is primarily effective for mild to moderate acne and is usually applied as a topical gel or cleanser. Users may experience mild dryness or peeling, which can be mitigated by moisturizing properly.
Benzoyl Peroxide
Known for its antibacterial properties, benzoyl peroxide targets acne-causing bacteria and reduces inflammation, making it suitable for more active or inflamed acne. It comes in various strengths and forms like creams, gels, or washes. Initial side effects may include dryness, peeling, or redness, but these often diminish with continued use.
Sulfur
Sulfur works as a drying agent and antibacterial agent, helping to draw out excess oil and prevent bacterial proliferation. It is often used in masks or spot treatments. Care should be taken to avoid overuse, as sulfur can increase skin alkalinity and cause irritation if applied excessively.
Glycolic Acid
An alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) that promotes gentle exfoliation and enhances skin cell turnover. This helps prevent clogged pores and improves skin texture. As it increases photosensitivity, using sunscreen during the day is strongly recommended to prevent sun damage.
Isotretinoin
A powerful oral medication that drastically reduces sebaceous gland size, decreasing oil production. It is often prescribed for severe or resistant adult acne that does not respond to other treatments. Due to potential side effects, including birth defects, isotretinoin should only be used under strict medical supervision, especially by women of childbearing age.
Beyond topical treatments, healthcare professionals often prescribe oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or minocycline for resistant or inflammatory acne outbreaks. In some cases, laser therapy or light-based treatments are recommended to eradicate acne-causing bacteria, reduce oil production, and improve skin texture. Combining these approaches can lead to better outcomes and faster recovery.