Comprehensive Guide to Diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Tests, and Medical Insights
This comprehensive article provides an in-depth look at diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis, covering symptoms, physical exams, blood tests, and imaging techniques. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective management of RA, and understanding these diagnostic tools helps patients recognize signs and seek timely treatment. The article explores current challenges and future advancements in RA diagnosis, emphasizing the importance of a combined clinical approach for accurate detection and improved patient care.
Comprehensive Guide to Diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Tests, and Medical Insights
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a complex autoimmune disorder that primarily targets the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and potential joint deformity. Understanding how this condition is diagnosed is crucial for early intervention and effective management. This extensive guide explores the symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and medical tests utilized by healthcare professionals to identify RA accurately.
RA affects about 1.5 million adults in the United States, predominantly impacting women over the age of 40. It most commonly involves small joints of the hands and feet but can also cause systemic issues affecting organs such as the eyes, skin, lungs, and blood vessels. Early diagnosis is vital for preventing severe joint damage and improving quality of life.
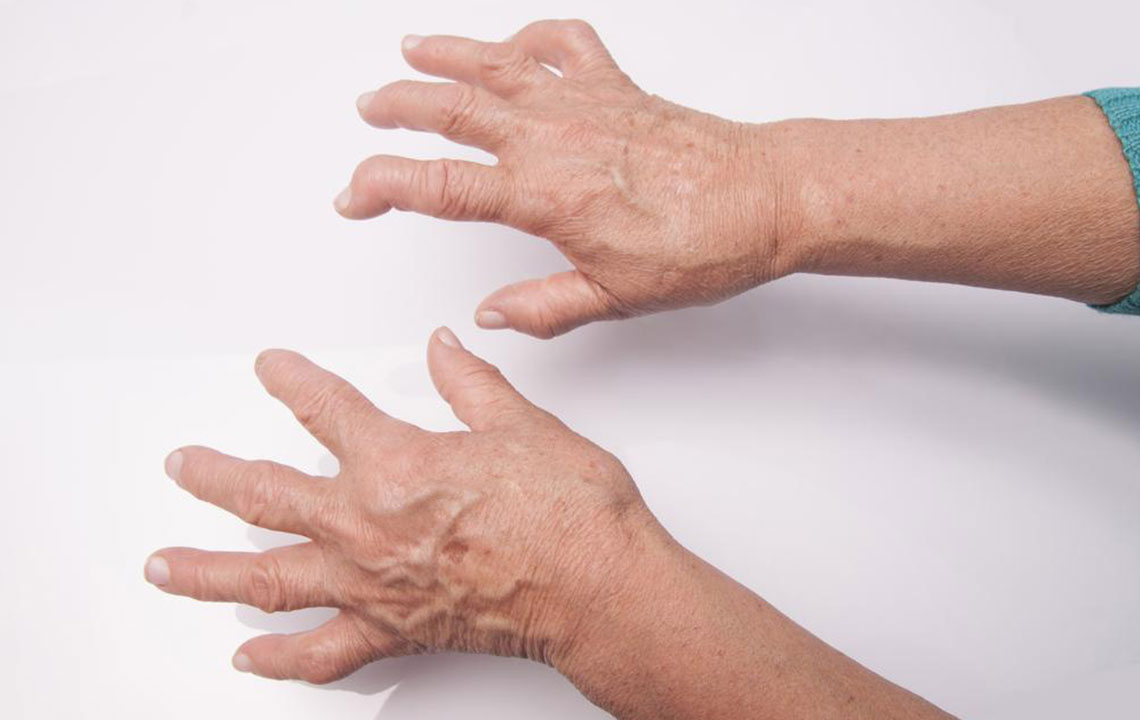
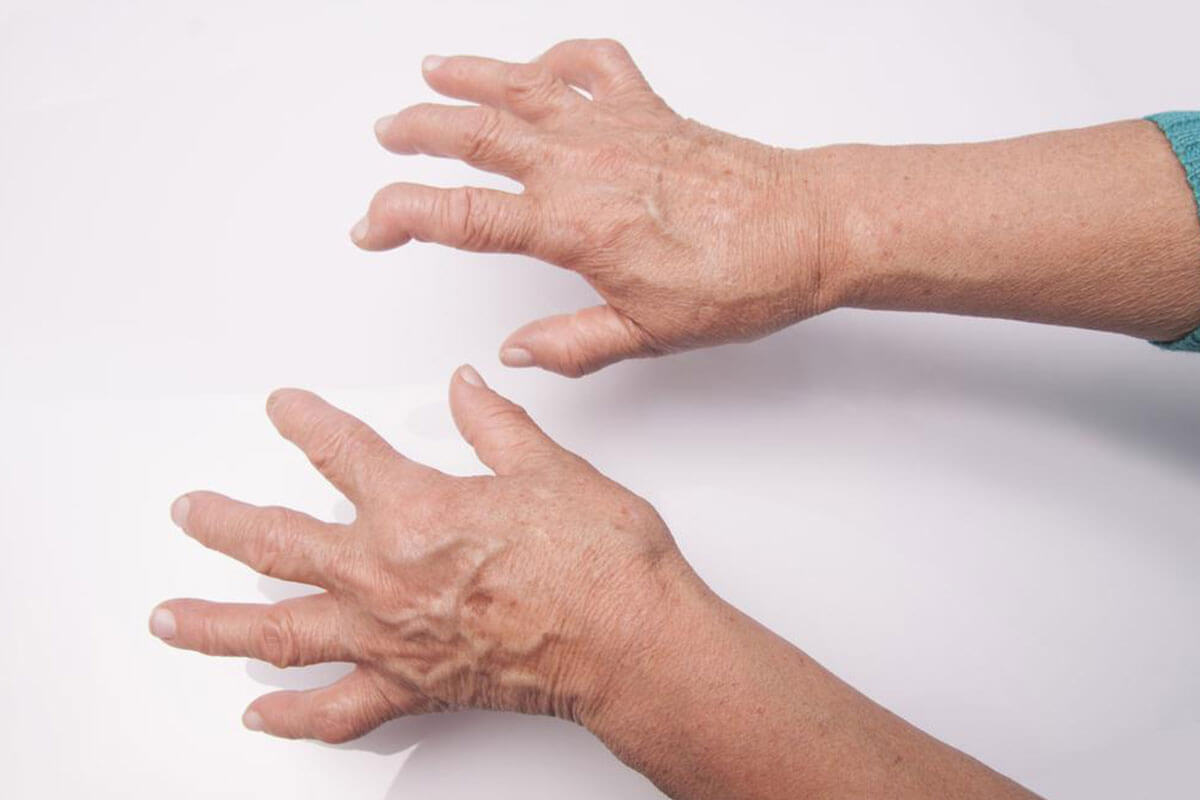
Recognizing symptoms like persistent fatigue, unexplained fever, morning stiffness lasting more than an hour, swelling in the joints, and unexplained weight loss are key indicators. These symptoms typically manifest symmetrically, affecting both sides of the body, and tend to fluctuate in intensity over time. Without proper treatment, RA can cause the joints to misalign and deform, severely impairing mobility.
Discovering the exact cause of RA remains a challenge for medical science. While the precise origin of this autoimmune disease is unknown, early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. Diagnosis involves a combination of physical examinations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies, as no single definitive test exists for RA. Healthcare providers carefully evaluate symptoms, medical history, and test results to arrive at an accurate diagnosis.
Physical Examination and Clinical Evaluation
When a patient presents with symptoms indicative of RA, the doctor begins with a comprehensive physical assessment. This includes inspecting affected joints for signs of swelling, redness, and warmth, which are hallmarks of inflammation. Muscle strength, reflexes, and range of motion are also tested to evaluate joint function.
The physician may ask about the duration and pattern of symptoms, family history of autoimmune diseases, and any systemic symptoms such as fatigue or fever. This helps distinguish RA from other forms of arthritis and inflammatory conditions.
Laboratory Tests for RA Diagnosis
Since no single laboratory test can definitively confirm RA, physicians rely on a series of blood tests that provide clues about inflammation and autoimmune activity. These include:
CRP (C-reactive protein) Test: This blood test measures the level of CRP, a protein produced by the liver during systemic inflammation. Elevated CRP levels signal active inflammation but are not specific to RA.
Rheumatoid Factor (RF) Test: RF is an antibody present in many RA patients. However, it can also be positive in other autoimmune diseases and certain infections, making it a suggestive but not conclusive marker.
Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (Anti-CCP) Test: This test detects antibodies specific to RA and is highly indicative when positive, especially in early disease.
Complete Blood Count (CBC): Analyzes blood components, often revealing anemia common in RA patients. While anemia supports the diagnosis, it is not exclusive to RA.
Imaging Studies in RA Diagnosis
In addition to blood tests and physical evaluations, imaging techniques play a pivotal role in diagnosing and monitoring RA progress. These methods help visualize joint damage, inflammation, and deformities:
X-Ray Imaging: Standard X-rays reveal bone erosion, joint space narrowing, and deformities. They are useful for assessing disease progression over time.
Ultrasound: This modality detects subtle joint inflammation and synovitis not visible on X-rays, guiding treatment decisions.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI provides detailed images of soft tissues, cartilage, and bone marrow, enabling early detection of joint inflammation and damage before irreversible changes occur.
Challenges and Future Directions in RA Diagnosis
Diagnosing RA can be complex due to overlapping symptoms with other joint diseases, such as osteoarthritis or psoriatic arthritis. The variability in symptoms and the absence of a single definitive test make clinical judgment critical. Emerging biomarkers and advanced imaging techniques continue to improve early detection, allowing for more targeted therapies.
Innovations in genetic profiling and molecular diagnostics hold promise for personalized treatment strategies aimed at halting disease progression at its earliest stages.
Conclusion
Understanding the diagnostic process for rheumatoid arthritis is essential for patients and healthcare providers alike. Early recognition of symptoms, combined with targeted blood tests and imaging studies, can lead to timely diagnosis and intervention. Although the exact cause of RA remains elusive, ongoing research is enhancing our ability to detect and treat this autoimmune condition effectively. If you experience persistent joint pain, swelling, or systemic symptoms, consulting a healthcare provider promptly can make a significant difference in your health outcomes.