Comprehensive Guide to Skin Cancer: Types, Detection, and Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive guide on skin cancer covers the main types, stages, early warning signs, and practical prevention tips. Learning to identify symptoms early and adopting protective measures can significantly reduce your risk of developing this serious condition. The article emphasizes the importance of regular skin checks, understanding different skin cancer types like melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma, and adopting sun safety habits. Protecting your skin is vital for maintaining overall health; early detection and prevention play crucial roles in treatment success and overall well-being.

Comprehensive Guide to Skin Cancer: Types, Detection, and Prevention Strategies
Enjoying time in the sun is a common activity, whether at the beach, park, or during outdoor sports. However, prolonged or unprotected exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun significantly increases the risk of developing skin cancer, a serious health concern affecting millions worldwide. Recognizing the early signs of skin cancer, understanding its different types and stages, and implementing effective prevention strategies are crucial steps in safeguarding your skin and overall health. This article provides a detailed overview of skin cancer, including its primary types, progression stages, warning signs, and practical tips to lower your risk.
Understanding the Main Types of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer encompasses a range of abnormal growths that originate in the skin's cells. The most common types include basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Each type varies in appearance, growth patterns, severity, and treatment approaches. Recognizing these differences is essential for early detection and effective management.
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Basal cell carcinoma is the most prevalent form of skin cancer, accounting for approximately 80% of cases. It often appears as small, translucent or pearly bumps, primarily on areas frequently exposed to the sun such as the face, ears, neck, and hands. BCC tends to grow slowly and invade surrounding tissues rather than metastasizing to distant organs. Despite its less aggressive nature, early diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent significant disfigurement. Common signs include open sores that persist for weeks, shiny or waxy nodules, or pinkish patches that bleed or become scaly over time.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
SCC originates in the flat squamous cells in the outermost layer of the skin. It typically manifests as firm, red, scaly patches or nodules that may crust or bleed. These lesions frequently develop on sun-exposed areas like the ears, lips, face, and hands. SCC can sometimes invade deeper tissues and, if left untreated, may spread to lymph nodes or other body parts. Risk factors include chronic sun exposure, scars, or previous skin injuries. Early detection and removal of SCCs can prevent complications and more invasive treatments.
Melanoma
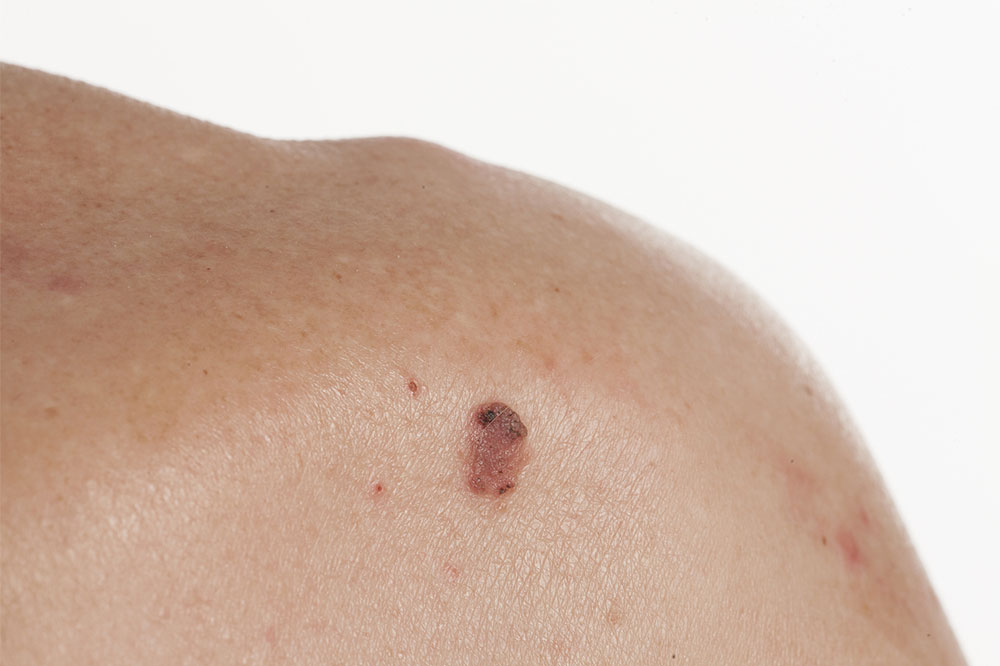
Melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer, originating from pigment-producing melanocytes in the skin. It often begins as an asymmetrical mole or dark spot that changes in size, shape, or color over time. Melanomas may ulcerate, itch, or bleed, and they have the potential to metastasize rapidly if not treated early. Early diagnosis through regular skin checks is crucial, as melanoma accounts for the majority of skin cancer-related deaths despite being less common than BCC or SCC. Recognizing the ABCDEs of melanoma—Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter over 6mm, and Evolution—is essential for early detection.
Other Non-melanoma Skin Cancers
Besides BCC, and SCC, there are other non-melanoma skin cancers that are generally less aggressive but still require attention. These may include keratoacanthomas and some rarer variants. They often appear as raised, flesh-colored, pink, or red bumps that may be smooth or scaly. Although these tumors tend to stay localized, they can cause tissue damage and warrant professional evaluation and treatment.
Stages of Skin Cancer Progression
Understanding the stages of skin cancer is vital for assessing severity and choosing appropriate treatment options. The progression includes pre-cancerous stages, early malignant stages, and advanced, metastatic stages.
Pre-cancerous Stage
This early phase involves growths like actinic keratosis or in situ melanomas. These lesions are not yet invasive but have the potential to develop into malignant skin cancers if neglected. Recognizing and treating pre-cancerous lesions can prevent progression.
Early Stage
At this stage, cancer remains confined to the outermost layers of the skin—epidermis—and has not yet spread to lymph nodes or internal organs. Superficial melanomas or early BCC and SCC fall into this category and can often be cured with surgical excision or other localized therapies.
Advanced Stage
Advanced skin cancer involves metastasis, where the tumor cells spread beyond the original site to lymph nodes, nearby tissues, or distant organs. This stage presents significant challenges and requires comprehensive treatment regimens such as wide surgical removal, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, or chemotherapy. Prognosis depends heavily on early detection and the extent of spread.
Recognizing Early Warning Signs
Early identification of skin cancer symptoms plays a critical role in successful treatment. Keep vigilant for persistent or new skin abnormalities, including:
Unhealed sores or wounds that do not recover over several weeks
Unusual growths or bumps that enlarge over time
Lesions that change in shape, size, or color
Scaly patches, reddish or flesh-colored bumps, or flat discolored areas
Any mole or spot that looks different from others or evolves suddenly
If any of these signs are observed, consulting a dermatologist promptly is essential to determine diagnosis and treatment options. Early intervention can dramatically improve outcomes and reduce the risk of severe complications.
Effective Prevention Strategies
Preventing skin cancer involves minimizing exposure to UV radiation and adopting protective behaviors. Here are proven strategies to help safeguard your skin:
Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. Apply generously to all exposed areas at least 15 minutes before sun exposure, and reapply every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
Limit direct sun exposure, especially between 10 am and 4 pm when UV rays are most intense.
Wear protective clothing such as long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and UV-protective fabrics.
Seek shade whenever possible during peak sun hours.
Avoid tanning beds and artificial UV sources, which can increase skin cancer risk.
Perform regular self-skin examinations to detect new or changing moles and skin lesions.
Schedule annual skin checks with a dermatologist, especially if you have a history of sunburns, high sun exposure, or skin cancer in your family.
Adopting these preventive measures can significantly reduce your risk of developing skin cancer and help in early diagnosis if abnormalities arise. Maintaining awareness and proactive skin health practices are essential components of long-term skin wellness.