Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing and Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
This comprehensive guide provides in-depth information on the symptoms, risk factors, early signs, and management strategies of rheumatoid arthritis. It emphasizes the importance of early detection and proactive treatment to prevent joint damage and improve overall health. Covering systemic effects and signs to watch for, the article equips readers with essential knowledge to identify RA early and seek appropriate care for better outcomes. An ideal resource for patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals alike.
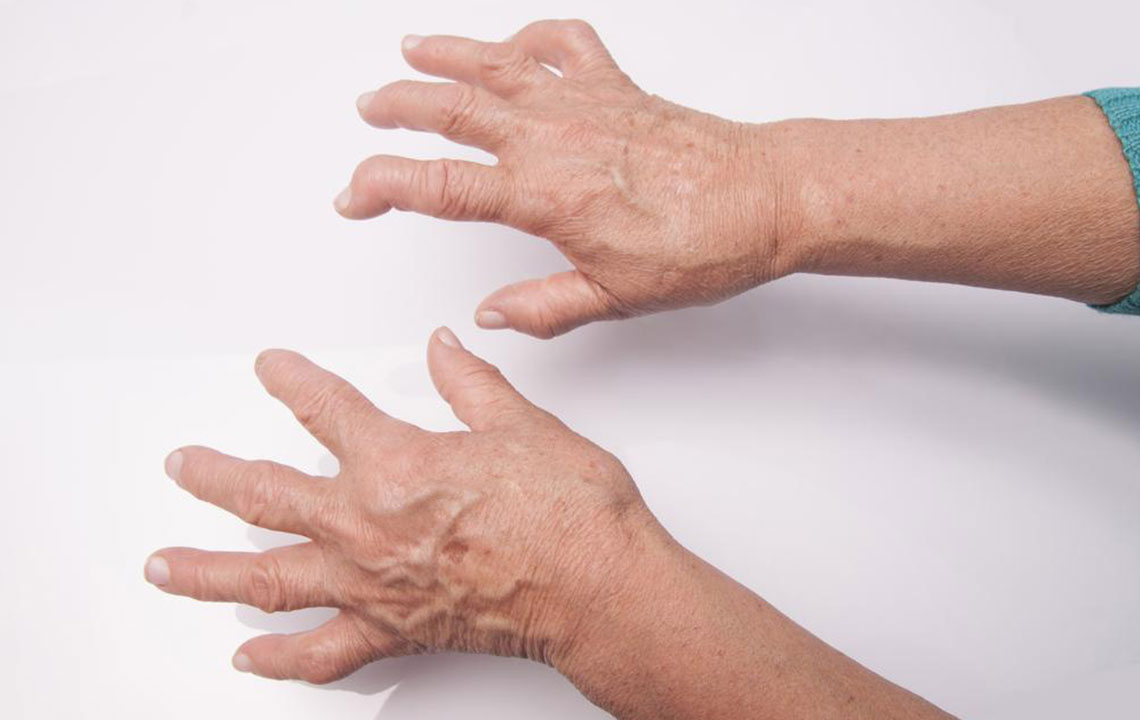
A Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing and Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a prevalent autoimmune disease that affects millions of people globally. Unlike common joint pains or routine aches, RA is characterized by persistent inflammation of the joints, which can lead to long-term joint damage if not diagnosed and managed early. The disease originates from an abnormal immune response where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own joint tissues, causing swelling, pain, and stiffness. Understanding the symptoms and effective management strategies of RA is essential for patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers to optimize quality of life and prevent irreversible damage.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis and How It Differs from Other Rheumatic Conditions
RA often gets confused with general joint discomfort or osteoarthritis. However, it has distinct features. RA presents as ongoing joint pain, swelling, and tenderness that persist over time, whereas conditions like articular rheumatism result from structural changes such as bone deformities or tissue degeneration. Essentially, RA involves systemic immune dysregulation leading to inflammation that affects multiple joints symmetrically, primarily targeting the synovial lining of joints. Recognizing these differences is crucial for prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
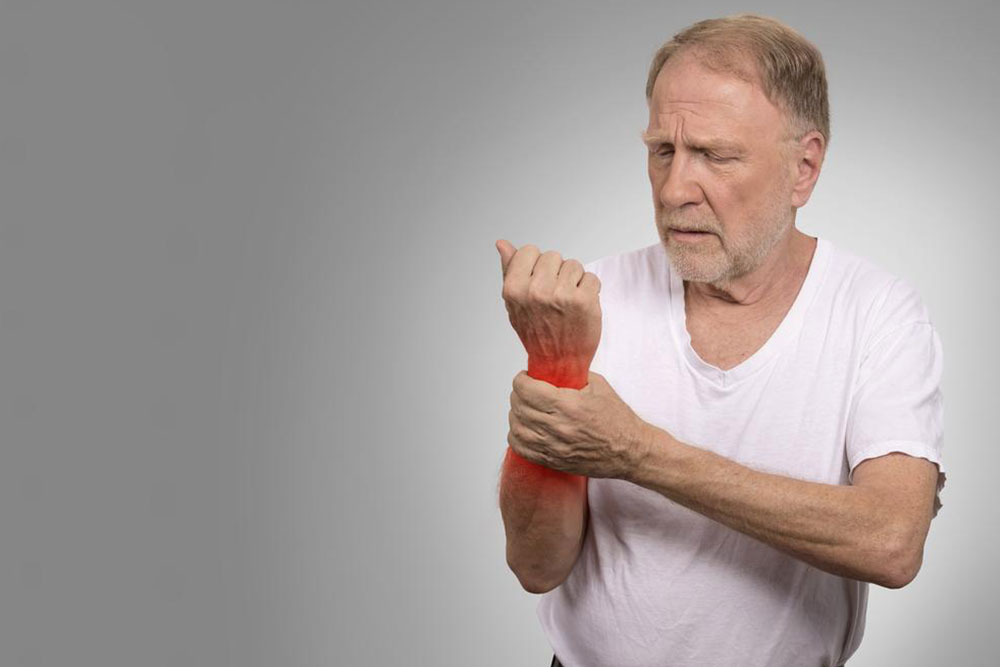
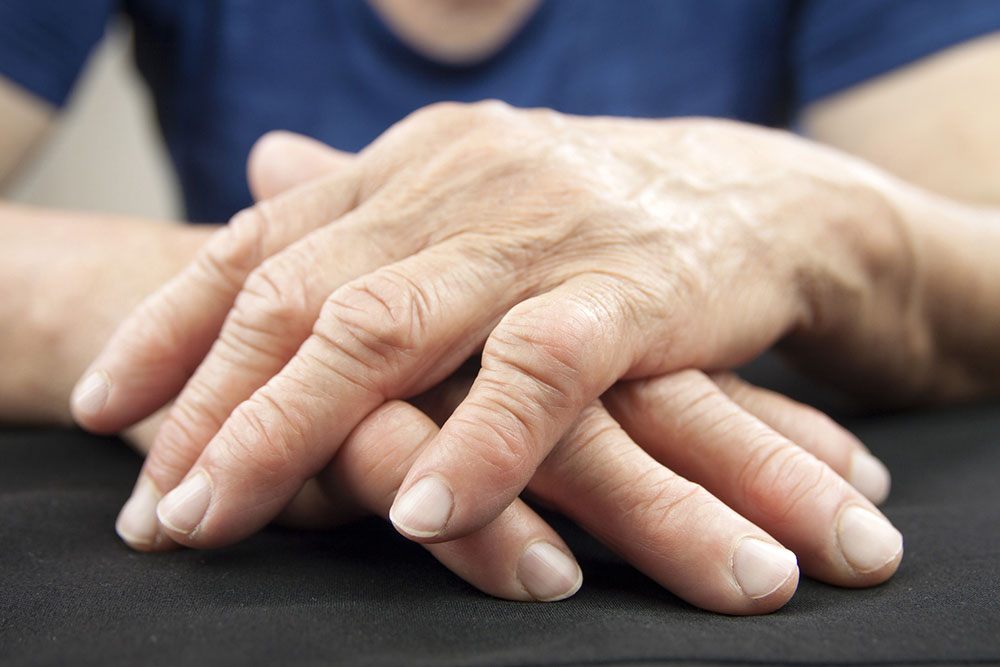
The hallmark of RA is the progressive deterioration of joint tissues, particularly affecting soft tissues around the joints. Patients often experience tenderness, swelling, and stiffness that can significantly impair mobility. These symptoms typically manifest in joints such as the knees, wrists, elbows, fingers, toes, and neck. A common early sign is morning stiffness lasting for an hour or more, which gradually eases as the day progresses. Such stiffness is a distinctive feature that helps differentiate RA from other joint conditions.
Who is Most Susceptible to Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Generally, RA is diagnosed in adults aged 30 and above, with women exhibiting higher susceptibility, especially between the ages of 30 and 60. Research indicates that hormonal factors, genetic predispositions, and environmental triggers play roles in disease onset. Men are less frequently affected but can still develop RA. The disease primarily targets the synovial lining of joints but can progress to affect other organs if left untreated, leading to potential mobility issues or partial paralysis. Early detection plays a vital role in preventing severe joint destruction.
Managing rheumatoid arthritis effectively requires understanding its signs and initiating early treatment. Since joint swelling and pain are early indicators, prompt diagnosis allows for interventions such as medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Simple remedies like rest, applying cold or hot compresses, adopting anti-inflammatory diets, and engaging in gentle massage techniques can significantly alleviate discomfort. Establishing a regular routine for these activities and adhering to prescribed treatments is key to maintaining joint health and preventing further damage.
Recognizing Early Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
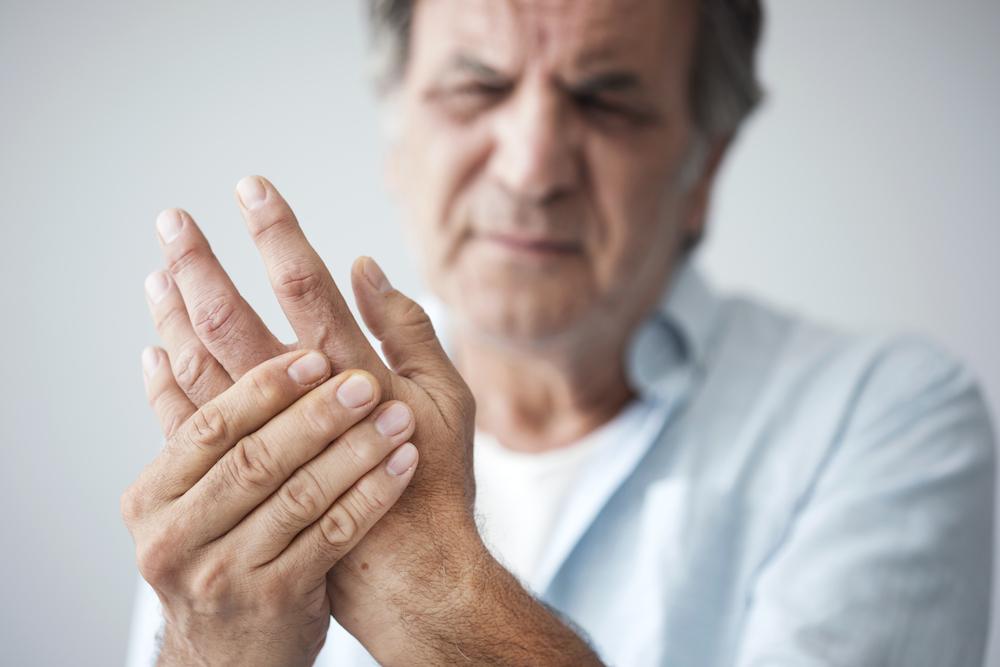
Early symptoms of RA often go unnoticed because initial signs may be subtle—joint redness and swelling might not be immediately apparent. The most common early complaints include persistent joint pain and tenderness, which last for weeks or even over a month. Recognizing these early signs is essential for timely intervention. Typical early symptoms include:
Joint tenderness, stiffness, or swelling lasting more than five weeks
Persistent fatigue and reduced energy levels
Morning stiffness lasting at least 30 minutes or more
Multiple joint pain, especially involving small joints like the wrists, fingers, and toes
Overall fatigue combined with mild fever, decreased appetite, and general discomfort
Impact on Other Body Systems
Beyond joint issues, RA can affect various organ systems, leading to more serious complications during flare-ups. These include:
Eyes—causing dryness, redness, pain, and potential vision problems
Mouth—resulting in dryness, soreness, or infections
Skin—appearance of rheumatoid nodules or lumps beneath the skin
Lungs—inflammation that may cause shortness of breath or chest discomfort
Blood vessels—leading to vasculitis, swelling, or organ damage
Blood components—potential development of anemia due to chronic inflammation
Additional Indicators and Tips for Early Detection
Since RA symptoms can vary significantly among individuals, early diagnosis can be challenging without proper testing. Monitoring changes in weight, appetite, swelling, and numbness can alert individuals and healthcare providers to early signs. Noticing symptoms such as weight loss and fluid accumulation around joints or limbs, coupled with tingling sensations, can signal an impending flare-up. Being vigilant and seeking medical advice when these symptoms emerge significantly improve chances for effective management.
If you experience unexplained weight loss
Unusual swelling in ankles, knees, or wrists
Persistent numbness, tingling, or burning sensations in extremities
Decrease in appetite or general malaise
Proactive health monitoring and early intervention can help reduce disease severity, prevent joint deformities, and improve quality of life over time.