Comprehensive Guide to Skin Lesions: Types, Causes, and Effective Treatments
This comprehensive guide provides extensive information on skin lesions, covering their types, causes, and treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and understanding symptoms associated with benign and serious skin conditions, including skin cancer. The article aims to educate readers on recognizing signs requiring medical attention and highlights various treatment methods to ensure effective management. Maintaining skin health and timely intervention can prevent complications, making this guide a valuable resource for anyone concerned about skin abnormalities.

Introduction to Skin Lesions
Skin lesions are changes or abnormalities on the skin that can present as bumps, patches, or growths. While many skin lesions are harmless and resolve independently, they can sometimes be indicators of underlying health issues, including infections or even skin cancer. Understanding the various types of skin lesions, their causes, and treatment options is crucial for maintaining health and seeking timely medical attention when needed. This extensive guide aims to shed light on what skin lesions are, differentiate between benign and serious conditions, and provide practical advice on management and treatment.
Defining Skin Lesions
Skin lesions are abnormal changes in the skin’s appearance, which may include bumps, discolorations, ulcers, or other growths. They vary widely in appearance, size, texture, and color, often serving as signs of underlying health conditions or external influences such as injury or infection. While many skin lesions are benign, some require medical intervention due to their potential link to serious diseases like skin cancer. Recognizing these lesions early can facilitate prompt diagnosis and effective treatment, preventing complications and improving outcomes.
Commonly, skin lesions are categorized based on their features—whether they are flat or raised, painful or painless, slow or rapid to develop. Knowing these characteristics helps in assessing the urgency of medical evaluation and the appropriate course of treatment.
Common Causes and Risk Factors for Skin Lesions
Skin lesions can arise from a multitude of causes, including genetic predispositions, environmental exposures, infections, allergic reactions, or chronic skin conditions. Some of the primary causes include:
Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections often lead to skin lesions. Examples include impetigo, chickenpox, or fungal abscesses.
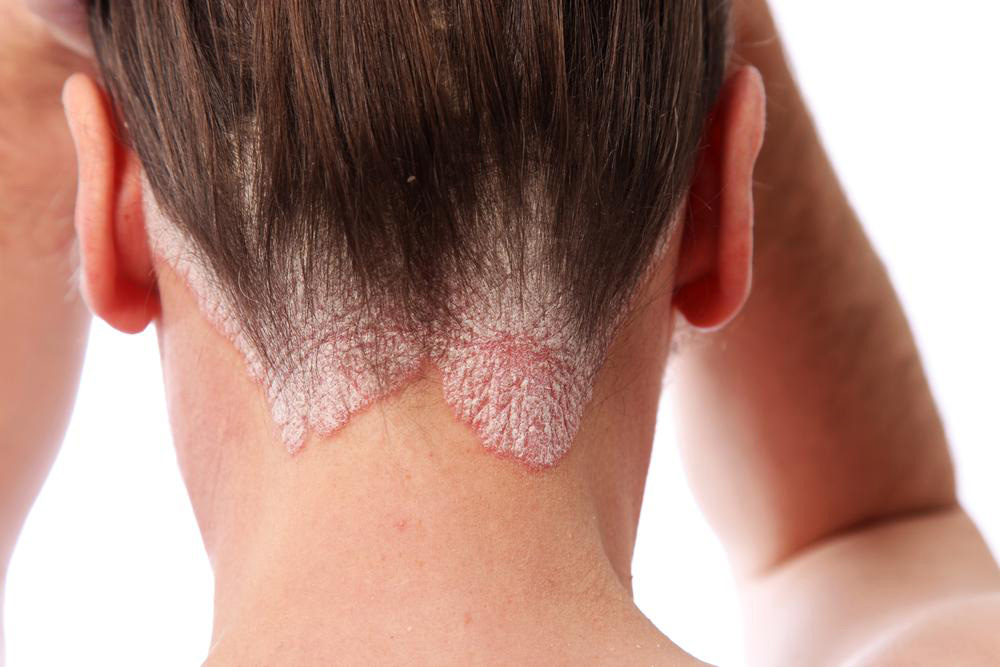
Skin Conditions: Chronic conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis frequently cause patches or bumps.
Injury and Trauma: Cuts, scrapes, or insect bites can lead to localized bumps or ulcers.
Sun Damage: Prolonged sun exposure increases the risk of lesions such as actinic keratosis and skin cancers.
Allergy and Hypersensitivity: Allergic reactions can present as hives or itchy patches.
Age and Lifestyle Factors: Aging skin and lifestyle choices like smoking or poor hygiene can influence lesion development.
Understanding these causes aids in both prevention and timely treatment, minimizing adverse health effects.
Types of Skin Lesions
Skin lesions can be broadly categorized into several types based on their appearance and etiology:
Acne and Pimples: Widespread inflammatory bumps common during adolescence, they can vary from blackheads to painful cysts, often affecting the face, back, and shoulders.
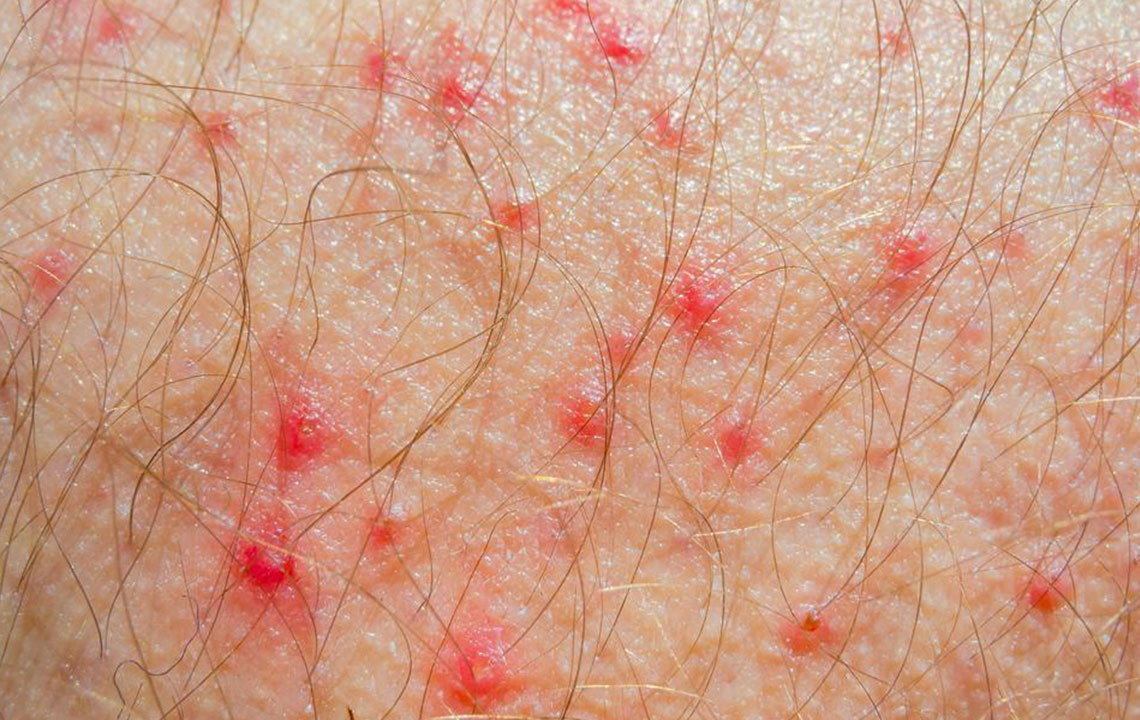
Boils (Furuncles): These are deep skin infections originating from hair follicles, characterized by swollen, painful, pus-filled lumps that often resolve with proper care.
Corns and Calluses: Thickened areas of skin caused by repeated pressure or friction, frequently on hands and feet, usually harmless but occasionally painful.
Other benign growths: These include skin tags, moles, warts, and cysts, often cosmetic but sometimes bothersome or prone to irritation.
Understanding these common types can help differentiate harmless from potentially dangerous lesions, guiding whether medical consultation is needed.
Serious Skin Conditions and the Need for Medical Evaluation
While most skin lesions are benign, certain persistent, unusual, or rapidly changing bumps may indicate severe underlying health issues. Recognizing these signs and seeking prompt medical evaluation is vital for early diagnosis and treatment. Notable conditions include:
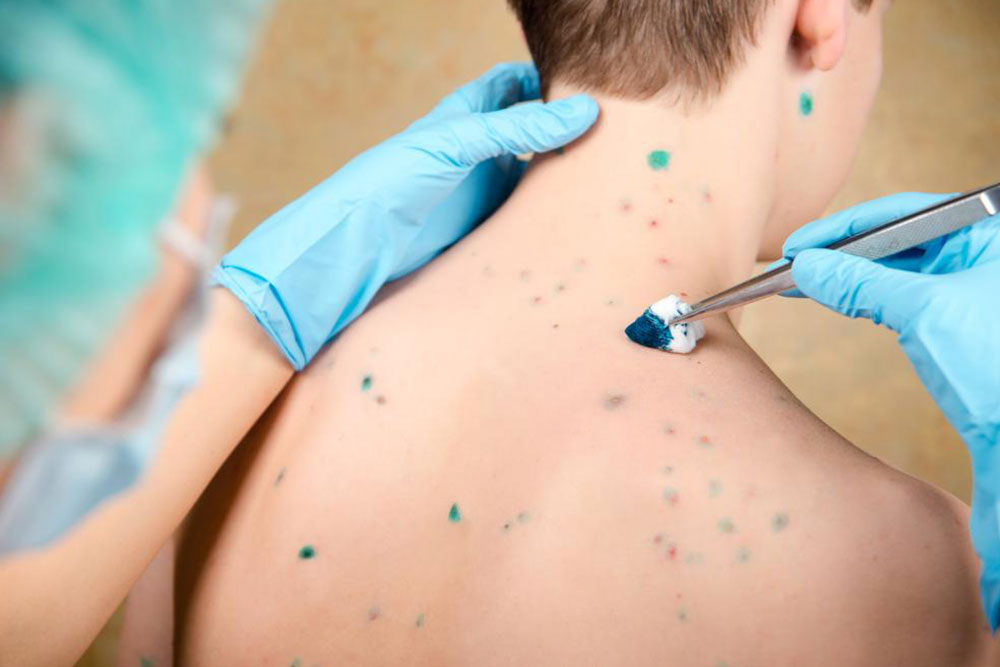
Chickenpox: This highly contagious viral infection causes itchy red spots that spread over the body and require medical attention, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
Impetigo: A bacterial skin infection characterized by crusted blisters, primarily affecting children, which can spread through contact.
MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus): An antibiotic-resistant bacterial infection that causes swollen, often painful bumps or abscesses with pus, warranting urgent medical management.
Other serious conditions include herpes zoster, fungal infections, and autoimmune skin diseases, which often require specific treatments administered by healthcare providers.
Skin Cancers and Precancerous Lesions
Certain abnormal skin growths are indicative of skin cancer or precancerous states, necessitating immediate evaluation. Key conditions include:
Actinic keratosis: Often seen as dry, scaly, and crusty patches on sun-exposed skin, these lesions may progress to squamous cell carcinoma if left untreated.
Basal cell carcinoma: Appearing as shiny, reddish, or pearly bumps that can bleed or ulcerate, these are the most common form of skin cancer.
Squamous cell carcinoma: Presents as sores or red patches that may ulcerate, primarily on sun-exposed areas, originating from the top layers of the skin.
Melanomas: Irregularly shaped, multicolored moles or spots that exhibit asymmetry, border irregularity, color variation, or diameter enlargement—these require immediate dermatological evaluation.
Early detection of these lesions significantly improves treatment success rates and survival outcomes.
When to Seek Medical Help and Available Treatment Options
Most skin lesions are benign and do not pose serious health risks; however, certain signs indicate the need for professional assessment:
If the lesion causes pain or discomfort.
If it changes in size, shape, or color over time.
If it develops an ulcer or bleeding without injury.
If there is rapid growth or irregular borders.
If multiple similar lesions suddenly appear or spread.
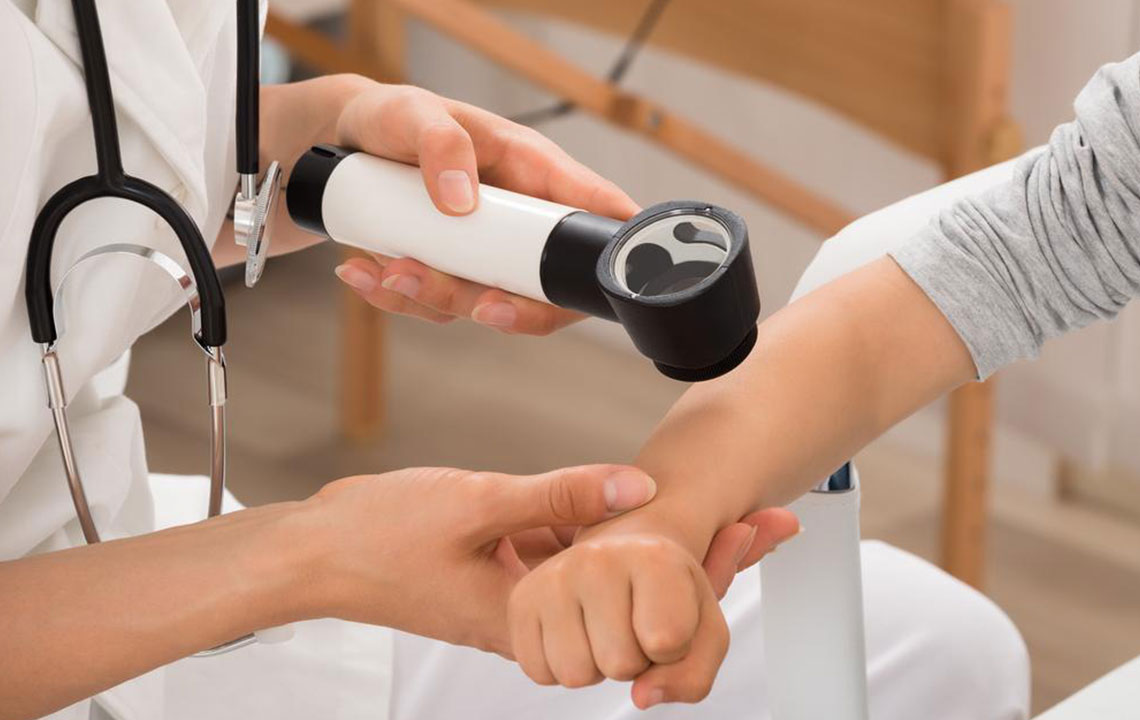
In such cases, consulting a dermatologist is essential. Professionals will perform a thorough examination, review medical history, and may recommend a biopsy to determine the nature of the lesion.
Treatment options vary based on the diagnosis and lesion type, including:
Cryotherapy (freezing with liquid nitrogen) for benign lesions or precancerous patches.
Surgical removal for suspicious or malignant growths.
Medications such as topical creams, antibiotics, or corticosteroids.
Laser therapy or light-based treatments for cosmetic improvements.
Addressing infectious or contagious diseases like chickenpox or MRSA may require specific medications and home care under medical supervision. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing and prevent recurrence or progression.
In conclusion, understanding skin lesions, their causes, and available treatments empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their skin health. Early diagnosis and appropriate care can significantly reduce the risk of complications and ensure long-term skin health and overall well-being.