Identifying the 7 Key Signs of Excessive Sugar Consumption and Its Impact on Health
Excessive sugar consumption can silently impact your health through symptoms like unexplained weight gain, high blood pressure, skin issues, energy fluctuations, sleep disturbances, mood swings, intense sweet cravings, and joint pain. Recognizing these signs early enables better dietary choices and improves overall well-being. This detailed guide explores each indicator thoroughly, emphasizing the importance of limiting sugar intake for a healthier lifestyle and longer-term health benefits.

Recognizing the 7 Common Indicators of Excessive Sugar Intake and Its Effects on Your Well-Being
Sugar, a widely addictive and pervasive ingredient, is present in countless foods and beverages we consume daily. From processed snacks and fast food to sweetened drinks, it's often challenging to limit sugar intake without conscious effort. While some people diligently monitor their diets, others may unwittingly consume excessive amounts of sugar, leading to adverse health effects. Understanding the key signs of sugar overconsumption can help you make informed dietary choices and maintain optimal health.
Unexplained Weight Gain One of the most noticeable signs of excessive sugar consumption is sudden or unexplained weight gain. Sugars are processed rapidly by the body to provide quick energy but offer little nutritional benefit. Processed foods with high sugar content usually contain empty calories, lacking essential nutrients like proteins, fibers, or healthy fats that help satisfy hunger and promote satiety. As a result, individuals tend to eat more, leading to weight gain over time. Persistent overeating driven by sugar-laden foods can also disrupt hormonal regulation of appetite, making weight management more difficult.
Increased Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Risks High sugar intake has been directly linked to elevated blood pressure levels, which pose significant risks for heart health. Excess glucose can cause damage to the lining of blood vessels, promoting inflammation and making blood vessels more vulnerable to cholesterol deposits. Over time, this can lead to arterial narrowing, reduced blood flow, and an increased likelihood of hypertension and cardiovascular diseases. Reducing sugar consumption can help manage blood pressure effectively and support overall heart health.
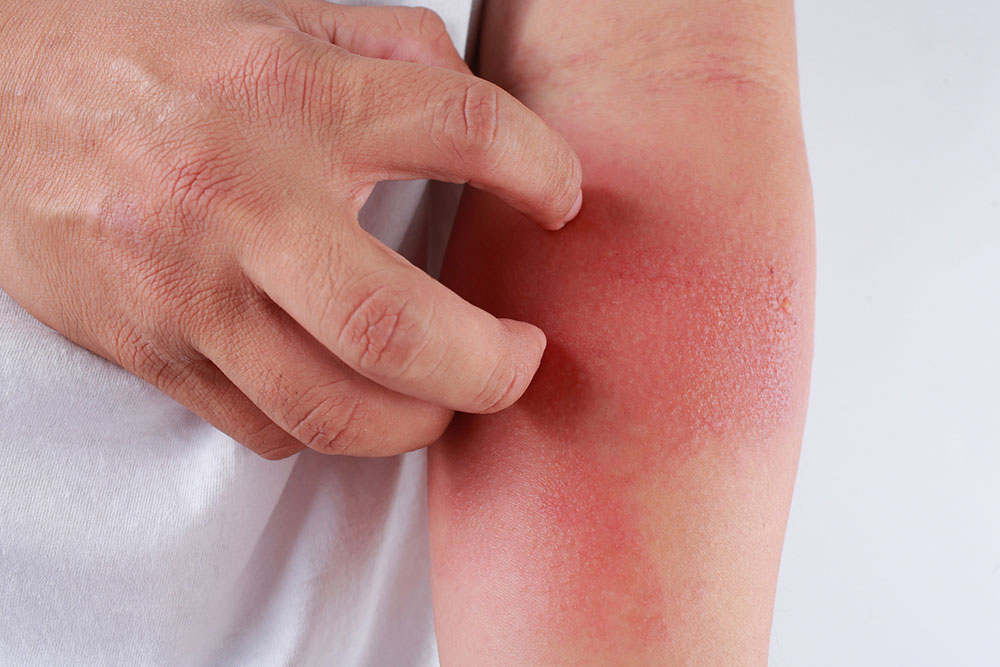
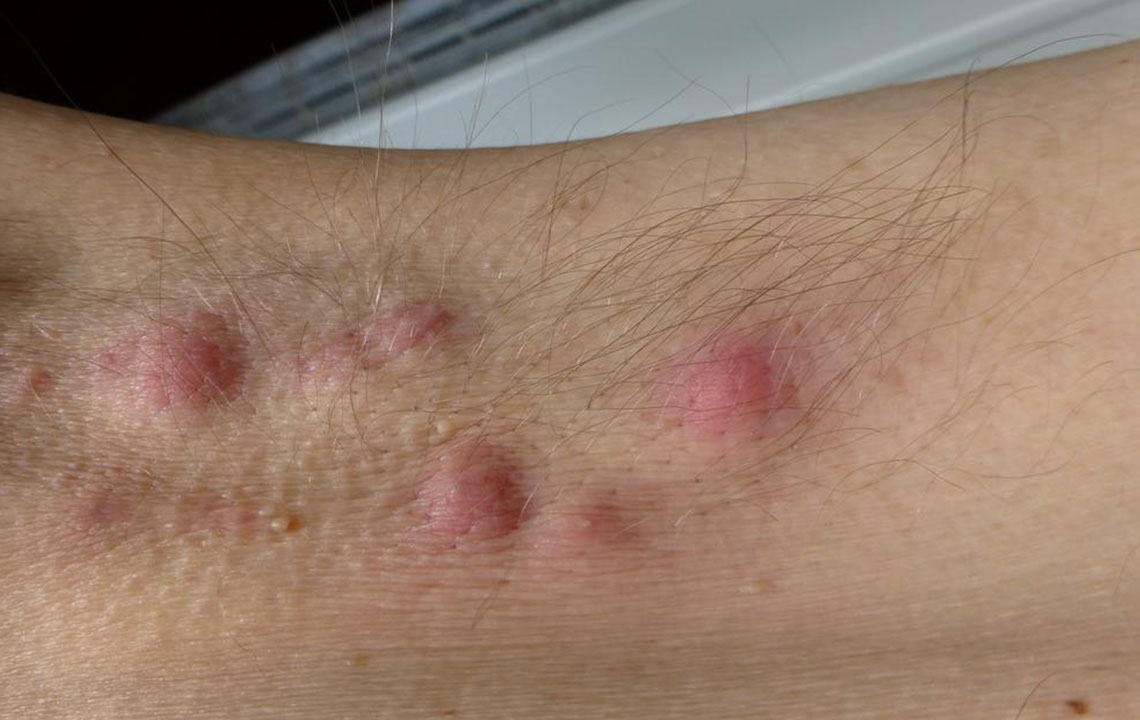
Skin Issues: Breakouts and Premature Aging Consuming too much sugar stimulates the production of androgens, hormones linked to acne development. Elevated blood sugar levels can also cause the skin to appear dull, less elastic, and prone to premature aging signs such as wrinkles and fine lines. Maintaining well-hydrated skin, limiting sugar intake, and detoxifying regularly can significantly improve skin clarity and youthfulness over time.
Energy Instability and Fluctuations One of the more immediate effects of excessive sugar intake is noticeable energy swings. The rapid digestion and absorption of sugars lead to sudden spikes in blood glucose levels, providing short-term bursts of energy. However, these are often followed by rapid drops, leaving individuals feeling tired, lethargic, and craving more sugar to regain energy. This cycle contributes to ongoing fatigue and poor energy management throughout the day.
Sleep Quality and Disturbances Research indicates that high sugar consumption negatively impacts sleep quality, affecting both the duration and restorative quality of sleep. Fluctuating blood sugar levels can interfere with the body's ability to relax and maintain uninterrupted sleep cycles. Balanced blood sugar levels are essential for restful, rejuvenating sleep, contributing to overall health and daytime alertness.
Mood Swings, Irritability, and Mental Health Excess sugar intake influences brain chemistry, often leading to mood swings and increased irritability. High sugar consumption triggers inflammation, which can impair mental health over time. Moreover, insulin spikes caused by sugar intake influence brain function, potentially resulting in feelings of anxiety or depression. Reducing sugar intake and opting for nutrient-dense foods can support better mental stability and emotional well-being.
Intense Cravings for Sweets Sugar stimulates the reward centers in the brain by releasing dopamine, creating pleasurable feelings akin to a high. This hormonal response fosters ongoing cravings for sweet foods, reinforcing a cycle of dependence. Breaking this cycle requires strategic dietary adjustments, including replacing sugary snacks with whole, nutrient-rich foods to help curb these persistent urges.
Joint Pain and Systemic Inflammation High levels of sugar can contribute to systemic inflammation, which may exacerbate joint pain, especially in individuals suffering from rheumatoid arthritis or similar conditions. Recognizing dietary triggers, reducing processed sugar, and focusing on anti-inflammatory foods can help alleviate symptoms and improve joint health over time.