Identifying the Hidden Signs of Excessive Sugar Intake and Its Impact on Your Health
Excessive sugar consumption can lead to a range of health issues, including mood swings, weight gain, skin problems, and cardiovascular risks. Recognizing the signs early allows for dietary adjustments to improve overall well-being. This comprehensive guide explains the key indicators of high sugar intake and offers tips for better health management.

Recognizing the Symptoms of Overconsumption of Sugar
Sugar, a naturally occurring carbohydrate, plays a significant role in our diet by providing a quick source of energy and enhancing the flavor of many foods. It is present in a multitude of products, from desserts like cookies, chocolates, and pastries to processed snacks, soft drinks, and even certain sauces. While moderate sugar consumption can be part of a balanced diet, excessive intake poses serious health risks that can subtly undermine your well-being over time. Understanding the signs that indicate you might be consuming too much sugar is crucial for maintaining optimal health and preventing chronic conditions.
Mood Swings and Emotional Instability
Experiencing sudden shifts in mood, irritability, or heightened stress levels can often be linked to high sugar consumption. Rapid fluctuations in blood sugar levels, caused by consuming foods high in refined sugars and low in essential nutrients like proteins and healthy fats, can impact mood regulation. Such spikes and crashes in blood sugar can trigger feelings of anxiety, irritability, and fatigue, making it harder to maintain emotional balance throughout the day.

Reduced Tolerance for Sweet Flavors
An interesting sign of excessive sugar intake is when foods that are typically sweet no longer taste as sugary. You might notice that you need higher amounts of sugar to achieve the same level of sweetness, leading to increased consumption. This tolerance can diminish the natural enjoyment of less sugary foods and can also make it more challenging to cut back on sugar, fostering a cycle of overindulgence.
Accumulation of Visceral Fat and Hormonal Disruption
Excess sugar intake is closely linked to the development of visceral fat, which is fat stored around the abdominal organs. High consumption of sugary processed foods influences hormones like leptin, which regulates hunger and satiety. When leptin signaling becomes impaired, it can lead to increased appetite, overeating, and weight gain, particularly around the waistline. Moreover, sugar contributes to insulin resistance, elevating the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
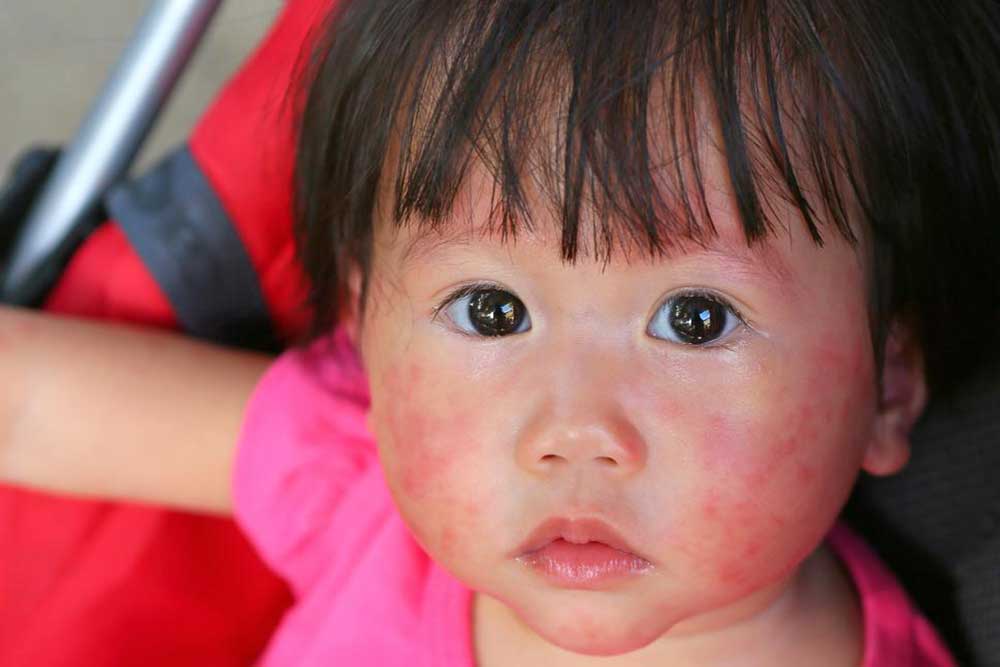
Skin Breakouts and Acne
Elevated blood sugar levels can trigger hormonal changes that promote oily skin and acne. Consuming a diet high in sugary beverages and snacks can elevate androgen levels and insulin-like growth factors, which stimulate excess oil production and inflammation, leading to skin breakouts.
Increased Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Risks
Consuming too much sugar can damage the lining of blood vessels, leading to lipid deposits and arterial stiffening. These changes contribute to elevated blood pressure and increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension, heart attacks, and strokes.
Joint Pain and Inflammation
Many individuals notice increased joint discomfort, especially after consuming sugary foods. High sugar diets can exacerbate inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis by promoting the release of inflammatory cytokines, thus worsening joint pain and swelling.
Sleep Disruptions and Fatigue
Excess sugars can interfere with sleep quality by causing blood sugar spikes and crashes during the night. This fluctuation hampers the natural circadian rhythm, making it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep, which leads to fatigue and decreased productivity during the day.
Digestive Problems and Gastrointestinal Discomfort
Overconsumption of sugar can irritate the gastrointestinal tract, leading to symptoms like stomach cramps, bloating, diarrhea, and general digestive discomfort. Excessive sugar intake can also disrupt the balance of healthy gut bacteria, further impairing digestion.
In summary, while sugar is a common component of many diets, excessive intake can quietly undermine your health in multiple ways. Recognizing the signs such as mood swings, diminished sweetness sensitivity, visceral fat accumulation, skin issues, elevated blood pressure, joint pain, sleep disturbances, and digestive troubles allows for early intervention. Reducing the consumption of processed sugary foods and replacing them with nutrient-dense alternatives can significantly improve overall health and prevent chronic diseases associated with high sugar intake.