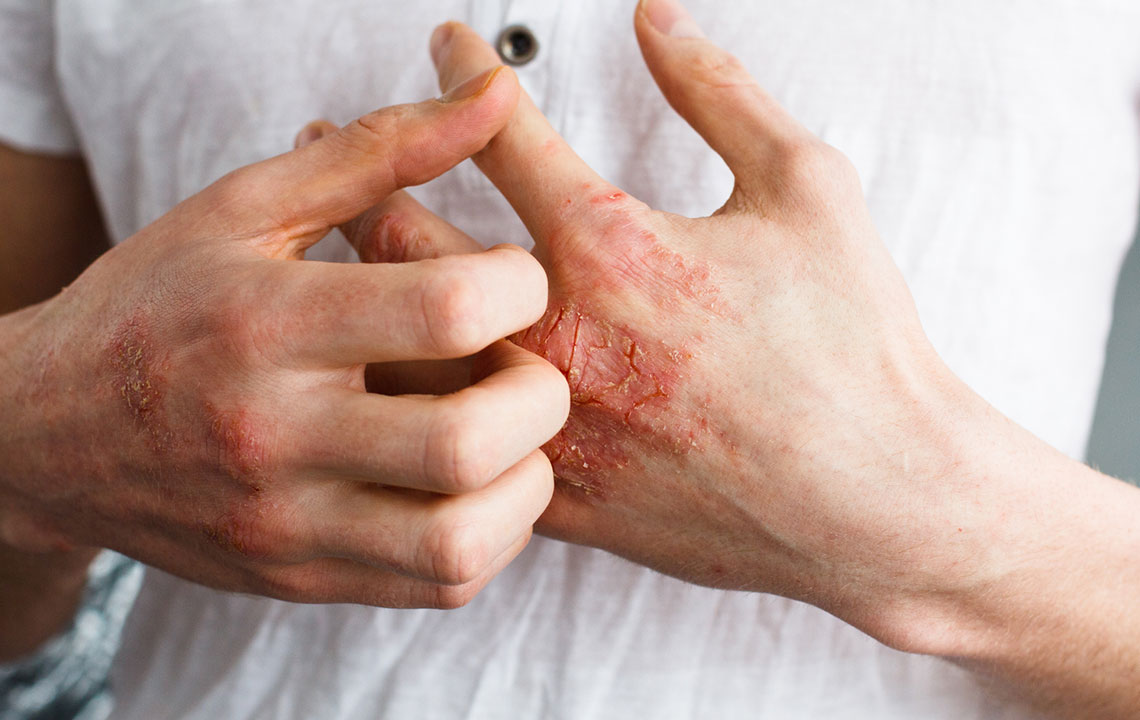
Effective Dietary Approaches to Reduce Eczema Flare-Ups and Improve Skin Health
Discover comprehensive dietary strategies to effectively manage eczema. Learn about anti-inflammatory foods, key nutrients like omega-3s, probiotics, and identify common dietary triggers. This guide offers practical tips on food choices and elimination diets to reduce flare-ups and promote healthy, resilient skin. A personalized approach to nutrition can significantly alleviate eczema symptoms and improve overall skin health.
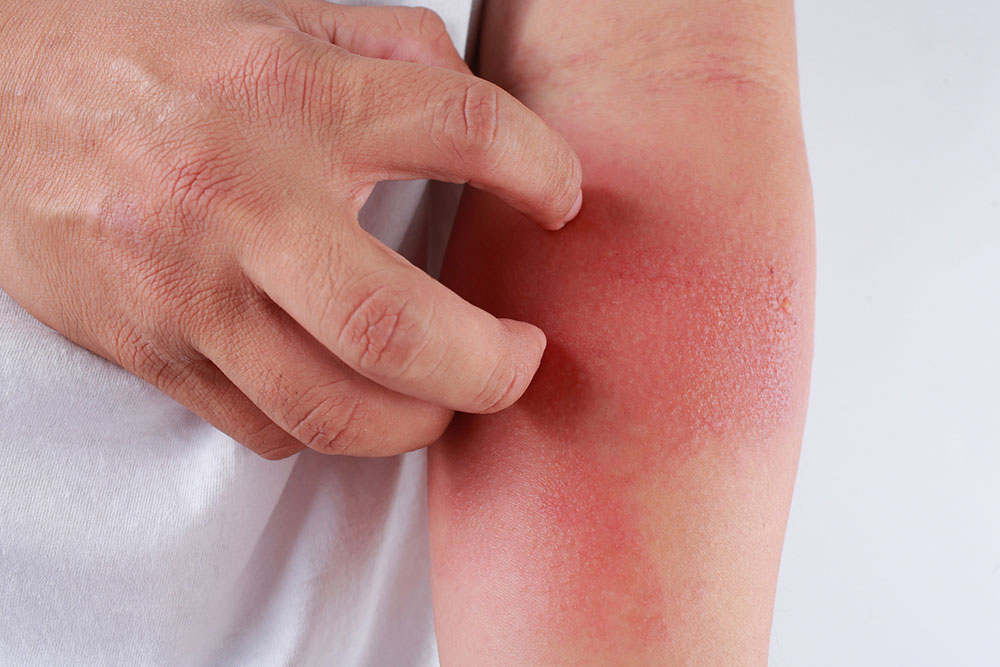
Effective Dietary Approaches to Reduce Eczema Flare-Ups and Improve Skin Health
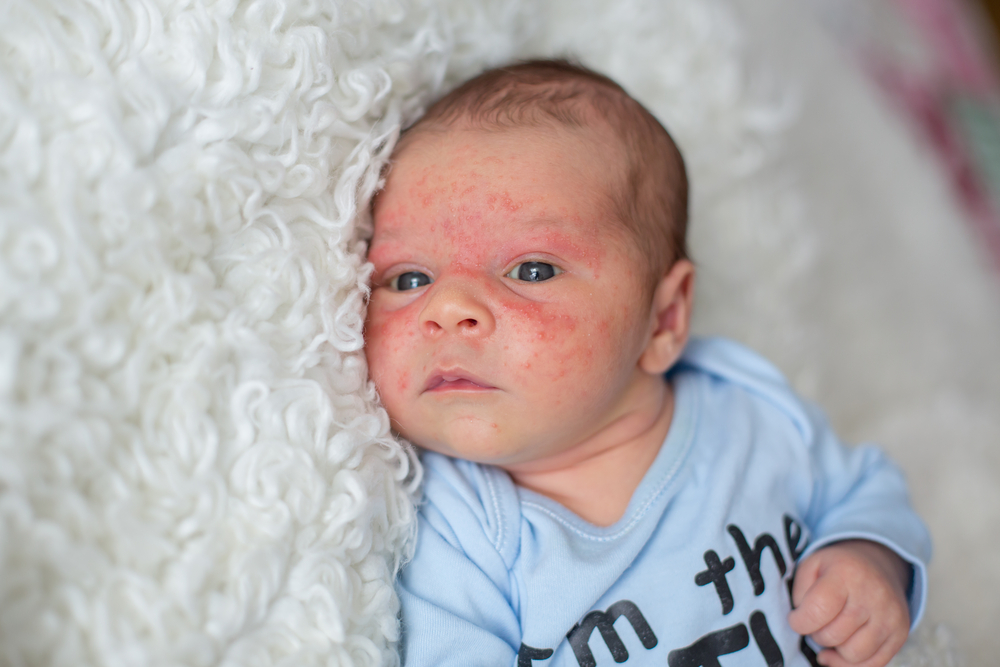
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a persistent and often frustrating skin condition characterized by inflammation, dryness, redness, itching, and discomfort. While genetic predisposition plays a role in eczema, environmental factors and dietary habits significantly influence the severity and frequency of flare-ups. For many sufferers, managing diet is a key component in controlling symptoms, reducing allergic reactions, and promoting overall skin wellness.
Understanding how certain foods impact eczema is vital for developing an effective nutrition plan. With a strategic approach that emphasizes anti-inflammatory foods and identifies personal allergen triggers, individuals can experience a marked improvement in their skin condition. This comprehensive guide explores the best dietary practices, beneficial foods, and common dietary triggers linked with eczema, offering valuable insights to empower patients in their journey toward healthier skin.
Why Diet Matters in Managing Eczema The link between diet and eczema is well-documented. Certain foods can trigger immune responses or worsen inflammation, leading to more intense and frequent flare-ups. Conversely, consuming nutrient-rich, anti-inflammatory foods can support skin repair, bolster immune defenses, and reduce the intensity of eczema symptoms. Personalized dietary modifications are often necessary, as triggers can vary between individuals.
Implementing Proper Nutrition for Eczema Relief Proper nutritional strategies involve focusing on foods that calm inflammation and strengthen skin barriers. Incorporating foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, probiotics, and fiber can make a significant difference. Simultaneously, it’s important to identify and eliminate foods that exacerbate symptoms, which may include common allergens or foods high in certain metals like nickel.
A well-balanced diet tailored to individual sensitivities can alleviate eczema symptoms, reduce itching, and promote healthier skin. The right food choices support the body’s natural healing processes and can significantly improve quality of life for those affected by chronic skin conditions.
Key Beneficial Foods for Eczema Management Incorporating certain foods into your daily diet can help mitigate inflammation and support skin health. These foods contain bioactive compounds that work to reduce swelling, redness, and itching associated with eczema.
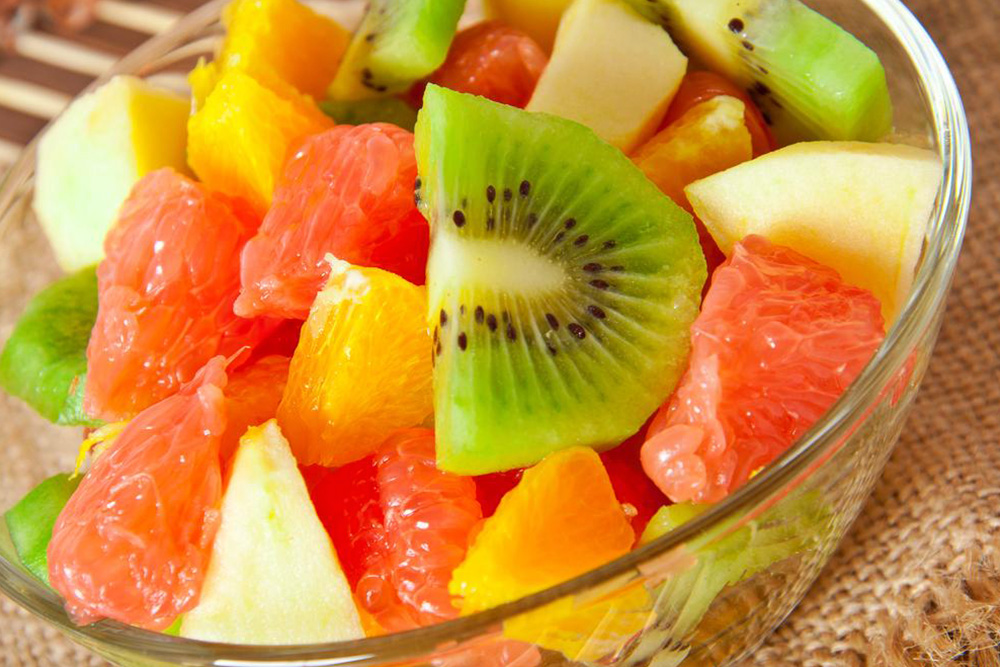
Rich in Quercetin: Quercetin is a potent antioxidant that naturally occurs in many fruits and vegetables, imparting vibrant colors and health benefits. It acts as a natural antihistamine, helping to decrease allergic reactions and inflammation in sensitive individuals. Consuming foods high in quercetin like apples, blueberries, broccoli, spinach, cherries, and kale can help lower the severity of eczema flare-ups.
Probiotics for Gut and Skin Health: A healthy gut flora is crucial in regulating immune responses and reducing allergic symptoms. Probiotics, the beneficial bacteria found in fermented foods, support gut health and overall immunity. Regularly eating probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, unpasteurized sauerkraut, kefir, and tempeh can help regulate immune responses and potentially lessen eczema severity.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Known for their renowned anti-inflammatory properties, omega-3s significantly contribute to calming skin inflammation and reducing eczema symptoms. Dietary sources include fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, sardines, along with plant-based options like chia seeds, flaxseeds, walnuts, and hemp seeds. Incorporating these foods regularly can help soothe inflamed skin and support skin barrier repair.
High-Fiber Foods for Inflammation Control: Dietary fiber is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system and modulating immune responses. Consuming fiber-rich foods such as whole grains, legumes, mangoes, nuts, and seeds can help reduce systemic inflammation, promoting healthier skin. Adequate fiber intake supports the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, further enhancing immune regulation.
Foods to Avoid or Limit in Eczema Diets Certain foods may trigger or worsen eczema symptoms, especially in sensitive individuals. An elimination diet can help identify these personal triggers. Avoiding or limiting these foods can result in fewer flare-ups and more controlled skin conditions.
Eggs: Eggs are among the most common food allergens responsible for exacerbating eczema in some people. Rapid immune responses triggered by eggs can lead to increased itching and skin inflammation.
Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, and other dairy foods can worsen eczema symptoms, particularly in children. While some individuals tolerate dairy well, others find that dairy products cause flare-ups. Dairy alternatives such as soy milk, almond milk, or oat milk are excellent substitutes.
Gluten: Present in wheat, rye, barley, and other gluten-containing grains, gluten can be problematic for individuals with sensitivities or intolerances. Eliminating gluten from the diet may help reduce systemic inflammation and eczema severity.
Nickel-Rich Foods: Foods containing high levels of nickel include beans, oats, chocolate, canned foods, and soy. Nickel sensitivity can cause increased itching, redness, and irritation. Emphasizing fruits and vegetables low in nickel can alleviate these symptoms.
Managing eczema through dietary modifications requires patience and careful monitoring. Consulting a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can help develop a personalized, effective diet plan that eases symptoms and promotes overall skin health. Combining dietary changes with other treatments, such as moisturizers and medications, offers a comprehensive approach to managing this chronic condition effectively.
This expanded guide emphasizes the importance of nutrition in eczema management, offering detailed insights into beneficial foods, triggers, and personalized dietary strategies that can improve quality of life for eczema sufferers.