Comprehensive Nutritional Approaches for Managing Psoriasis Symptoms
Discover comprehensive dietary strategies that can support psoriasis management. Learn about anti-inflammatory foods, nutrients, and dietary modifications to help reduce flare-ups and improve skin health. Personalizing nutrition plans with healthcare guidance can enhance treatment results and overall well-being.
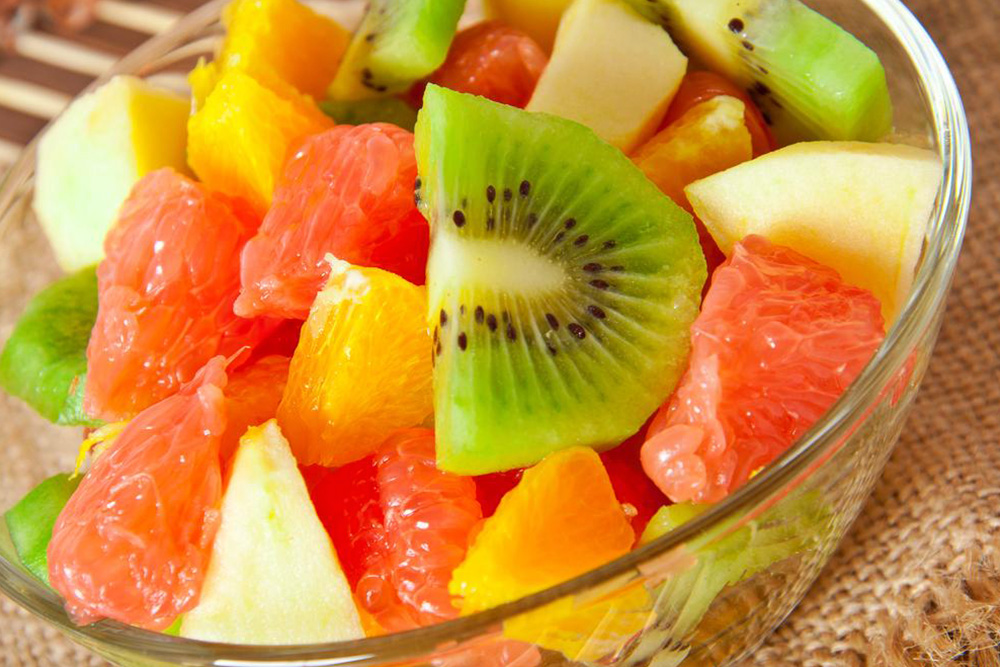

Effective Nutritional Strategies for Alleviating Psoriasis Symptoms
Living with psoriasis presents numerous challenges, including managing triggers that can lead to flare-ups. Common triggers include stress, abrupt weather changes, infections, and certain lifestyle habits. Among these, dietary choices have garnered increasing attention for their potential role in influencing disease severity. Many patients and healthcare professionals alike are exploring how specific foods can either aggravate or alleviate symptoms, aiming for a complementary approach to traditional treatments. Incorporating targeted dietary modifications can offer a non-invasive way to support skin health and reduce inflammation, making a notable difference in daily life.
Understanding the impact of diet on psoriasis involves recognizing how certain nutrients can influence inflammation and immune response. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is widely advocated for its anti-inflammatory properties. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and healthy fats that can help combat oxidative stress and support overall immune function. Conversely, some foods may act as triggers or exacerbate symptoms, emphasizing the importance of mindful dietary choices.
Adding foods high in antioxidants—such as vitamins C and E, selenium, and beta-carotene—can further mitigate inflammation and promote skin repair. For example, berries like blueberries, strawberries, and cherries are excellent sources of antioxidants, as are leafy greens such as spinach and kale. Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids, predominantly found in oily fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, supports anti-inflammatory processes in the body. Herbs such as thyme, sage, cumin, and ginger not only add flavor but also contribute anti-inflammatory compounds. Extra virgin olive oil, whole grains like oats and brown rice, as well as nuts and seeds, form the backbone of a health-promoting anti-inflammatory diet.
On the other hand, foods that tend to promote inflammation or worsen psoriasis symptoms should be limited. These include processed foods high in refined sugars, trans fats, and artificial additives, as well as fatty cuts of red meats, dairy products, and fast foods. Reducing intake of processed snacks, sweets, and sugary beverages can help decrease systemic inflammation. In some cases, individuals with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease may experience symptom improvement by adopting a gluten-free diet. While scientific research is ongoing, some patients report notable benefits from reducing or eliminating gluten from their diet. Implementing such a diet should ideally be done with medical guidance to ensure nutritional adequacy and suitability for individual health conditions.
It is important to note that dietary strategies should be personalized, as triggers and responses vary among individuals. Consulting healthcare professionals such as dermatologists or registered dietitians can help craft a comprehensive nutritional plan tailored to specific needs. A diet that emphasizes anti-inflammatory foods while minimizing potential triggers complements medical therapies and lifestyle modifications, helping patients manage psoriasis more effectively and improve their quality of life.