Comprehensive Guide to the 8 Most Common Causes of Foot Discomfort and How to Address Them
Foot discomfort can be caused by numerous factors such as injuries, structural issues, or medical conditions. This comprehensive guide explores the top 8 causes of foot pain, including ligament injuries, plantar fasciitis, bunions, gout, ingrown toenails, flat feet, corns, and Achilles tendon issues. It offers detailed insights into symptoms, causes, and effective treatment options, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and professional care. Maintaining healthy feet is crucial for overall mobility and quality of life, making awareness of these common issues essential.
Comprehensive Guide to the 8 Most Common Causes of Foot Discomfort and How to Address Them
Our feet are remarkable structures that carry the weight of the entire body, enabling mobility, balance, and stability. Despite their resilience, feet are vulnerable to a variety of issues that can lead to discomfort, pain, and even long-term health problems if left unmanaged. Understanding the common causes of foot discomfort is essential for early intervention and effective treatment. This comprehensive guide explores the eight most frequently encountered reasons for foot pain, along with practical advice on managing each condition to maintain optimal foot health.
Foot discomfort can arise from various factors, including injuries, degenerative conditions, structural abnormalities, or external influences like footwear. Recognizing these causes helps in timely management and prevents the progression to more serious issues. Here, we delve into the most common foot problems faced by many individuals, their symptoms, causes, and available treatment options.
1. Ligament and Muscle Injuries
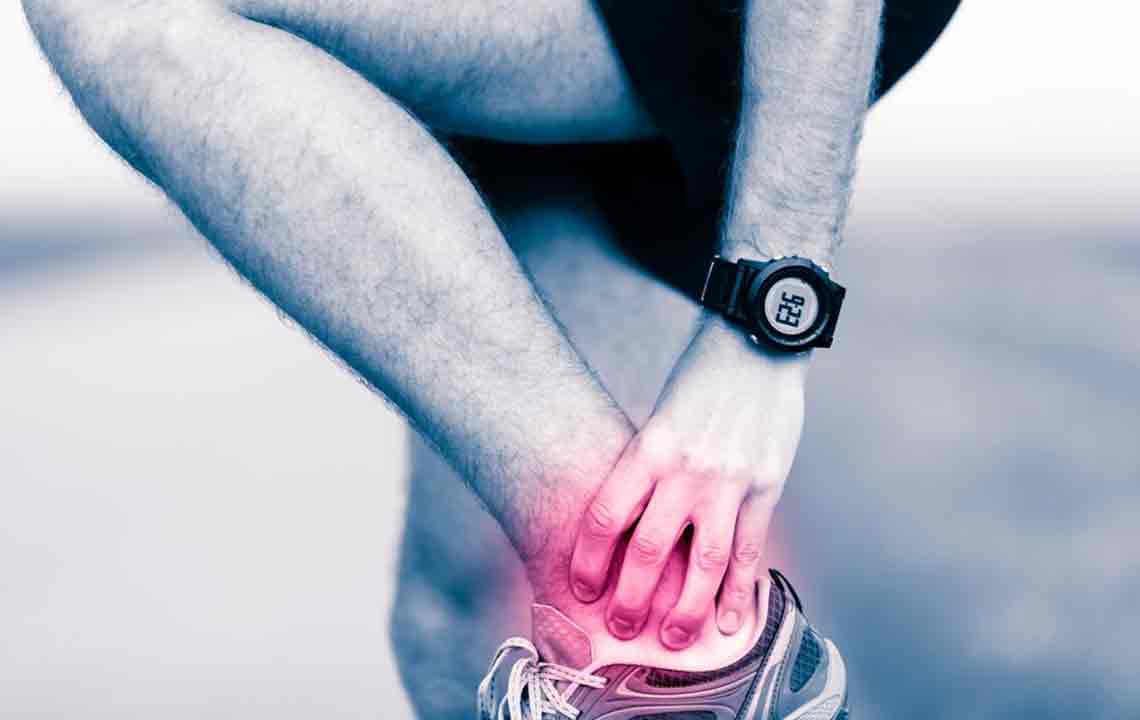
Foot sprains and strains are among the prevalent injuries affecting ligaments and muscles. Sprains typically involve overstretching or twisting ligaments, often resulting from sudden missteps, falls, or impacts. Strains occur when muscle fibers tear due to overexertion or improper movement. These injuries are characterized by pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty moving the affected foot. Fortunately, most mild injuries respond well to home remedies such as ice applications, over-the-counter pain medications, and rest. However, severe injuries may require medical evaluation, physiotherapy, or even surgical intervention to ensure proper healing and prevent chronic problems.
2. Plantar Fasciitis
One of the most common causes of heel pain, plantar fasciitis involves inflammation or degeneration of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue running along the bottom of the foot. This condition predominantly affects athletes, people over the age of 40, or individuals who stand on their feet for extended periods. Pain is typically worse in the morning or after periods of rest, easing with activity but worsening as the day progresses. Management strategies include physical therapy, stretching exercises, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), custom orthotic insoles, and footwear modifications. Proper diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent potential chronic pain or foot deformities.
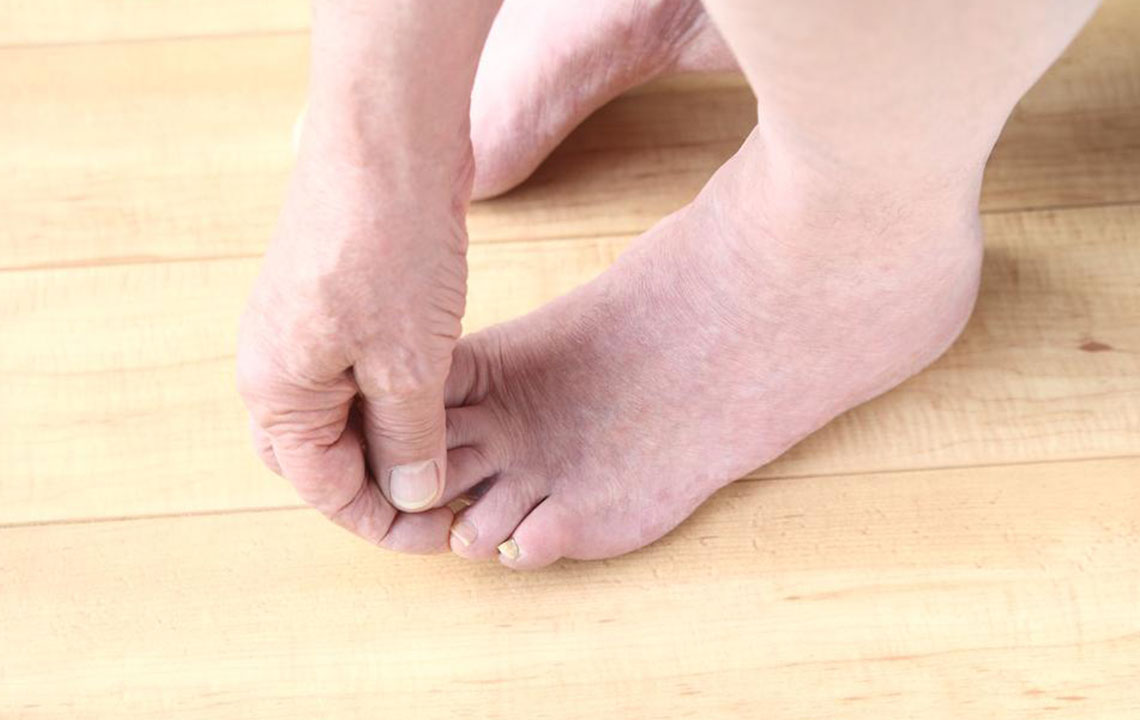
3. Bunions
Bunions are bony protrusions that develop at the base of the big toe, causing the toe to deviate inward towards other toes. This deformity often results from genetic predisposition, footwear choices, or underlying structural abnormalities. Early-stage bunions may not cause significant pain, but as they progress, they can lead to discomfort, calluses, swelling, and restricted toe movement. Conservative treatments include padded insoles, pain-relief medications, and wearing roomier shoes. Severe cases might require surgical correction to realign the toe and alleviate symptoms.
4. Gout
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, frequently affecting the big toe. Sudden episodes of intense pain, swelling, redness, and warmth are characteristic of gout attacks. Managing gout involves medications to reduce uric acid levels and dietary adjustments, such as reducing intake of purine-rich foods like red meats, alcohol, and seafood. Adequate hydration and lifestyle modifications further help in controlling flare-ups and preventing long-term joint damage.
5. Ingrown Toenails
When the edges of a toenail grow into the surrounding skin, it results in pain, redness, swelling, and sometimes pus formation. Causes include improper nail trimming, tight footwear, injury, or genetic predisposition. Mild cases can be managed at home with warm soakings, proper trimming techniques, and antibiotics if infection occurs. Severe cases may require medical procedures such as partial nail removal or other surgical interventions to prevent recurrence and resolve discomfort.
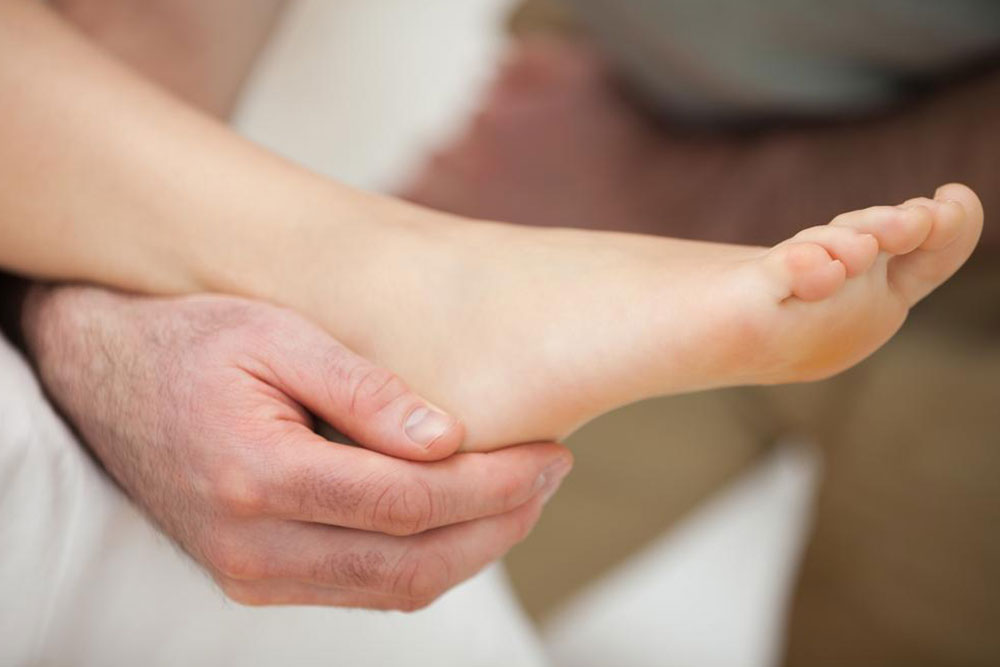
6. Flat Feet
Also called fallen arches, flat feet occur when the natural arch of the foot collapses, leading to an increase in stress on foot structures. While some individuals experience no symptoms, others may suffer from foot pain, especially during walking or standing for long periods. Flat feet can develop in childhood or result from injury or degeneration over time. Treatments include supportive footwear, arch supports, strengthening exercises, and, rarely, surgical correction.
7. Corns and Calluses
These are thickened skin patches that develop as a protective response to repetitive pressure or friction. Corns are smaller, with a central core often causing discomfort when pressed, whereas calluses are larger and tend to be less painful but still may hinder movement. Removal involves softening the skin with pumice stones, medicated patches, or professional debridement. Wearing properly fitted shoes and using padding or orthotic devices can prevent their recurrence.
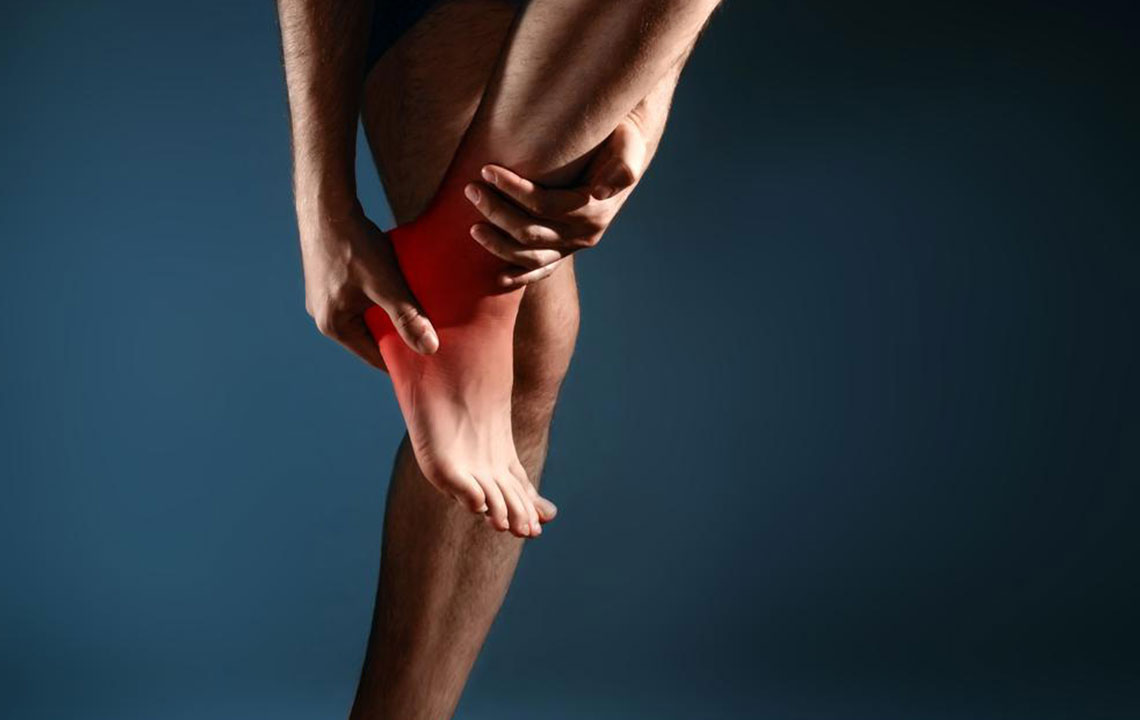
8. Achilles Tendon Problems
Pain at the back of the heel may indicate Achilles tendinopathy or rupture. Overuse, intense physical activity, or inadequate stretching can cause inflammation or tears in the Achilles tendon. Symptoms include stiffness, swelling, pain, and difficulty walking or standing on tiptoe. Mild cases respond to rest, ice, NSAIDs, and stretching exercises. Severe injuries like ruptures often require surgical repair and immobilization to restore function and prevent chronic weakness.
9. Verrucas
Also known as plantar warts, verrucas appear on the soles of the feet as flat, black-dotted lesions caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They are often mistaken for corns but tend to have a rougher texture and may cause discomfort. Verrucas usually resolve spontaneously but can be treated with over-the-counter topical treatments, salicylic acid patches, or cryotherapy. Maintaining foot hygiene reduces the risk of spreading or developing new verrucas.
Understanding the causes of foot pain is essential for timely treatment and avoiding complications. If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional or a specialist like a podiatrist is recommended. Early diagnosis and proper management can significantly improve quality of life, reduce discomfort, and maintain healthy foot function for years to come.