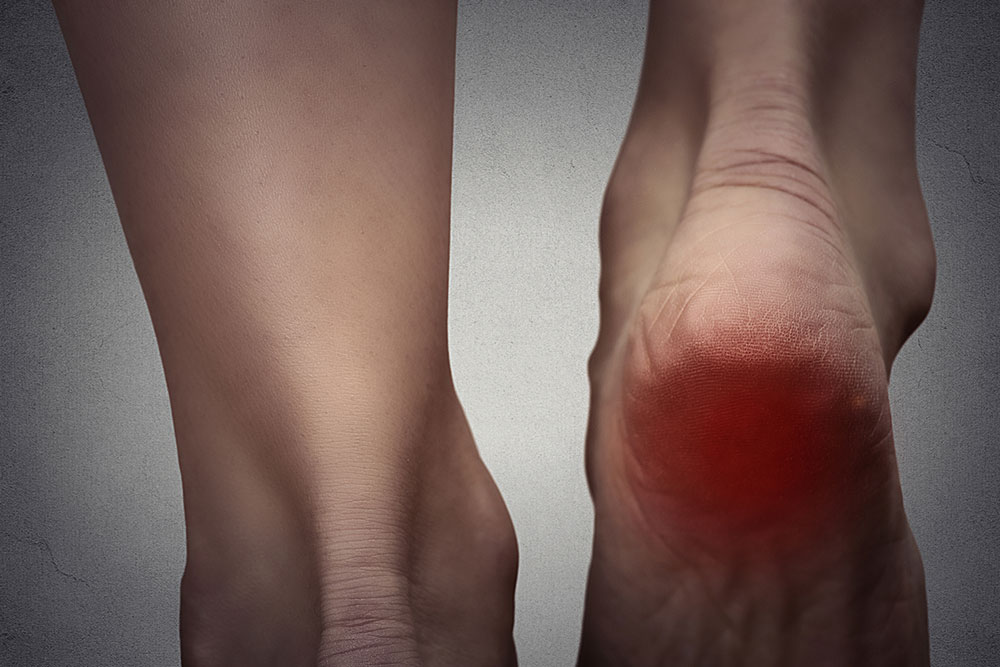
Comprehensive Guide to Common Causes of Foot Discomfort and How to Address Them
This comprehensive guide explores the common causes of foot discomfort, including inflammation, nerve issues, bone injuries, and structural problems. It emphasizes early diagnosis and effective treatment options like physical therapy, orthotics, and medical interventions. The article also offers practical tips for prevention and maintaining foot health to prevent long-term issues. Suitable for anyone experiencing persistent foot pain, this detailed overview aims to educate readers on the importance of timely medical consultation for optimal foot care and comfort.
Understanding The Main Causes of Foot Discomfort and Effective Solutions
Our feet are complex structures composed of bones, tendons, ligaments, muscles, and connective tissues. They support our entire body weight and enable mobility, which makes them vulnerable to a variety of issues that can cause discomfort, pain, or even impair daily activities. If you're experiencing persistent foot discomfort, understanding the underlying causes is essential to seek appropriate treatment and prevent further complications. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the most common causes of foot pain, their symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatment options.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Foot and Its Vulnerabilities
The human foot contains 26 bones, over 30 joints, numerous tendons, and ligaments. Each part plays a critical role in stability, movement, and shock absorption. Due to this intricate structure, various issues can develop from injuries, biomechanical abnormalities, or systemic conditions. Recognizing the specific cause of foot discomfort is crucial for targeted treatment.
Primary Causes of Foot Discomfort
Inflammation and Overuse Injuries
Inflammation is a common culprit behind foot pain. It often results from injuries such as sprains, strains, or repetitive stress from activities like running, walking, or standing for long periods. Repetitive motion can cause inflammation in tendons like the Achilles tendon or plantar fascia, leading to conditions such as tendonitis or plantar fasciitis. Symptoms typically include a burning sensation, swelling, warmth, numbness, or sharp pains that worsen during activity. Chronic inflammation may result in strain on surrounding tissues, causing persistent discomfort.
Neuropathic and Nerve-Related Conditions
Nerve damage or compression can significantly contribute to foot pain. Neuropathy, especially diabetic peripheral neuropathy, is a prevalent cause among adults with diabetes. This condition can cause numbness, tingling, burning sensations, or shooting pains. Nerve entrapment syndromes, such as tarsal tunnel syndrome, can also cause localized nerve compression, leading to persistent pain, weakness, or loss of sensation. Understanding nerve-related causes is vital for proper management and avoiding worsening symptoms.
Bone Injuries and Structural Abnormalities
Bone injuries, including fractures, stress fractures, and growths like bone spurs (osteophytes), are frequent causes of foot discomfort. These injuries often result from trauma, overuse, or aging processes. Symptoms may include localized pain, swelling, bruising, or difficulty bearing weight. Proper diagnosis through imaging studies and medical evaluation is essential for effective treatment, which may involve rest, immobilization, or surgical intervention.
Arch Problems and Biomechanical Issues
Structural variations such as flat feet (fallen arches) or high arches can predispose individuals to discomfort and injury. Flat feet, characterized by a collapse of the medial arch, can cause overpronation, leading to uneven weight distribution and strain on musculature and joints. Conversely, high arches often lead to increased pressure on the heel and ball of the foot. Both conditions can cause pain, instability, and an increased risk of ankle sprains or plantar fasciitis. Custom orthotics, stretching, and strengthening exercises are often recommended to manage these issues.
Other Contributing Factors
Infections: Fungal infections like athlete’s foot can cause itching, cracking, and discomfort.
Systemic Conditions: Rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and other inflammatory diseases may manifest with foot pain.
Improper Footwear: Ill-fitting shoes or worn-out soles can lead to blisters, calluses, and pressure points that cause pain and deformities.
Diagnostic Approach and When to Seek Medical Advice
If foot discomfort persists beyond a few days or worsens over time, consulting a healthcare professional is imperative. A detailed history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound often aid in diagnosis. Early diagnosis enables targeted treatment, which may include physical therapy, medications, orthotic devices, or surgical procedures.
Effective Treatments and Preventive Measures
Treatment options vary depending on the cause but generally include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Over-the-counter pain relievers like NSAIDs can help reduce inflammation and pain. For structural issues, custom orthotics provide support and correct biomechanical abnormalities. Physical therapy helps strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and restore function. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair fractures, remove bone spurs, or correct deformities.
Preventive strategies are equally important. Wearing supportive, well-fitting shoes and avoiding prolonged standing or high-impact activities can reduce strain on the feet. Regular stretching and strengthening exercises enhance foot stability. Maintaining a healthy weight decreases load on the feet. Addressing systemic conditions like diabetes promptly can prevent nerve damage and other complications. Staying vigilant about foot health and seeking early medical intervention can significantly improve quality of life.
Conclusion
Foot discomfort can stem from numerous causes ranging from inflammation and nerve conditions to structural abnormalities and systemic diseases. Recognizing the signs early and obtaining proper diagnosis are key to effective treatment and long-term relief. Adopting preventive measures and maintaining good foot health practices can help keep your feet healthy and pain-free, supporting an active and comfortable lifestyle. If you experience persistent or severe foot pain, do not hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for expert guidance and personalized treatment plans.