Comprehensive Guide to Foot Discomfort: Identifying Causes and Effective Prevention Strategies
Foot discomfort can hinder daily activities and signal underlying health issues. This comprehensive guide explores common causes like bunions, plantar fasciitis, and heel spurs, highlighting early symptoms and preventive measures. Proper footwear, lifestyle changes, and medical consultation are key to alleviating pain and avoiding complications. Recognizing early signs such as persistent pain, deformities, or difficulty walking enables timely intervention. Implementing supportive footwear, maintaining healthy weight, and seeking professional help if symptoms persist are essential steps to ensure optimal foot health and a pain-free life.
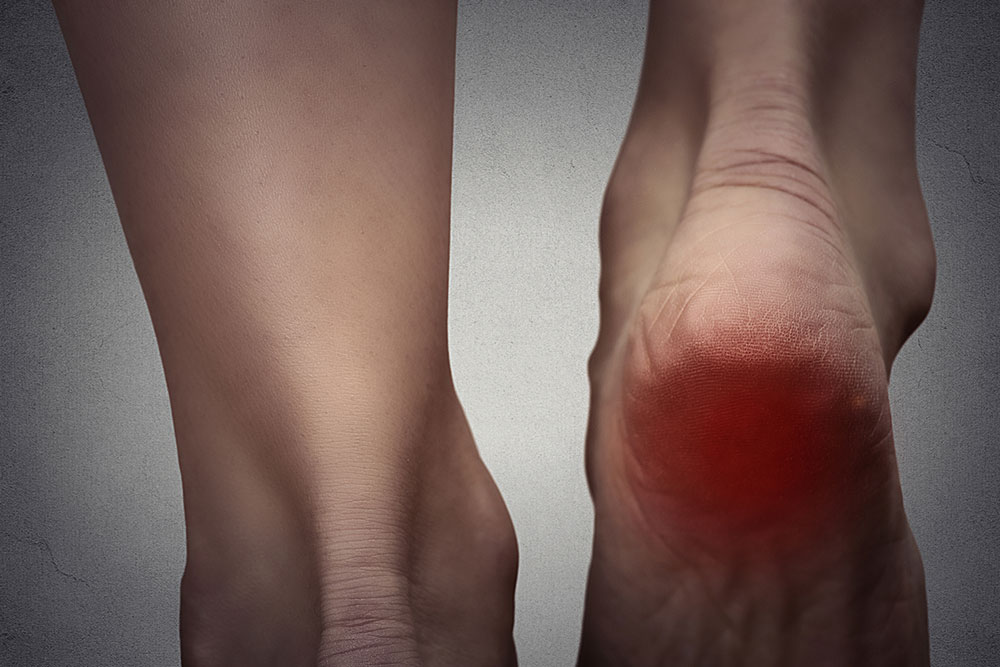
Comprehensive Guide to Foot Discomfort: Identifying Causes and Effective Prevention Strategies
Foot discomfort is a common issue that affects millions of individuals worldwide, often leading to disrupted daily activities and diminished quality of life. While mild pain may be transient and alleviated by simple rest or changes in activity, persistent or severe foot pain should never be overlooked, as it could be indicative of underlying health conditions that require medical attention. Understanding the root causes of foot discomfort, recognizing early symptoms, and adopting preventive measures can significantly improve foot health and overall wellbeing.
There is a wide range of foot conditions that can cause pain, discomfort, and functional limitations. Among the most prevalent are bunions, heel spurs, and plantar fasciitis. Each of these conditions presents unique symptoms and requires specific management strategies. Recognizing early warning signs such as persistent pain, visible deformities, or difficulty walking can prevent the progression of these ailments and reduce the risk of complications.
**Common Causes of Foot Discomfort**
Bunions (Hallux Valgus): This deformity manifests as a bony bump on the joint at the base of the big toe. Often caused by wearing narrow, ill-fitting shoes or high heels, bunions can lead to swelling, redness, and pain, especially when walking or wearing constrictive footwear.
Plantar Fasciitis: Characterized by stabbing or burning pain at the bottom of the foot, particularly noticeable during the first steps after waking up or after periods of rest. It results from inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue supporting the arch of the foot.
Heel Spurs: Bony growths on the heel bone, usually caused by calcium deposits that develop over time due to repetitive stress or strain. Heel spurs can cause sharp pain during walking or standing and might be associated with plantar fasciitis.
Achilles Tendinitis: Inflammation of the Achilles tendon that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone, often resulting from overuse, intense physical activity, or improper footwear.
Osteoarthritis and Bursitis: Degenerative joint diseases that affect the foot joints, leading to stiffness, swelling, and pain.
Morton’s Neuroma: Thickening of tissue around a nerve leading to the toes, causing burning pain in the ball of the foot, numbness, or tingling sensations.
**Early Symptoms and Signs to Watch Out For**
Persistent, dull or sharp pain that persists beyond initial activity.
Difficulty walking or discomfort after rest that alleviates with activity, or vice versa.
Visible deformities, bumps, swelling, or redness around the affected areas.
Stabbing sensations, numbness, or tingling in the toes or bottom of the foot.
Changes in gait or walking pattern to compensate for pain.
**Effective Treatment and Prevention Tips**
Managing foot discomfort primarily involves a combination of medical intervention, lifestyle modifications, and proper footwear. For mild cases, over-the-counter pain relievers, rest, and stretching exercises can be effective in alleviating symptoms. For more severe or persistent issues, consulting a healthcare professional such as a podiatrist or orthopedic specialist is essential for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans.
Wearing supportive, well-fitting shoes is crucial in both preventing and managing foot problems. Shoes with a wide toe box, good arch support, and cushioned insoles can reduce strain on the foot structures. Avoiding narrow, high-heeled shoes, which can exacerbate deformities like bunions, and opting for low-heeled or flat shoes with proper support are recommended habits.
Additional preventive measures include maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the feet, engaging in regular foot-strengthening exercises, and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or walking on hard surfaces without supportive footwear. Using orthotics or custom insoles can help realign the foot, distributing pressure more evenly, and preventing worsening of existing conditions.
If foot pain persists despite these measures or if symptoms worsen, seeking medical evaluation is critical. Early intervention can prevent chronic problems, reduce the need for invasive procedures, and improve overall foot health.