Comprehensive Guide to Alleviating Heel Pain Effectively
This comprehensive article explores the causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for heel pain, emphasizing both non-invasive methods like stretching, ice therapy, and supportive footwear, as well as surgical options. It highlights the importance of early intervention for effective relief and recovery. Whether you're experiencing mild discomfort or chronic pain, understanding these strategies can help you manage heel issues effectively and restore foot health.
Comprehensive Guide to Alleviating Heel Pain Effectively
Heel pain is a common and often debilitating condition that affects individuals across all age groups and activity levels. Whether due to repetitive stress, injury, or underlying health issues, heel discomfort can significantly impact daily life, making simple activities like walking, standing, or even sleeping uncomfortable. Understanding the diverse causes of heel pain and exploring effective treatment options are essential for relief and recovery. This extensive guide delves into the root causes of heel pain, describes diagnostic procedures, and discusses both conservative and surgical treatment options to help individuals regain mobility and comfort.
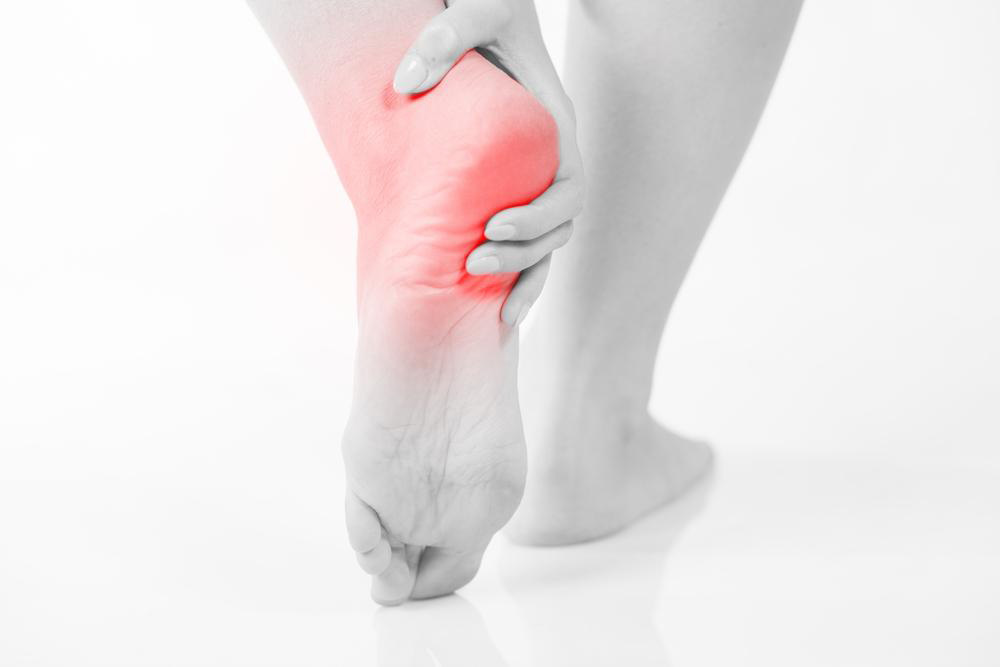
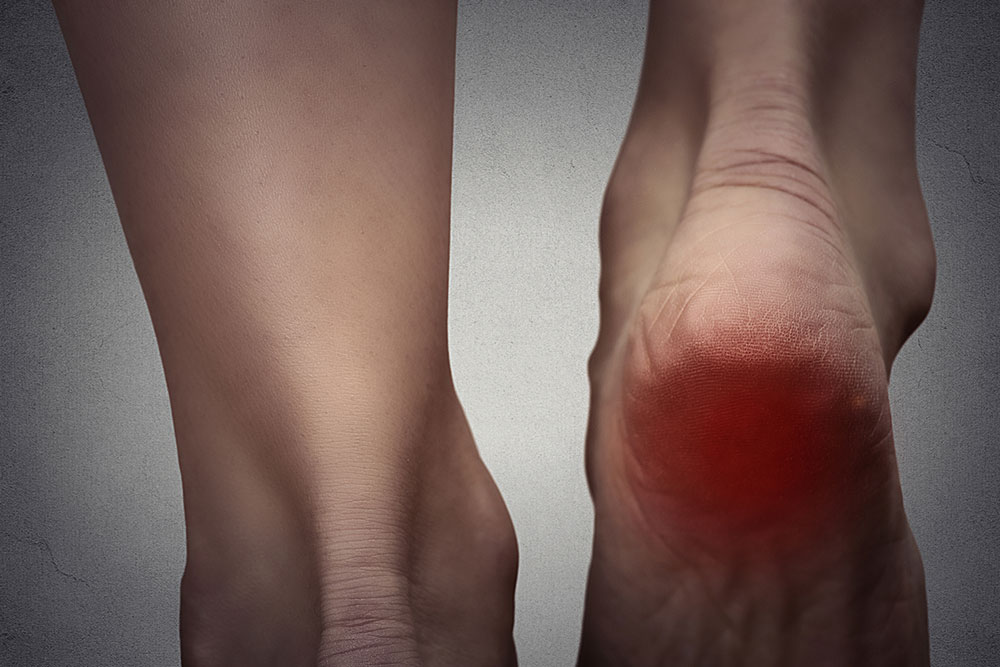
Heel discomfort can originate from multiple sources including stress fractures, tendinitis, heel spurs, and joint inflammation. Among these, plantar fasciitis is identified as the most prevalent cause, accounting for a significant percentage of heel pain cases. Plantar fasciitis involves inflammation of the thick band of tissue called the plantar fascia, which runs along the bottom of the foot connecting the heel bone to the toes. This condition often results from repetitive strain, overuse, improper footwear, or excessive weight, leading to heel discomfort and stiffness.
Identifying the exact cause of heel pain is critical for effective treatment. Symptoms such as pain location, timing, and associated signs like swelling can provide clues to the underlying issue. Heel pain often worsens after waking up in the morning or after periods of prolonged standing or walking. For some individuals, the pain may be a constant ache that intensifies throughout the day, making routine activities difficult.
In certain cases, heel pain is accompanied by swelling or tenderness. Overweight individuals are at a higher risk of developing heel pain due to increased stress placed on the heel structure. The presence of swelling and other symptoms warrants thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional to determine the precise cause and appropriate treatment plan.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Proper diagnosis involves a comprehensive assessment that includes a detailed medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. A healthcare provider will examine the heel for signs of inflammation, swelling, tenderness, or deformity. Medical history helps identify risk factors such as recent injuries, activity levels, footwear habits, and underlying health conditions. Imaging techniques like X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound are employed to detect fractures, bone spurs, soft tissue damage, or other abnormalities surrounding the heel.
Effective Treatment Strategies
Managing heel pain effectively depends on understanding its cause. Many cases can be resolved with conservative, non-invasive methods, while others may require surgical intervention if initial treatments fail or if structural damage is evident.
Most individuals experience significant improvement and often complete recovery through a combination of lifestyle modifications, medical treatments, and proper footwear. Patience and adherence to recommended therapies are key to long-term relief.
Conservative Treatment Methods
Non-surgical management is typically the first line of defense against heel pain. These approaches are aimed at reducing inflammation, relieving discomfort, and addressing contributing factors.
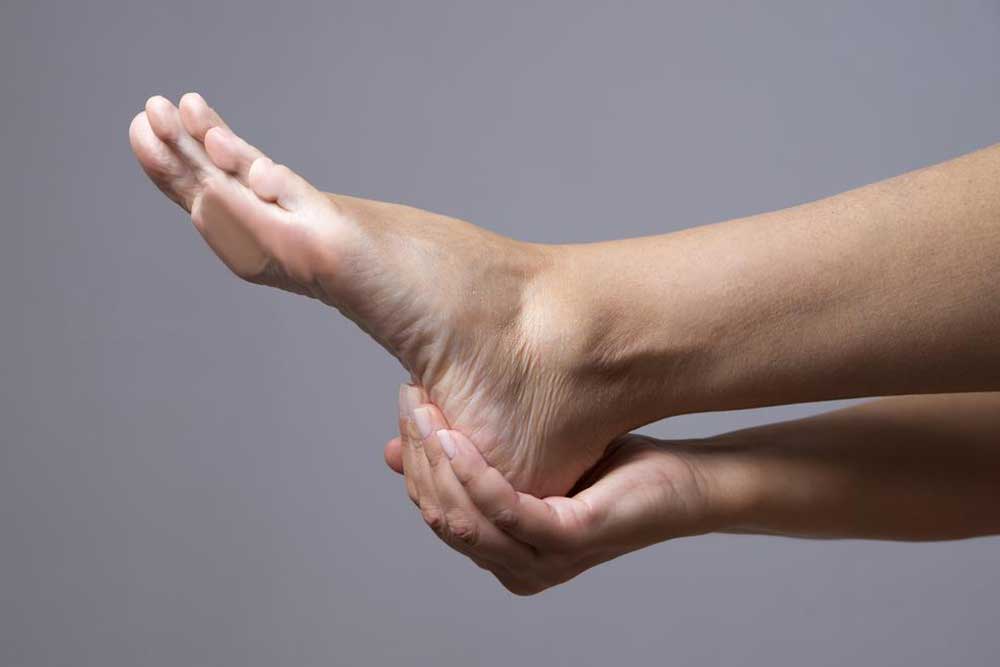
Stretching Exercises: Gentle stretching routines targeting the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia can help relieve tension in these tissues. Specific stretching techniques, such as calf stretches and toe stretches, improve flexibility and decrease strain on the heel.
Cold Therapy: Applying ice packs or cold compresses to the affected area helps reduce inflammation and numb pain. Cold therapy is most effective when used several times daily, especially after activities that worsen symptoms.
Medication: Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen or naproxen can alleviate pain and decrease swelling. These medications should be used responsibly and according to medical advice.
Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that exacerbate heel pain, such as extended standing or high-impact exercises, allows inflamed tissues to heal. Elevating the foot and taking frequent breaks can also help manage symptoms.
Footwear and Orthotics: Wearing properly fitting shoes with good arch support and cushioning can prevent further strain. Custom orthotic inserts designed to support the heel and foot arch can distribute pressure evenly and promote healing.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical procedures are considered when conservative treatments fail to provide relief over an extended period or in cases involving structural damage such as severe heel spurs or chronic plantar fasciitis. Common surgical options include procedures to remove heel spurs, repair torn tissues, or release tight fascia. Surgical decisions are personalized based on the patient's specific diagnosis, overall health, and activity level. Recovery after surgery varies but generally involves a period of immobilization, physical therapy, and gradual return to normal activities.
Heel pain symptoms typically begin with discomfort localized at the sole of the foot. Over time, untreated or persistent conditions can worsen, leading to significant mobility issues and diminished quality of life. Early diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies are essential for effective resolution, minimizing discomfort, and preventing chronic problems.