Comprehensive Guide to Heel Pain: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention Tips
This comprehensive guide explores the common causes of heel pain, including injuries and chronic conditions like plantar fasciitis and Achilles tendinitis. It offers detailed treatment options such as home remedies, lifestyle changes, physical therapy, and when to seek medical attention. Preventive tips focus on proper footwear, maintaining a healthy weight, and regular stretching to keep heels healthy. Understand your heel pain better and learn how to manage or prevent it for better mobility and overall foot health.

Comprehensive Guide to Heel Pain: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention Tips
Understanding Heel Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Solutions
The human foot is a marvel of engineering, comprising 26 bones, 33 joints, and an intricate network of muscles, tendons, and ligaments that work together to facilitate movement, balance, and support. The heel, being the largest bone in the foot, plays a crucial role in weight-bearing and mobility. However, heel pain and discomfort are common issues affecting people of all ages, often resulting from everyday activities, injuries, or underlying health conditions. Recognizing the causes and early signs of heel discomfort is vital for timely intervention and effective treatment.
Common Causes of Heel Discomfort
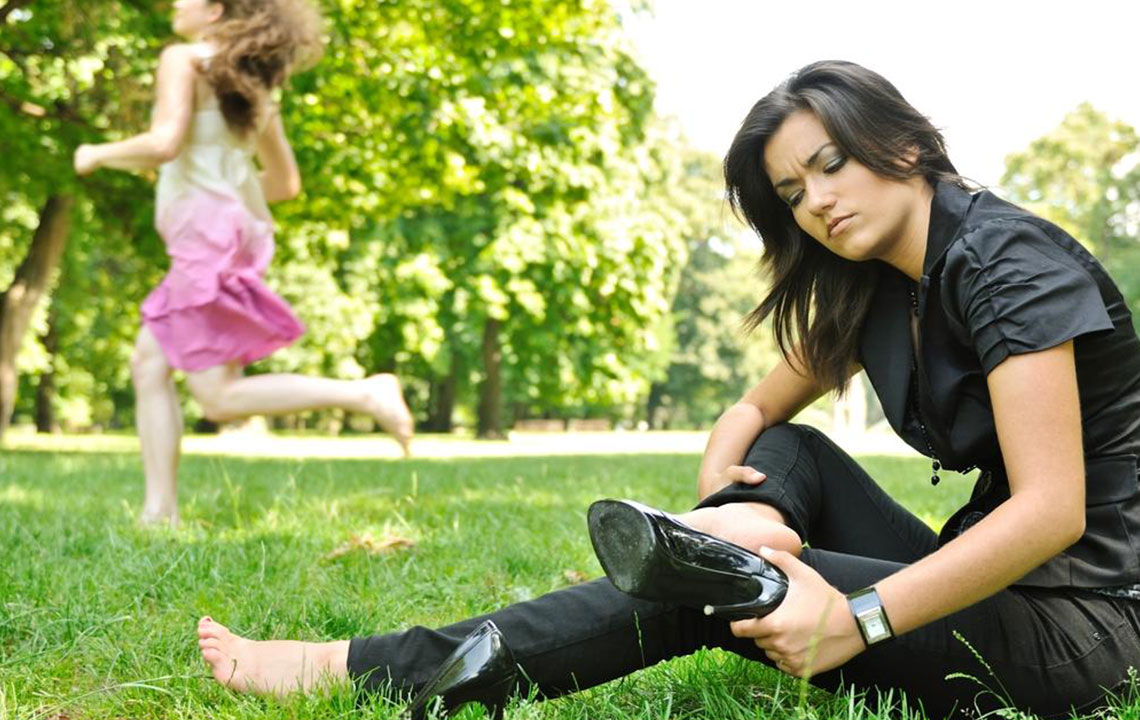
Heel pain can originate from various factors, ranging from minor injuries to chronic conditions. Understanding these causes helps in seeking appropriate treatment and preventing future issues.
Injuries and Trauma
Sprains and Strains: External forces, such as twisting or sudden impact, can cause stretching or tearing of ligaments and muscles around the heel, resulting in pain, swelling, and limited mobility. These injuries are often caused by falls, sports activities, or accidental impacts.
Heel Fractures: A break in the heel bone can occur due to high-impact trauma like falls from significant heights or car accidents. Such fractures are often severe, requiring urgent medical attention, and may involve immobilization or surgery.
Contusions and Bruises: Direct blunt trauma can cause bleeding within tissues, leading to painful swelling and discoloration.
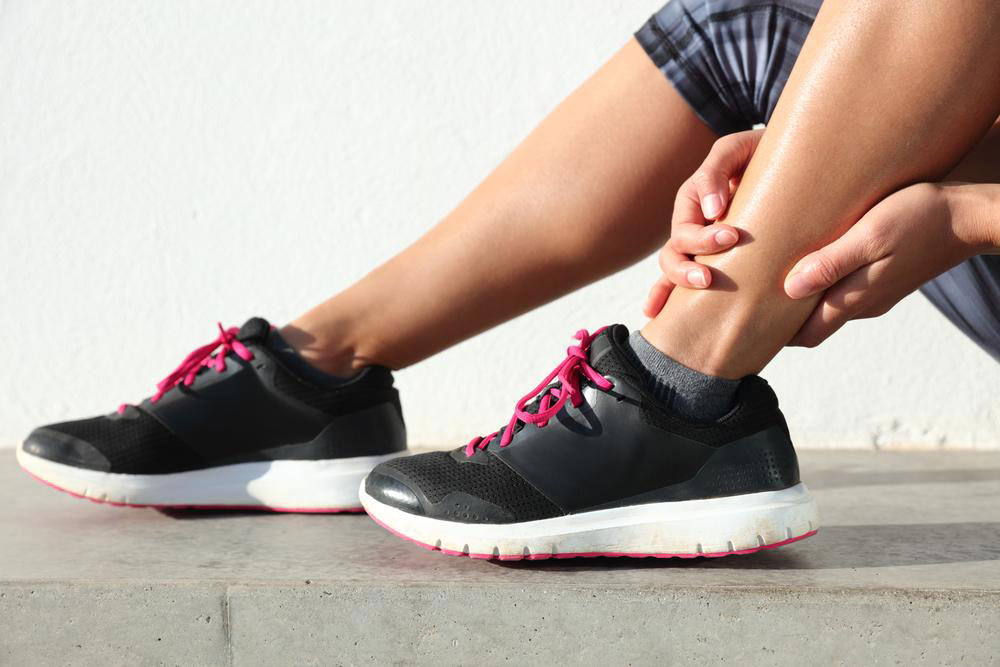
Chronic and Overuse Conditions
Plantar Fasciitis: One of the most common causes of heel pain, this condition involves inflammation of the plantar fascia—a thick ligament connecting the heel bone to the toes. Repetitive stress from running, prolonged standing, or unsuitable footwear can cause micro-tears, leading to stabbing pain, particularly noticeable in the morning or after rest.
Achilles Tendonitis: Overuse or excessive strain on the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone, can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness in the back of the heel. This condition often affects runners, dancers, or individuals engaging in activities with sudden accelerations or jumps.
Heel Spur: A calcium deposit that forms on the underside of the heel bone, often associated with plantar fasciitis, can cause chronic, sharp pain and tenderness on the heel bottom.
Other Contributing Factors
Metabolic and Systemic Disorders: Conditions such as gout, rheumatoid arthritis, or neuropathy can lead to heel discomfort through inflammation, nerve damage, or joint issues.
Nerve Compression: Entrapment of nerves around the heel area can cause shooting pain, tingling, or numbness.
Accurate diagnosis of heel pain involves a physical examination, medical history review, and sometimes imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans. Identifying the root cause is essential for implementing an effective treatment plan.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Heel Pain
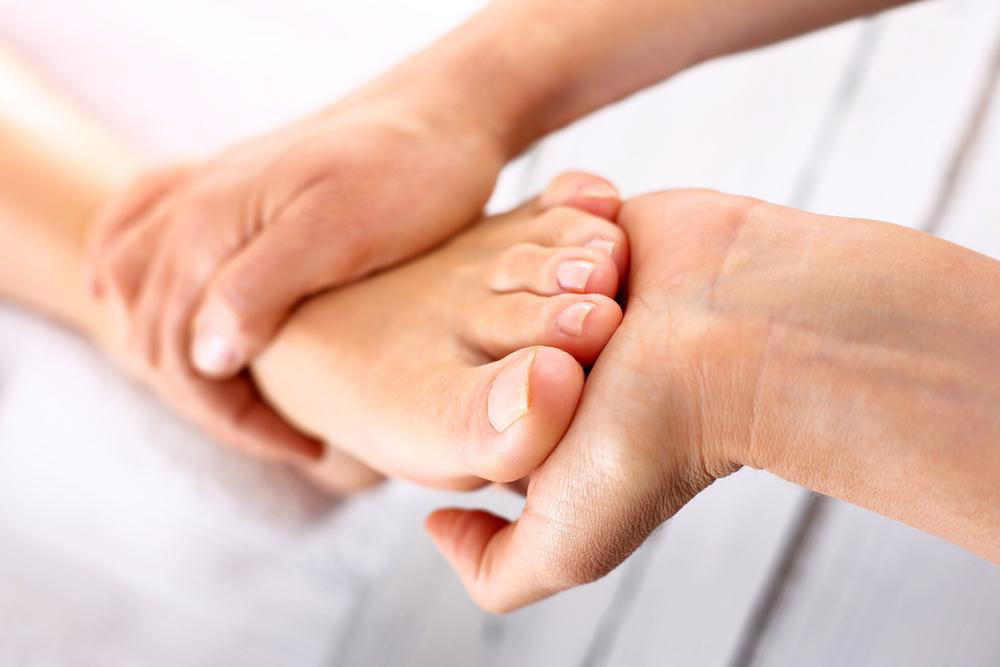
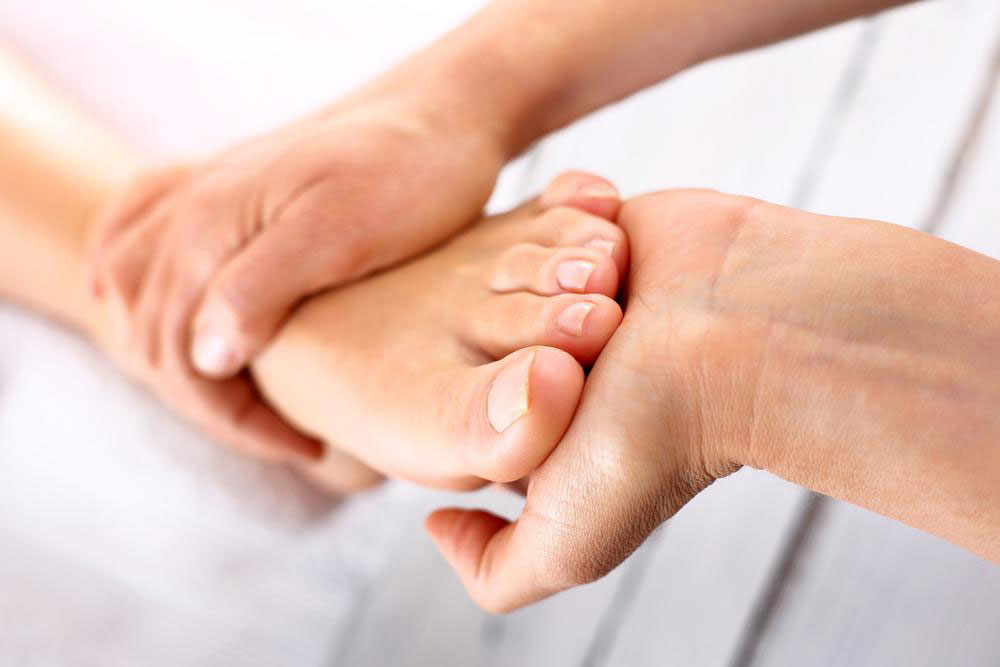
Addressing heel discomfort often involves a combination of home remedies, lifestyle modifications, and medical interventions. The goal is to reduce pain, promote healing, and prevent recurrence.
Home Care and Lifestyle Adjustments
Applying ice packs for 10 to 15 minutes, two to three times daily, reduces inflammation and alleviates pain.
Wearing supportive, well-fitted footwear with cushioned soles helps minimize stress on the heel and improves comfort during daily activities.
Using custom or over-the-counter orthotic inserts and heel lifts can redistribute pressure and provide relief, especially during prolonged standing or walking.
Night splints are beneficial in certain conditions like plantar fasciitis, as they keep the foot in a stretched position overnight, reducing morning pain.
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as NSAIDs (ibuprofen or naproxen), can help manage acute pain and inflammation.
Medical Treatments and Therapies
Physical therapy focusing on stretching, strengthening, and mobilization exercises can promote healing and improve foot mechanics.
In cases of persistent or severe pain, corticosteroid injections may be administered to reduce inflammation.
For heel spurs or chronic conditions unresponsive to conservative treatment, minimally invasive procedures or surgery might be necessary.
Advanced interventions like shockwave therapy or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections are emerging options for stubborn cases.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional if heel pain persists beyond a few days, worsens over time, or is accompanied by symptoms such as swelling, redness, numbness, or difficulty walking. Early diagnosis and treatment of underlying issues prevent complications and promote quicker recovery.
Preventive Measures for Healthy Heels
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces undue pressure on the heels.
Incorporating regular stretching and strengthening exercises for the foot and calf muscles can prevent overuse injuries.
Choosing appropriate footwear that provides adequate arch support, cushioning, and fits well is vital.
Avoiding excessive standing or high-impact activities without proper preparation can lower the risk of heel injuries.
Resting tired feet and giving sufficient time for healing after any injury are key components of heel health maintenance.
By understanding the causes of heel discomfort and adopting proactive strategies, you can enjoy pain-free walking and standing, preserving your mobility and quality of life. Regular check-ups and prompt attention to symptoms are essential for maintaining healthy heels and preventing chronic issues.