Comprehensive Guide to Relieving Heel Pain and Discomfort
Heel pain is a common issue that impacts many people, often caused by conditions like plantar fasciitis or Achilles tendinitis. Early management through medications, physical therapy, orthotics, and other interventions can effectively alleviate discomfort and promote healing. In severe or persistent cases, advanced treatments including shock wave therapy or surgery may be necessary. Preventive measures such as supportive footwear and stretching routines can help avoid future heel problems. Seeking timely medical advice is essential to prevent chronic issues and restore foot health, ensuring a better quality of life.
Effective Methods to Alleviate Heel Discomfort and Pain
Heel discomfort is one of the most prevalent issues affecting foot health globally. Many individuals experience heel pain at some point in their lives, which can significantly impact daily activities and overall well-being. The discomfort tends to originate underneath the heel, a condition known as plantar fasciitis, or behind the heel, indicating possible Achilles tendinitis. Despite the discomfort, heel pain is often not associated with life-threatening conditions but requires appropriate management to prevent chronic issues. Mild cases frequently resolve on their own, but persistent or intense pain necessitates professional intervention.
Heel pain tends to develop gradually without any specific injury, often triggered by activities such as wearing unsupportive footwear, standing or walking for extended periods, or prolonged inactivity. It commonly worsens after rest, particularly upon waking in the morning or after long periods of sitting, a phenomenon known as post-static dyskinesia. Severe pain accompanied by swelling, redness, fever, or numbness should prompt immediate medical consultation. When heel pain persists beyond a week, it's crucial to seek professional evaluation to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment options.
Fortunately, there are numerous effective strategies and treatments available to alleviate heel discomfort. Addressing heel pain early can prevent chronic issues and improve quality of life. Below are some of the most proven interventions:
Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications such as ibuprofen or naproxen help reduce pain, inflammation, and swelling. These are often the first line of treatment for acute heel pain and can be taken orally or applied topically as gels.
Corticosteroid Injections: For cases where NSAIDs are insufficient, corticosteroid injections can deliver potent anti-inflammatory effects directly to the affected area. These injections are usually administered under ultrasound guidance to ensure precision and minimize discomfort.
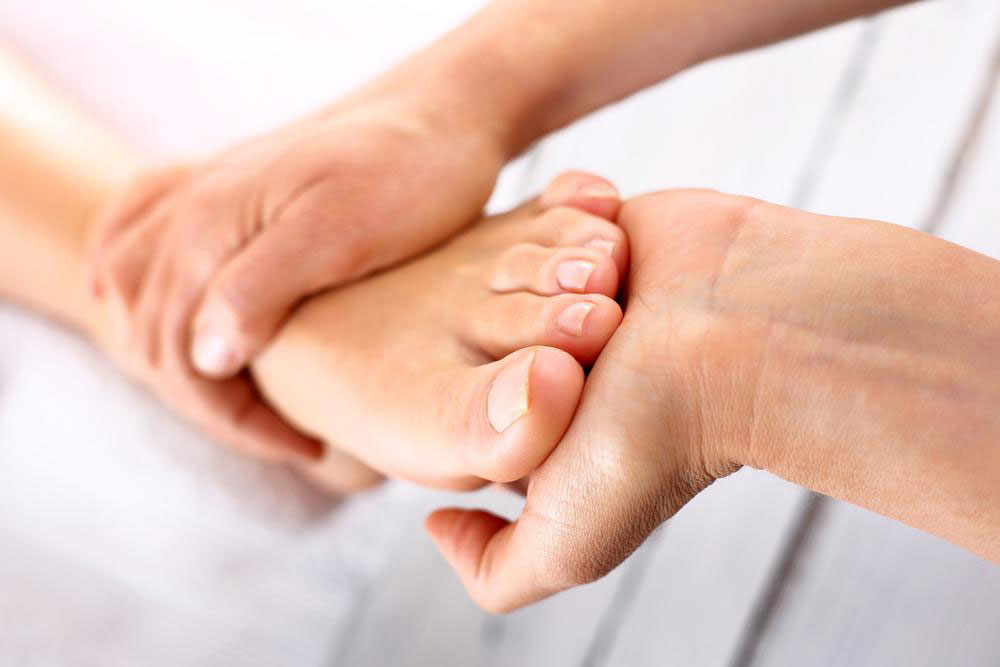
Physical Therapy: Customized physical therapy programs include stretching exercises for the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon, alongside strengthening routines for lower leg muscles. These therapies enhance foot stability, relieve tension, and promote healing.
Night Splints: Wearing night splints during sleep helps keep the heel and Achilles tendon in a stretched position, which decreases morning pain and encourages tissue repair.
Orthotic Devices: Custom insoles or supportive orthotics help correct foot alignment, distribute pressure evenly, and provide cushioning. This intervention is especially beneficial for individuals with flat feet or high arches.
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT): High-energy sound waves are focused on the affected tissues to stimulate healing and tissue regeneration. ESWT is particularly recommended for chronic heel pain cases unresponsive to conservative treatments.
Surgical Intervention: When all other treatments fail, surgical options such as plantar fascia release or removal of bone spurs may be considered. Surgery carries risks and should be approached only after thorough consultation with a foot specialist.
Prevention strategies also play a crucial role in managing heel discomfort. Regular stretching, wearing supportive footwear, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding abrupt increases in physical activity can significantly reduce the risk of heel problems. For persistent or worsening heel pain, professional medical assessment is essential to diagnose underlying conditions and formulate an effective treatment plan. Proper management and early intervention can restore foot function and prevent chronic complications, enabling individuals to resume normal activities without discomfort.