Comprehensive Guide to Identifying and Treating Foot Sole Pain
This comprehensive guide explores the common causes of sole foot pain, including overuse, injuries, and medical conditions. It offers practical advice on when to seek medical attention and discusses effective treatment options like rest, medication, and supportive devices. Understanding foot health is essential for maintaining mobility and preventing chronic problems. Proper care, early diagnosis, and appropriate interventions can significantly improve quality of life and foot function. Whether dealing with plantar fasciitis, sprains, or tendon issues, this article provides vital insights to help you manage and prevent foot sole pain effectively.

Comprehensive Guide to Identifying and Treating Foot Sole Pain
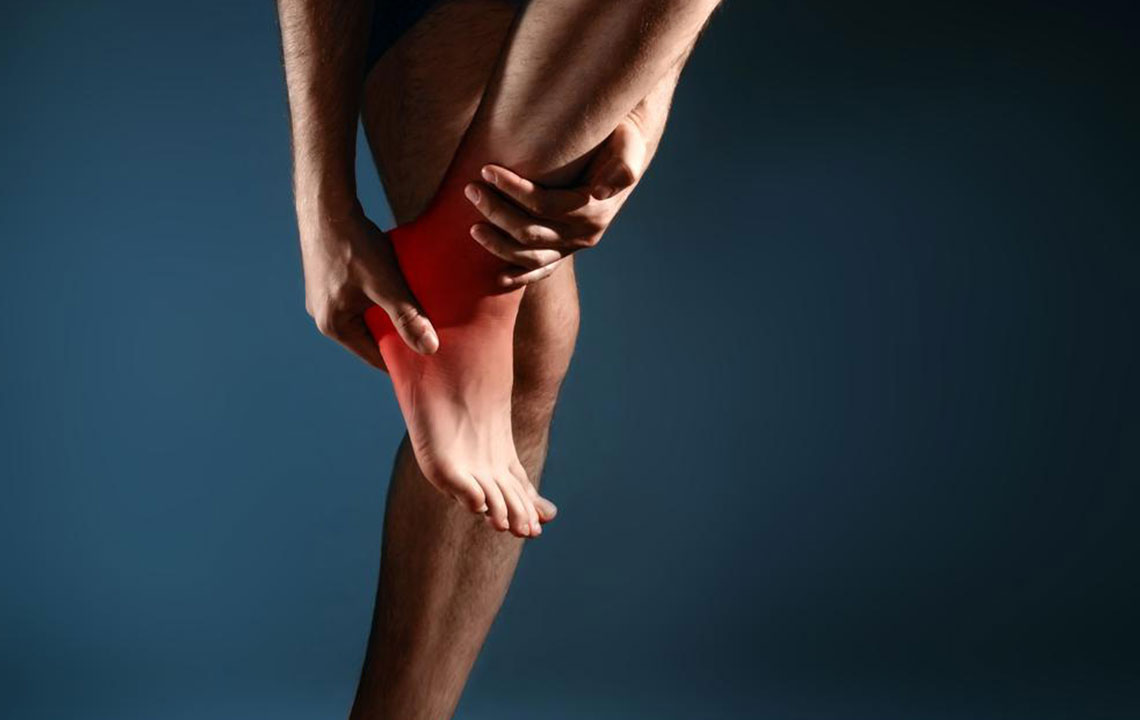
The human foot is a complex structure composed of numerous small bones, robust ligaments, tendons, and muscles that work together to support movement and balance. Due to its intricate design and constant use, the foot is prone to various injuries and discomforts, especially in the sole area. Even minor injuries or issues can significantly impair mobility and daily function, impacting personal and professional activities. With modern lifestyles becoming increasingly sedentary, many people walk less, rely more on transportation, and engage in fewer physical activities. This reduction in activity can lead to weakened foot muscles, tendons, and ligaments, making the sole more vulnerable to pain and injury. Persistent pain in the sole of the foot can be caused by a variety of factors, including overuse, trauma, and underlying medical conditions, all of which require proper understanding for effective management and prevention.
Understanding the Causes of Sole Foot Pain

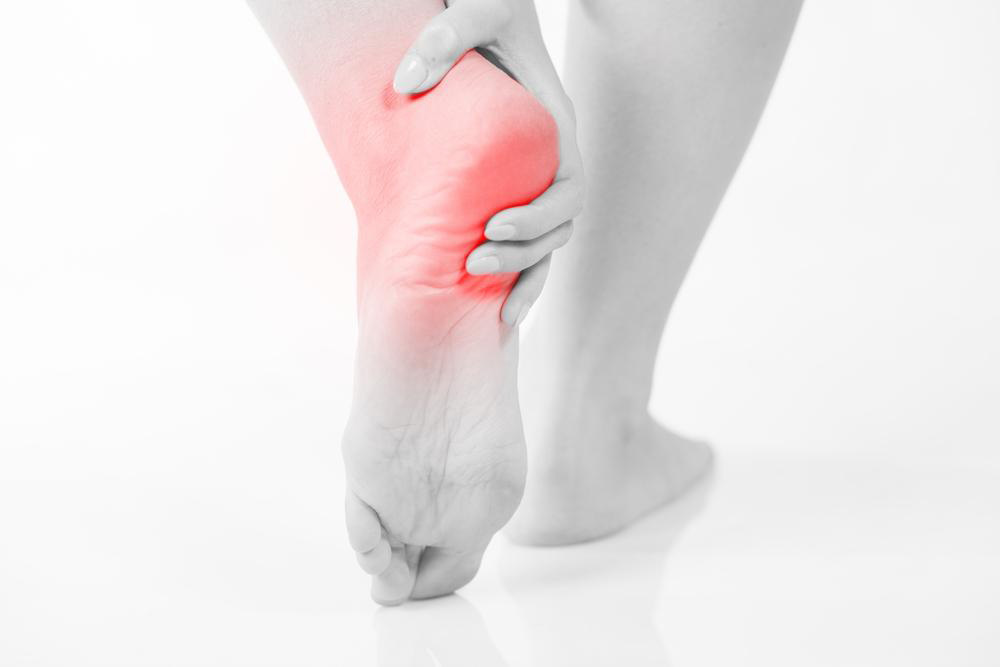
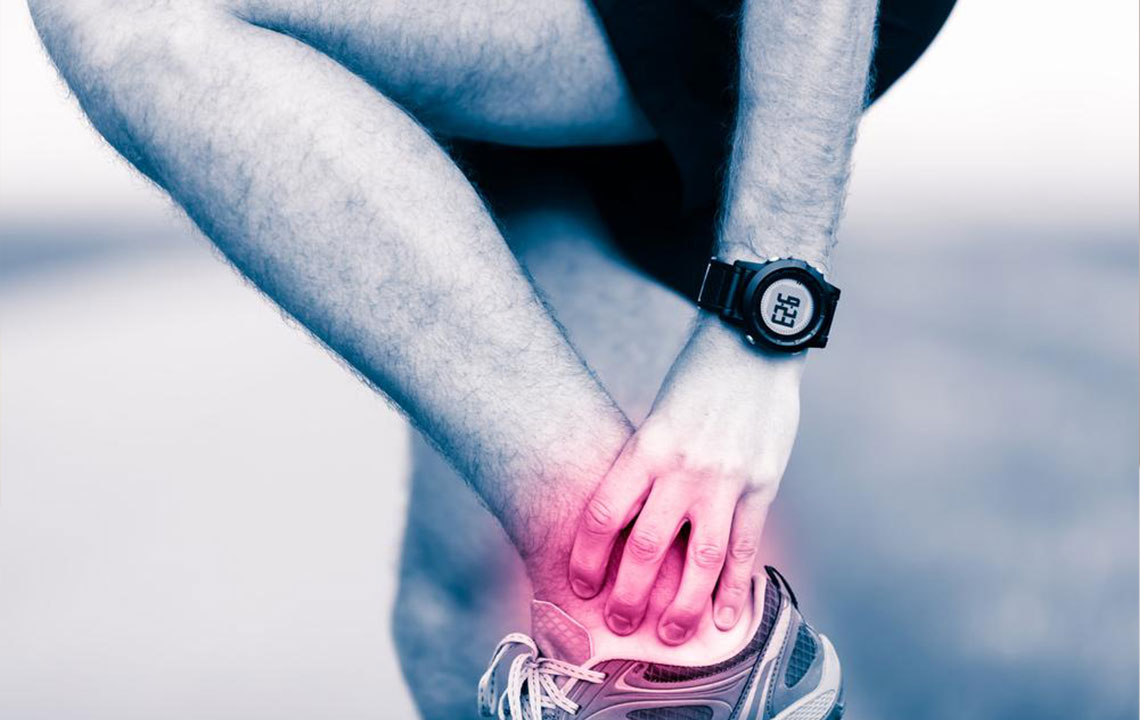
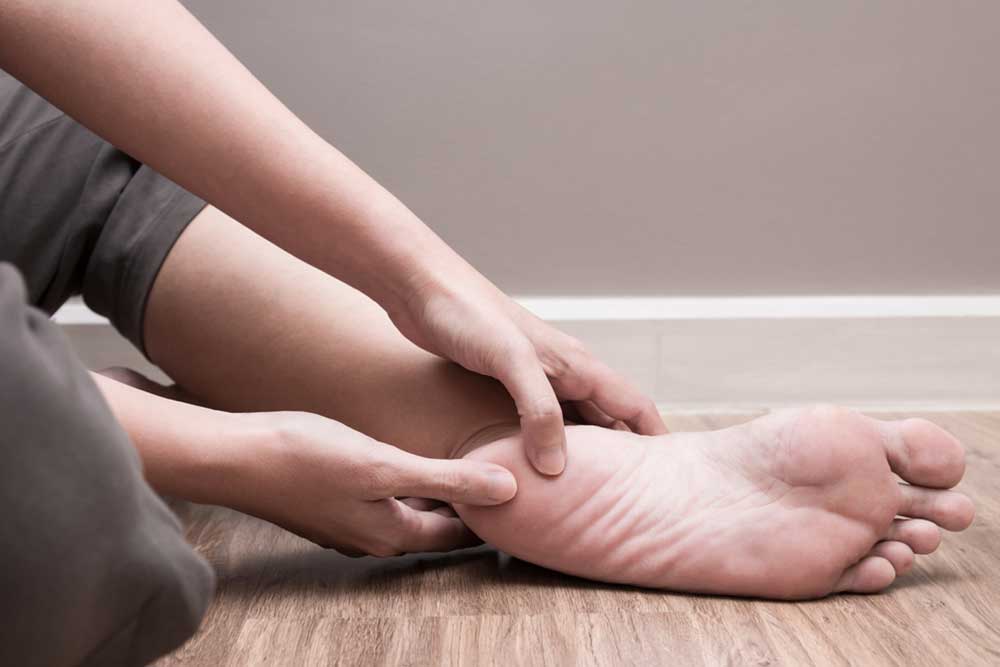
One of the primary causes of sole pain is excessive pressure on the foot, especially when this pressure exceeds the foot's capacity to withstand it. Such pressure can result from prolonged standing, improper footwear, or vigorous physical activity without adequate preparation. When the plantar fascia—the thick ligament that supports the arch—is overstressed, it can develop tears or inflammation, leading to a condition called plantar fasciitis, a common yet often painful issue affecting the sole of the foot. This condition manifests as sharp, stabbing pain, particularly with the first steps in the morning or after periods of rest. Besides overuse, sudden trauma from stumbling on uneven surfaces, twisting the foot, or dropping heavy objects can cause sprains, strains, or ligament tears resulting in discomfort and swelling. Other causes include Achilles tendinitis, which involves inflammation of the Achilles tendon, and reactive arthritis that can lead to joint inflammation in the foot. Proper understanding of these causes is crucial for timely intervention and effective treatment.
When to Seek Medical Advice for Foot Pain
If you experience severe or persistent pain in the sole of your foot, especially when accompanied by redness, swelling, or marked reduction in mobility, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. Sudden worsening of pain or inability to bear weight on the affected foot should never be ignored, as these signs indicate potential serious injury or underlying medical issues that require prompt diagnosis and treatment. Ignoring persistent pain can lead to chronic problems or further complications, emphasizing the importance of early medical intervention.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Foot Sole Pain
Managing pain in the sole of the foot involves a combination of rest, supportive measures, and medical treatment. Resting the foot and elevating it with supportive cushions can reduce swelling and alleviate pressure. Applying ice packs can help decrease inflammation and numb sharp pain. Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can provide temporary relief, but should be used according to medical advice. Physical therapy exercises focusing on stretching and strengthening the foot and ankle muscles may be recommended to prevent recurrence. In some cases, orthotic devices such as insoles or custom-made shoe inserts can provide additional support and distribute pressure evenly across the foot. Severe cases, especially those involving significant ligament tears or fractures, might require surgical intervention to repair the damaged tissues. However, most minor to moderate foot problems respond well to conservative treatments, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and proper care. Regular consultation with healthcare professionals ensures an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan, promoting faster recovery and preventing future issues.