Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Treating Hidradenitis Suppurativa Effectively
This in-depth guide explores how to effectively manage Hidradenitis Suppurativa, focusing on causes, symptoms, and treatment options. It emphasizes lifestyle changes, medical therapies, and the importance of early diagnosis to prevent complications. Supports emotional well-being through comprehensive care strategies for those affected by this chronic skin disorder.
Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Treating Hidradenitis Suppurativa Effectively
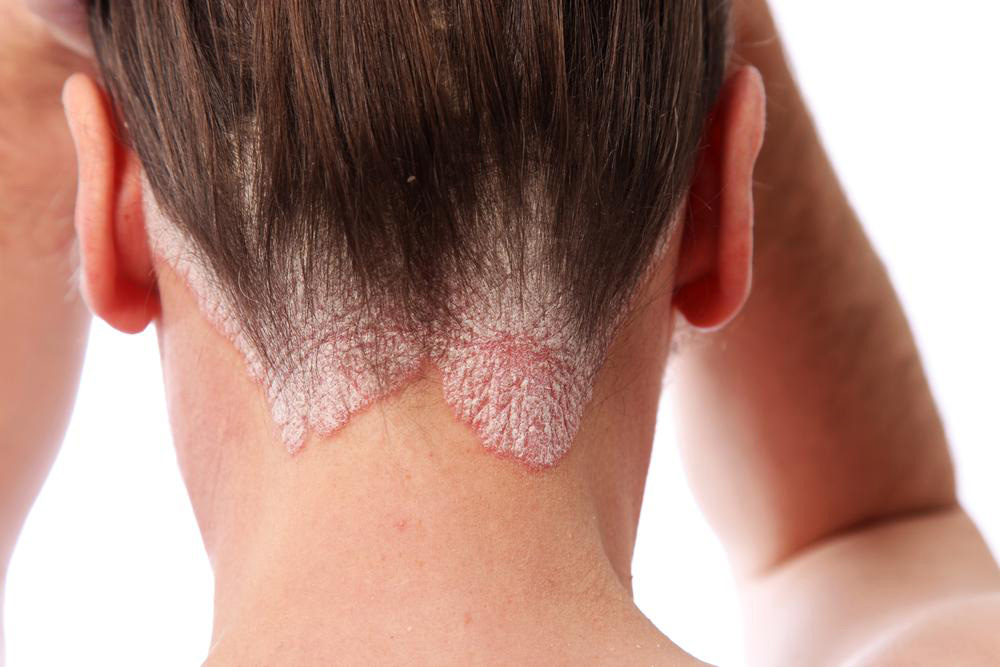
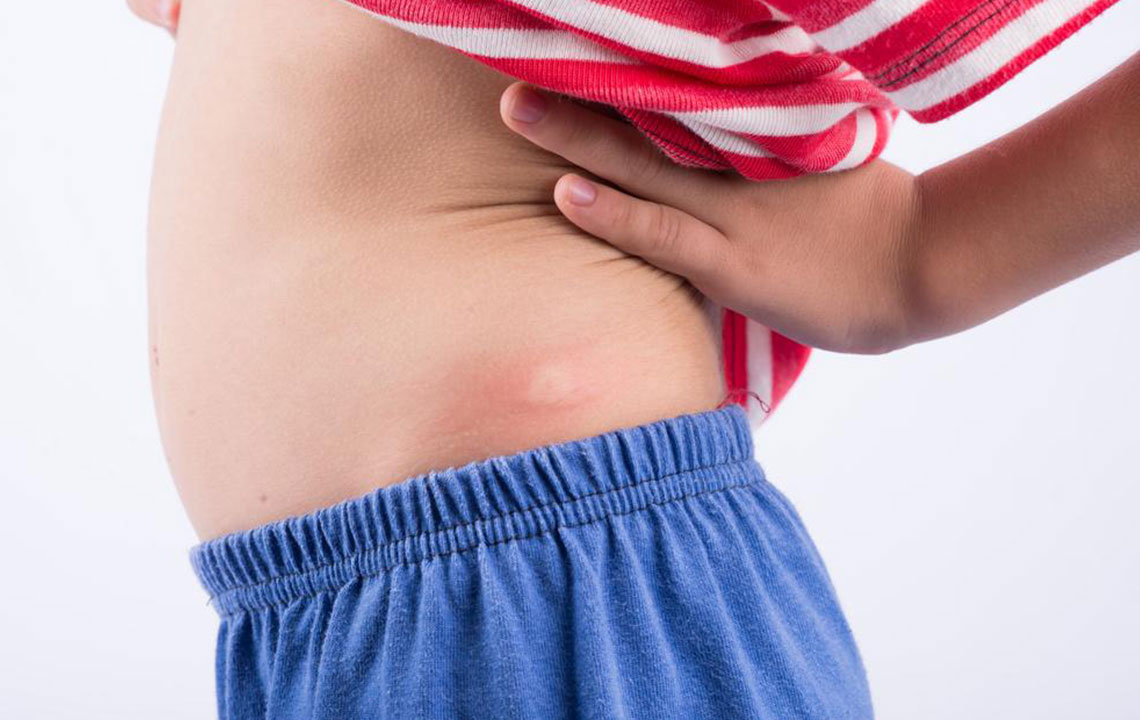
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is a complex and often distressing chronic skin condition that affects many individuals worldwide. Characterized by the development of painful, inflamed lumps beneath the skin, primarily in areas rich in sweat glands such as the armpits, groin, and the area between the buttocks, HS can significantly impact a person's quality of life. Despite ongoing research, there is currently no definitive cure for HS. However, with proper management strategies, lifestyle modifications, and medical interventions, sufferers can effectively control symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve their overall well-being.
Understanding HS is essential for patients and healthcare providers alike. The disease predominantly affects regions with apocrine (sweat) glands and often manifests as recurrent and painful nodules. These lumps frequently rupture, leading to abscess formation, scarring, and sometimes secondary infections if not addressed promptly. The psychological burden accompanying HS can be substantial, often resulting in emotional distress, social withdrawal, and decreased self-esteem. Therefore, comprehensive management should include not only medical treatments but also emotional and social support to assist individuals in coping effectively.
Management of HS requires a multifaceted approach tailored to the severity and spread of the condition. Patients are encouraged to seek consistent medical care and to adhere to personalized treatment plans designed by dermatologists or healthcare professionals experienced in handling this condition. To facilitate optimal outcomes, it's vital to understand the causes, symptoms, prevention strategies, and available treatment options for HS.
Causes and Risk Factors: While the precise cause of HS remains unclear, current research suggests it involves inflammation and blockage of hair follicles and sweat glands. These blockages lead to the formation of lumps that can become infected and inflamed. Several factors increase the risk of developing HS, including genetics, obesity, smoking, and hormonal influences. Women are more commonly affected, and the condition often starts during adolescence or early adulthood. Interestingly, HS is not related to hygiene products like deodorants or shaving, nor is it contagious. A hereditary component exists, with around one-third of patients reporting family members with similar issues.
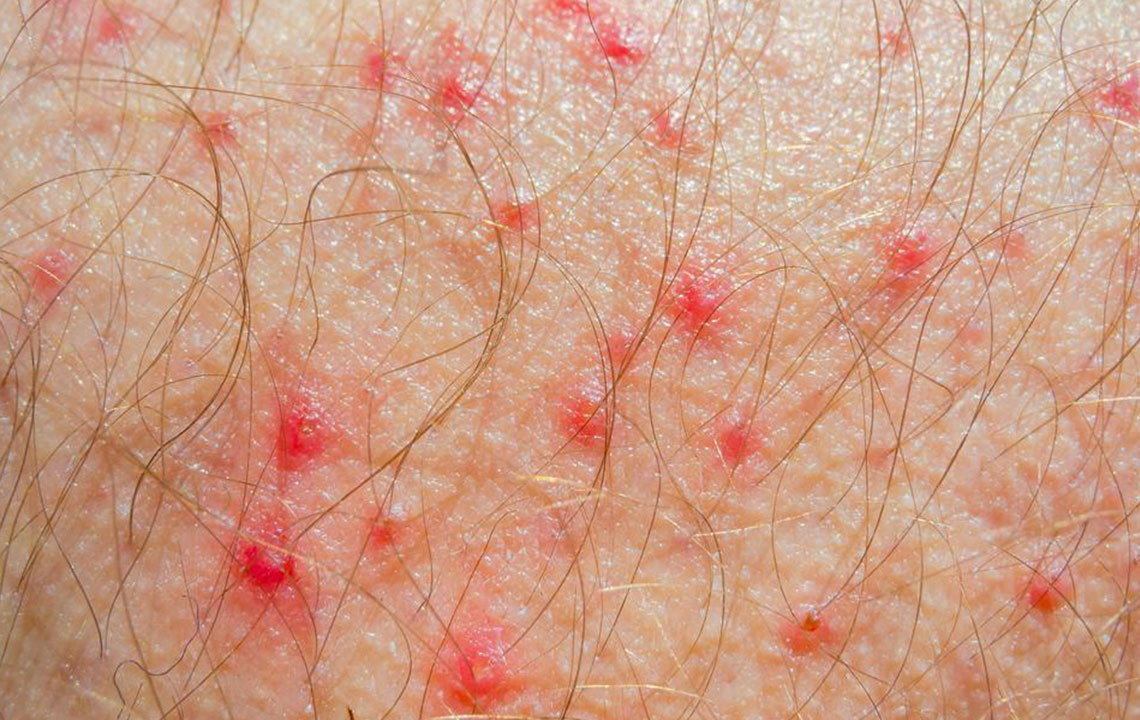
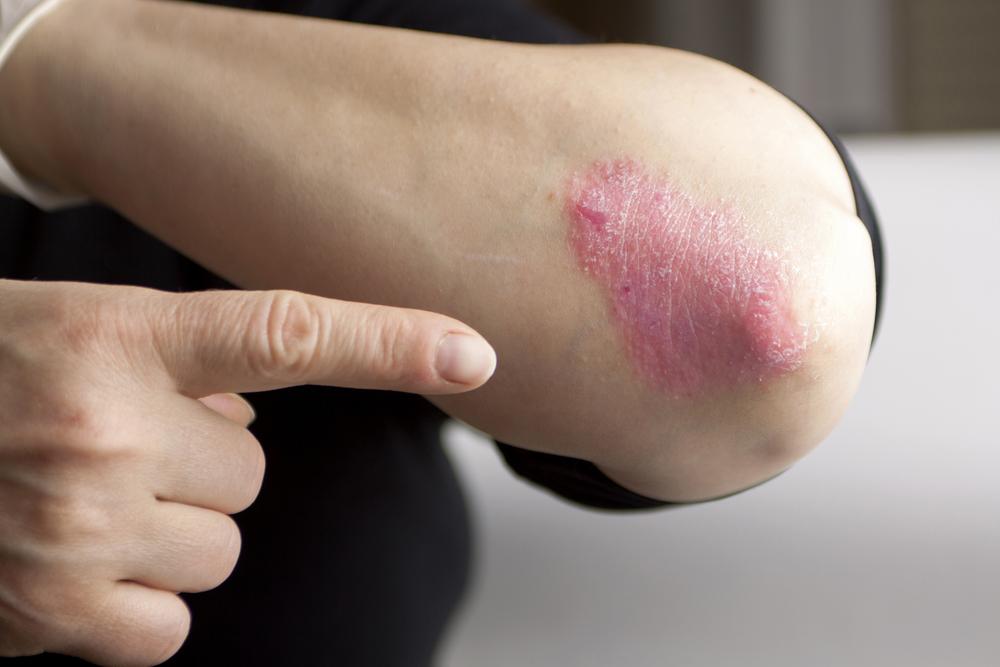
Recognizing Symptoms and Signs: The hallmark symptoms of HS include persistent, painful bumps that may resemble boils. These lesions often recur in the same area, forming abscesses filled with pus, which can emit a foul odor upon rupture. Over time, recurrent inflammation causes the formation of sinus tracts—long tunnels beneath the skin—resulting in scarring and tissue damage. Patients may also experience itching, swelling, and tender skin around the affected areas. In severe cases, HS can lead to persistent infections, mobility issues, and emotional distress.
Diagnostic Procedures: Diagnosis primarily relies on clinical examination and detailed patient history. Healthcare providers assess the pattern, severity, and recurrence of skin lesions, along with any familial history of similar conditions. In some cases, laboratory tests such as pus culture or biopsy are performed to distinguish HS from other skin infections or inflammatory conditions. Accurate diagnosis is critical in formulating an effective treatment plan and preventing unnecessary interventions.
Treatment Strategies and Lifestyle Considerations: Managing HS involves a combination of medical therapies and lifestyle changes. Mild cases may respond well to conservative measures like warm compresses, which help reduce inflammation and promote drainage. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can alleviate pain and swelling. Antibiotics—topical or systemic—are often prescribed to manage infection and reduce bacterial load. In more severe or resistant cases, advanced treatments such as corticosteroid injections, immunosuppressants, or biologic therapies might be recommended.
In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role. Weight management through a balanced diet and regular exercise reduces pressure on affected areas, which can help decrease flare-ups. Smoking cessation is strongly advised, as smoking is linked to increased severity and frequency of HS episodes. Personal hygiene should be maintained, but without excessive scrubbing, to avoid aggravating the skin. Wearing loose, breathable clothing minimizes friction and skin irritation. Patients should also discuss skincare routines with their healthcare providers for tailored advice.
Questions to Discuss with Your Healthcare Provider: Patients should proactively engage with their healthcare team and inquire about the severity of their condition, suitable treatment options, potential side effects, and the possibility of surgical interventions. Surgical procedures—such as drainage of abscesses or removal of affected tissue—may be necessary in advanced cases. Additionally, discussing lifestyle modifications that can help manage symptoms, including weight management and smoking cessation, is vital for comprehensive care. Regular follow-ups enable adjustments to treatment plans and timely management of flare-ups.
Proactive management and early intervention are essential in preventing disease progression and minimizing complications. Knowledge of HS and adopting a supportive, multidisciplinary approach can greatly enhance the quality of life for individuals living with this challenging condition. Education, patience, and persistence are key components in managing HS effectively.