Comprehensive Lifestyle and Dietary Strategies for Managing Psoriasis
This article offers an in-depth look into effective lifestyle and dietary strategies that can support psoriasis management. From adopting a Mediterranean diet to managing triggers and enhancing skin hydration, these holistic approaches aim to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life for psoriasis sufferers. Backed by healthcare insights, the tips provided can be integrated into daily routines for better skin health.

Comprehensive Lifestyle and Dietary Strategies for Managing Psoriasis
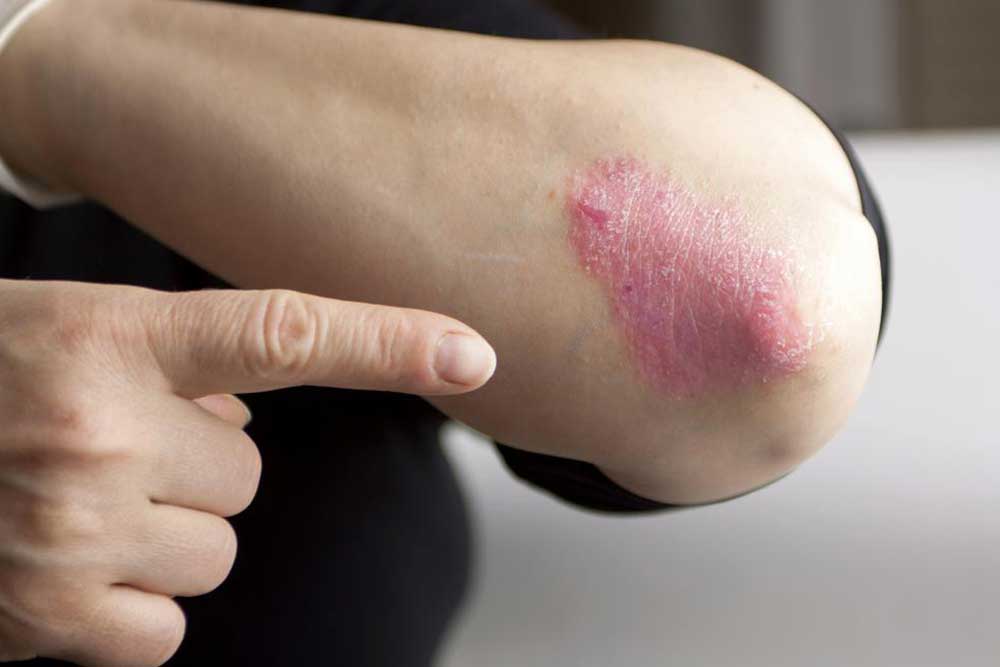
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by rapid skin cell buildup, leading to scaling, inflammation, and discomfort. While medical treatments such as topical therapies, phototherapy, and systemic medications are fundamental in controlling the symptoms, many patients seek additional ways to support their skin health through lifestyle and dietary modifications. These strategies, when combined with prescribed treatments, can potentially help in reducing flare-ups, minimizing symptoms, and improving overall quality of life.
Understanding how diet and lifestyle influence psoriasis is crucial. Although scientific evidence varies, numerous healthcare professionals and patients report noticeable improvements by adopting certain habits and dietary practices. Implementing these changes can be a proactive approach to managing psoriasis more holistically. In this comprehensive guide, we explore effective lifestyle adjustments and nutritional tips that may improve symptoms and promote healthier skin.
Adopt a Mediterranean Diet: Adherence to a Mediterranean-style diet is often recommended for individuals with psoriasis, especially since many sufferers also experience comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease, obesity, and diabetes. The Mediterranean diet emphasizes the consumption of a variety of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, lean sources of protein like fish, and healthy fats such as olive oil. Although definitive scientific studies linking this diet directly to psoriasis symptom reduction are limited, existing research indicates that its anti-inflammatory properties can benefit skin health. Incorporating fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, can be particularly helpful. Even partial adoption—such as adding fish a few times a week or increasing vegetable intake—can be advantageous.
Include Probiotics and Gut-Healthy Foods: The role of gut health in autoimmune and inflammatory skin conditions like psoriasis has gained increasing attention. Consuming probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria found in fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and other fermented vegetables, can help balance gut microbiota. Probiotic supplements are also available and may assist in reducing systemic inflammation. Healthy gut flora influence immune function and inflammatory responses, meaning that improved gut health could contribute to alleviating psoriasis symptoms. Incorporating prebiotic foods like garlic, onions, asparagus, and bananas supports probiotic growth and overall digestive health.
Prioritize Skin Moisturization with Safe Products: Dry skin exacerbates psoriasis symptoms, leading to increased itching, flaking, and discomfort. Applying high-quality petroleum jelly or other occlusive moisturizers can form a protective barrier, sealing in moisture and reducing dryness and irritation. The best time to apply these products is immediately after warm baths or showers when the skin is still damp. Select plain, fragrance-free, and chemical-free options to avoid potential sensitization or allergic reactions. Regular moisturization not only alleviates symptoms but also enhances skin barrier function, making the skin more resilient against environmental triggers.
Manage Dryness Through Bathing and Hydration Techniques: Short, warm baths with ingredients like colloidal oatmeal can soothe irritated and itchy skin. Oatmeal has anti-inflammatory and skin-calming properties, which can help reduce redness and flaking. Additionally, soaking in water infused with fragrance-free oils or Epsom salts can provide hydration and reduce flakiness. Always avoid hot water, as it can strip natural oils and worsen dryness. Hydrate your skin from within by drinking adequate amounts of water daily, supporting overall skin hydration and health.
Identify and Avoid Personal Triggers: Psoriasis flare-ups are often triggered by specific environmental, dietary, or emotional factors. Common triggers include stress, infections, certain medications, weather changes (especially cold and dry weather), smoking, alcohol consumption, and certain foods such as dairy or processed foods. Keeping a symptom diary can help in pinpointing individual triggers, enabling better management and avoidance strategies. Managing stress through relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can also significantly reduce flare-ups. Consulting with healthcare providers or dermatologists to develop a personalized trigger management plan is highly recommended.
In summary, while medication remains the cornerstone of psoriasis treatment, comprehensive lifestyle and dietary modifications can offer additional support. Incorporating an anti-inflammatory diet, supporting gut health, effective skin hydration, and trigger management contribute to a holistic approach aimed at minimizing flare-ups and enhancing skin quality. As each individual’s condition varies, consulting healthcare professionals before making significant dietary or lifestyle changes is essential. By adopting these strategies, psoriasis patients can empower themselves to improve their overall well-being and skin health, leading to a better quality of life.