Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, and Management Strategies
This comprehensive guide provides in-depth insights into rheumatoid arthritis, covering its causes, symptoms, and various management strategies. Understanding this autoimmune disorder is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. The article emphasizes the importance of medical therapies, lifestyle modifications, and nutritional considerations to improve quality of life for those affected by RA. Whether you are a patient, caregiver, or healthcare professional, this detailed overview aims to enhance awareness and promote proactive disease management for better health outcomes.

Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, and Management Strategies
Essential Information About Rheumatoid Arthritis You Need to Know
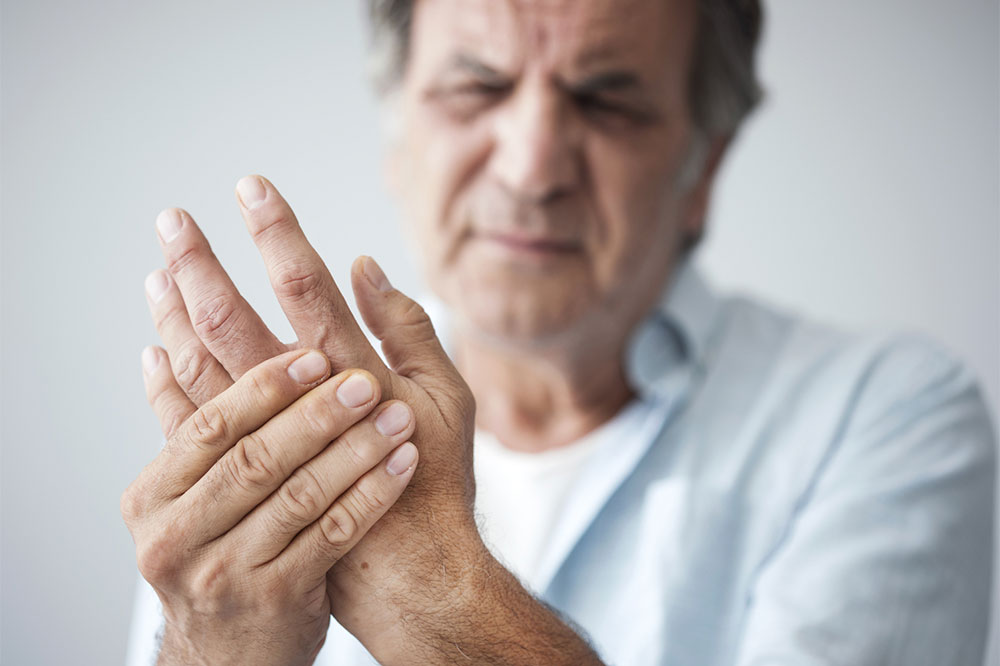
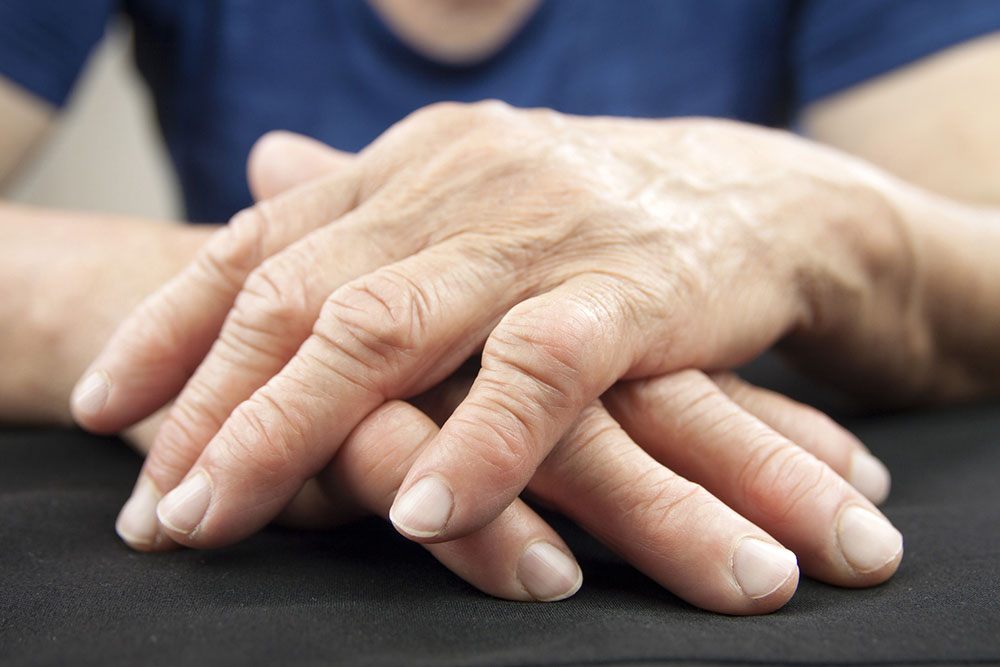
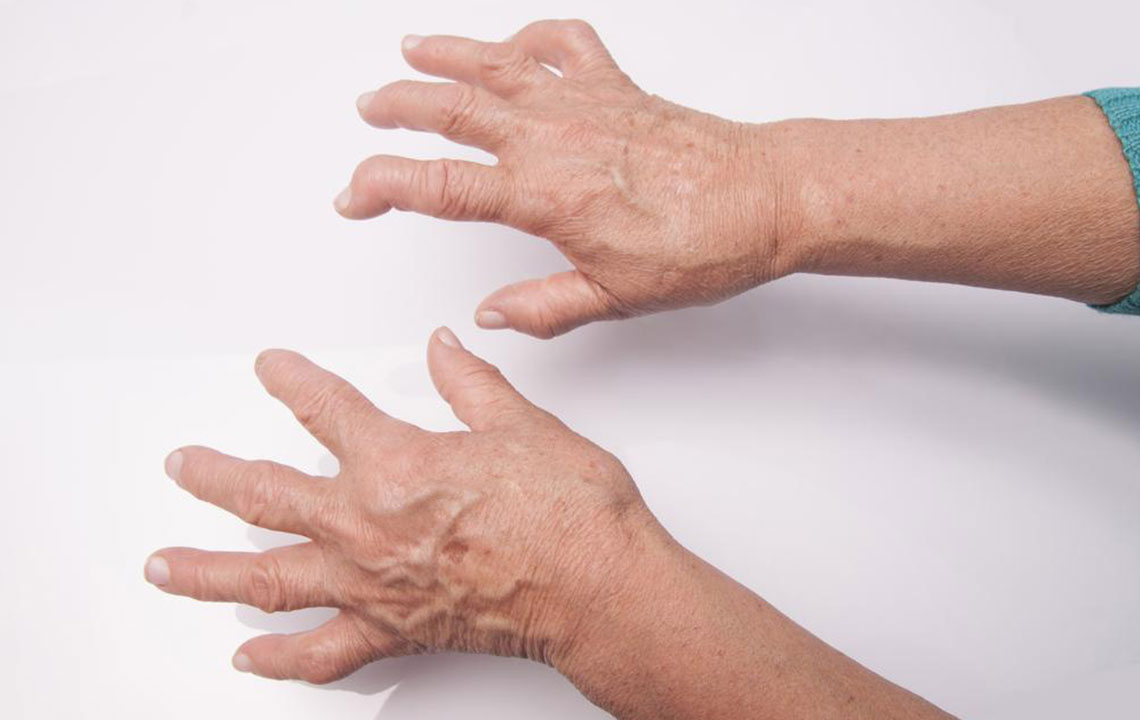
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a complex, chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by persistent inflammation that primarily affects the joints but can also potentially impact multiple systems within the body. This disease results from an abnormal immune response where the body's immune system mistakenly targets its own tissues, causing joint swelling, pain, erosion, and deformity. While the exact cause remains elusive, understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a persistent and often progressive disease, but with advances in medical science, many treatments can significantly reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. Typically, the disease involves symmetrical joint involvement, meaning both sides of the body are affected equally, and individuals often go through cycles of flares and remission. It can develop at any age, although it is most common between ages 30 and 60, making awareness and early intervention particularly important.
Below, we explore the essential aspects of rheumatoid arthritis, including its causes, symptoms, and comprehensive management strategies:
What factors contribute to the development of rheumatoid arthritis?
While the specific cause of RA remains unknown, research suggests that certain infections caused by viruses and bacteria might act as triggers in susceptible individuals.
Genetics play a significant role; a familial history of autoimmune diseases increases the risk of developing RA, indicating a hereditary component.
Environmental factors, such as smoking, exposure to pollutants, and occupational hazards, may activate abnormal immune responses, although more research is needed to clarify these links.
Effective management of rheumatoid arthritis
Although there is currently no cure for RA, a variety of treatments can effectively control symptoms, slow disease progression, and prevent joint deformities. Achieving optimal disease management involves a personalized approach combining medication, therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and sometimes surgical intervention.
Pharmacological treatments: The cornerstone of RA management involves medications like corticosteroids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic agents. These help reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and inhibit joint damage.
Surgical options: When medication is insufficient to control joint damage, surgical procedures such as joint fusion, tendon repair, and joint replacement surgeries may be necessary to restore function and alleviate pain.
Therapeutic interventions: Physical and occupational therapy are critical for maintaining joint mobility, improving function, and teaching techniques to perform daily tasks more comfortably. These therapies can significantly enhance a patient’s independence and quality of life.
Managing rheumatoid arthritis through lifestyle modifications
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes play a vital role in managing RA. Incorporating healthy habits can help reduce flare-ups, minimize joint damage, and improve overall well-being. Key lifestyle strategies include:
Regular, gentle exercise: Under medical supervision, engaging in low-impact activities such as swimming, walking, or stretching can help strengthen muscles around affected joints, decrease fatigue, and prevent joint stiffness.
Heat and cold therapy: Applying heat packs relaxes tense muscles and alleviates stiffness, while cold therapy reduces inflammation, swelling, and pain during flare-ups. Proper use of these therapies can greatly enhance comfort.
Stress management and relaxation techniques: Chronic stress can exacerbate RA symptoms. Activities like meditation, yoga, mindfulness, and hobbies help promote relaxation and prevent triggers of disease flares.
Dietary considerations for people with rheumatoid arthritis
While no specific diet cures RA, certain dietary choices can influence inflammation levels. Patients are advised to avoid foods that may trigger or worsen symptoms, including:
Gluten-containing grains: Such as wheat, barley, and rye, which can increase inflammatory responses in some individuals.
Processed and fast foods: These often contain preservatives, sugars, artificial flavors, and saturated fats that can exacerbate inflammation.
Red meats and fatty cuts: Rich in saturated fats and omega-6 fatty acids, which may promote inflammation and weight gain, putting additional stress on joints.
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish and flaxseed), and whole grains can help manage symptoms. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is recommended for personalized nutritional advice.
In conclusion, rheumatoid arthritis is a multifaceted autoimmune disease that requires a comprehensive approach to management. Staying informed about risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options empowers patients to actively participate in their care and improve their quality of life. Early diagnosis and a multidisciplinary treatment plan can help minimize joint damage and enable patients to maintain independence and mobility.