The Critical Link Between Diabetes and Erectile Dysfunction: Causes, Prevention, and Treatment
This comprehensive article explores the strong connection between diabetes and erectile dysfunction, highlighting causes, prevention, and treatment strategies. It emphasizes the importance of managing blood sugar levels, adopting healthy lifestyles, and seeking early medical intervention to prevent irreversible nerve and vascular damage. Both men and women affected by diabetes can benefit from proactive healthcare measures to restore and maintain sexual health, ultimately improving overall quality of life.
The Critical Link Between Diabetes and Erectile Dysfunction: Causes, Prevention, and Treatment
Historically, erectile dysfunction (ED) was often brushed aside as just a normal part of aging or temporary issues. However, recent medical research has highlighted a strong correlation between diabetes and sexual dysfunction, bringing increased attention to how unmanaged diabetes can profoundly impact both men's and women's sexual health. This article explores the causes of diabetes-related ED, preventive strategies, and effective treatments to help those affected regain their quality of life.
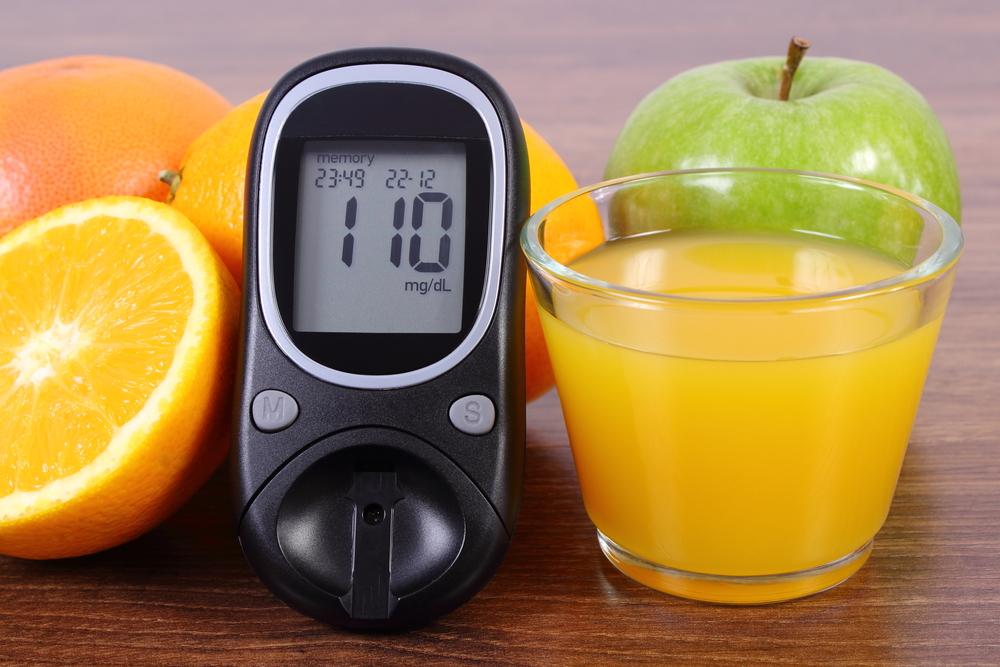
Diabetes mellitus, especially when poorly managed, significantly elevates the risk of developing erectile dysfunction. It is estimated that around 75% of men with uncontrolled diabetes will experience some level of sexual dysfunction during their lifetime. This condition primarily manifests as difficulty in achieving or maintaining an erection, which can severely affect personal relationships and overall well-being. Importantly, diabetes does not only influence male sexual health; women also experience sexual issues such as vaginal dryness, pain during intercourse, and decreased libido.
At the core of diabetes-related ED are nerve damage and vascular problems. High blood sugar levels can cause damage to small blood vessels and nerves, impairing the normal blood flow and nerve signals needed for an erection. In men, unhealthy blood vessel function hampers the entry of blood into penile tissues, making it difficult to achieve or sustain an erection suitable for sexual activity. Women may experience reduced vaginal lubrication due to nerve damage, leading to discomfort and pain during intimacy.
Furthermore, elevated blood glucose levels can interfere with hormone production, notably reducing testosterone levels in men, which further diminishes libido. Nerve damage not only affects sexual sensation but can also cause pain, numbness, or tingling in genital areas, complicating sexual activity. Several other factors exacerbate the problem, including high cholesterol, hypertension, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, chronic stress, and certain medications. These elements collectively impair vascular health and nerve functions, creating a complex web of contributing factors.
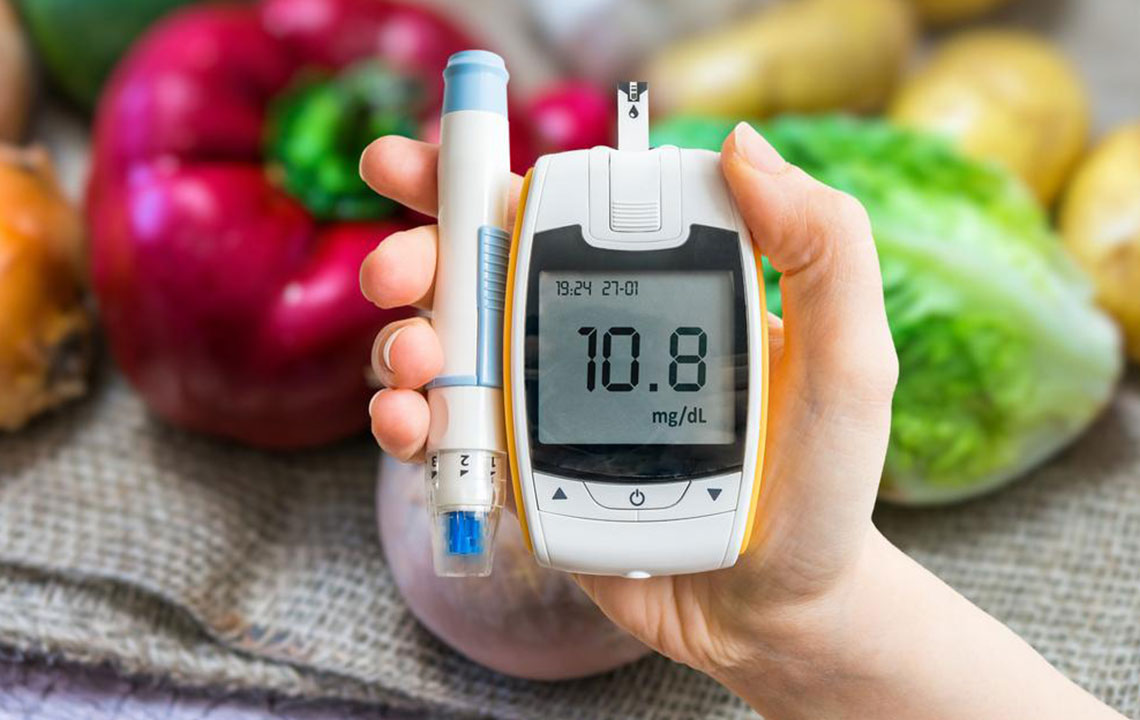
Preventing and effectively managing diabetes-related sexual dysfunction revolves around proactive healthcare strategies. Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels through diligent monitoring—using tools like regular A1C tests—is paramount. Lifestyle modifications such as a balanced diet, regular physical activity, quitting smoking, and moderating alcohol intake are fundamental steps. Medical interventions may include medications like phosphodiesterase inhibitors, device-based therapies, and counseling for psychological aspects. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent irreversible nerve or vascular damage, thereby preserving sexual health.
It is essential for diabetic patients to work closely with healthcare professionals to create personalized treatment plans. Routine check-ups, blood vessel function assessments, and nerve conduction studies can help target specific issues. Lifestyle changes not only improve blood sugar control but also enhance overall vascular health, reducing the risk of complications like ED. For women, addressing sexual health involves managing hormonal balance, pelvic health, and emotional well-being through multidisciplinary approaches.
The key to overcoming diabetes-associated sexual dysfunction lies in early intervention, consistent management of blood glucose, and adopting a healthy lifestyle. Regular communication with healthcare providers ensures prompt adjustments to treatment plans, increasing the chances of restoring normal sexual function. Awareness and proactive care are essential for improving quality of life, emotional intimacy, and overall health for individuals living with diabetes.