Comprehensive Lifestyle Approaches to Master Blood Sugar Control in Diabetes Management
Discover comprehensive lifestyle strategies for controlling blood sugar in diabetes management. This detailed guide covers hydration, stress management, exercise, diet, weight control, and sleep hygiene to help reduce complications and improve overall health. Implementing these habits can lead to effective blood sugar regulation and better quality of life.

Comprehensive Lifestyle Approaches to Master Blood Sugar Control in Diabetes Management
Diabetes has become a widespread health challenge affecting millions of individuals across the United States, with its prevalence rising steadily over recent years. This chronic condition, characterized by elevated blood glucose levels, results from the body's inability to produce sufficient insulin or from the body's cells resisting insulin's effects. The importance of effectively managing blood sugar levels cannot be overstated, as uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious health complications such as nerve damage, cardiovascular diseases, kidney issues, and infections.
Understanding the various factors that contribute to poor blood sugar regulation is key to effective management. Poor dietary habits, irregular or inadequate sleep, physical inactivity, chronic stress, and obesity are prominent contributors to the progression of diabetes. Recognizing the symptoms early, including unexplained weight fluctuations, tingling sensations, frequent urination, persistent fatigue, and slow wound healing, can facilitate timely diagnosis and intervention, ultimately reducing the risk of severe health issues.
Diabetes manifests primarily in several forms: Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, prediabetes, and gestational diabetes. While Type 1 and Type 2 can affect anyone regardless of age or background, gestational diabetes occurs exclusively during pregnancy and requires specialized attention. Individuals with diabetes are at increased risk for cardiovascular diseases, making lifestyle modifications a vital component of disease management alongside medication and medical guidance.
While medication remains essential for some, lifestyle changes are fundamental in controlling blood sugar levels. These adjustments focus on fostering long-term health through diet, exercise, stress management, and healthy habits. Adopting a comprehensive approach not only stabilizes blood glucose but also enhances overall quality of life.
Stay Hydrated: Consuming adequate water intake is fundamental for overall health and plays a crucial role in blood sugar regulation. Proper hydration assists the kidneys in flushing out excess glucose via urine, thereby reducing blood glucose levels. It’s advisable to avoid sugary beverages like soda and sweetened drinks, which can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar and undermine management efforts.
Manage Stress Effectively: Chronic stress triggers the release of hormones such as cortisol, which can elevate blood sugar levels. Incorporating relaxation techniques into daily routines, including yoga, meditation, deep-breathing exercises, and mindfulness practices, can help reduce stress hormones and support healthier blood sugar levels.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Consistent exercise improves insulin sensitivity and promotes efficient utilization of glucose by muscle cells. Incorporate activities such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or other forms of moderate-intensity workouts suitable for your fitness level. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting new exercise routines to ensure they align with your health status.
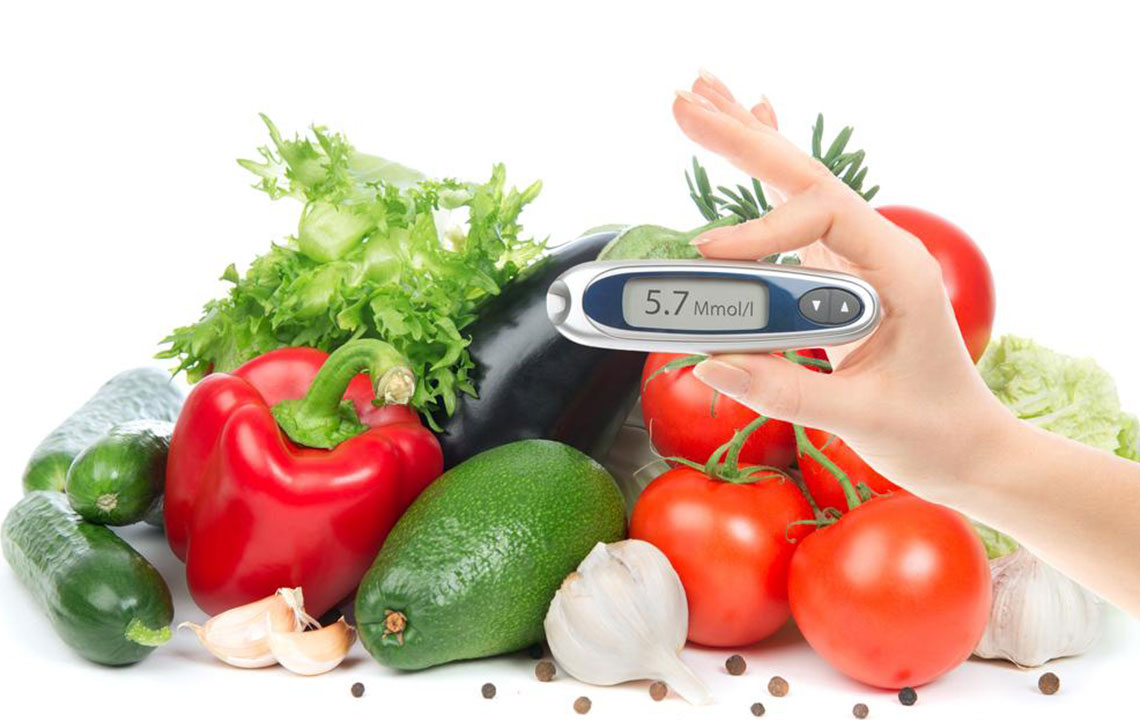
Boost Fiber Intake: Dietary fibers, especially soluble fibers found in vegetables, fruits, oats, and legumes, slow down the absorption of glucose in the digestive tract. This results in more stable blood sugar levels after meals and helps prevent sudden spikes.
Limit Carbohydrate Consumption: Carbohydrates have the most immediate impact on blood glucose. Focusing on a balanced diet rich in non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, healthy fats, and whole grains can help moderate blood sugar responses. Portion control and carbohydrate counting are effective strategies for dietary management.
Maintain a Healthy Body Weight: Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, greatly increases insulin resistance. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through dietary choices and physical activity significantly improves blood sugar control and reduces the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Prioritize Quality Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for metabolic health. Sleep deprivation or poor sleep quality can disturb hormonal balances, increase stress levels, and lead to higher blood sugar levels. Aim for 7 to 9 hours of restorative sleep each night, establishing consistent sleep routines to support optimal metabolic functioning.
Implementing these lifestyle strategies requires commitment but offers substantial benefits in managing diabetes effectively. These changes not only assist in controlling blood sugar but also promote overall health, enhance energy levels, and reduce the risk of developing related health issues. Working closely with healthcare providers to tailor these approaches can maximize their effectiveness and establish sustainable habits for lifelong health management.