Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Diabetic Nerve Damage and Neuropathy Prevention
This comprehensive guide explores diabetic nerve damage, its types, symptoms, and effective management strategies. It emphasizes the importance of blood sugar control, lifestyle changes, and early diagnosis to prevent severe complications. Learn how to take proactive steps to manage neuropathy and improve quality of life for diabetics. Perfect for patients and healthcare providers aiming for better nerve health.

The Complete Guide to Understanding and Managing Diabetic Nerve Damage
Diabetic nerve damage, medically referred to as diabetic neuropathy, is a common and potentially severe complication of diabetes mellitus. It occurs when elevated blood glucose levels over time cause damage to nerve fibers throughout the body. This nerve impairment can lead to a range of symptoms, diminish quality of life, and increase the risk of serious health issues if not properly managed. Understanding the underlying mechanisms, types, symptoms, and effective management strategies for diabetic neuropathy is essential for individuals living with diabetes and healthcare providers alike.
Chronic hyperglycemia, or persistently high blood sugar levels, hampers the body’s ability to process insulin effectively. This results in the deterioration of nerve tissues, especially in distal parts of the limbs such as the feet, legs, hands, and arms. Nerve damage progresses gradually, often silently, making early detection and intervention crucial. The different forms of diabetic neuropathy impact various parts of the nervous system, each presenting unique challenges and requiring tailored treatment approaches.
Types of Diabetic Neuropathy and Their Symptoms
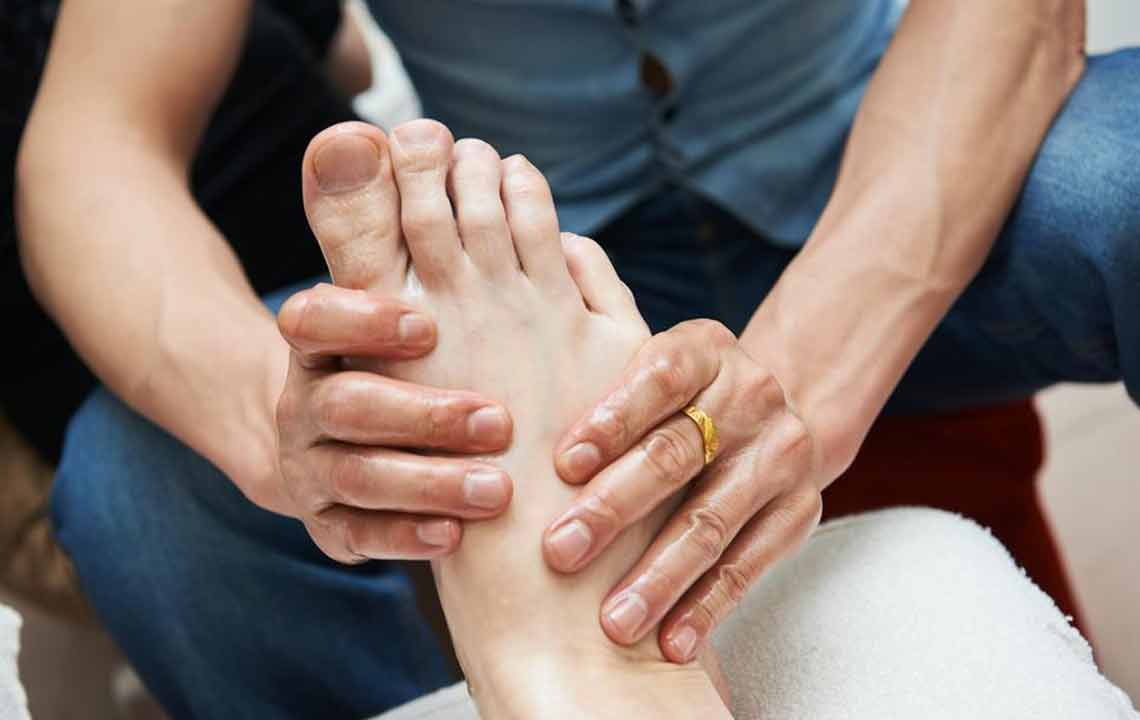
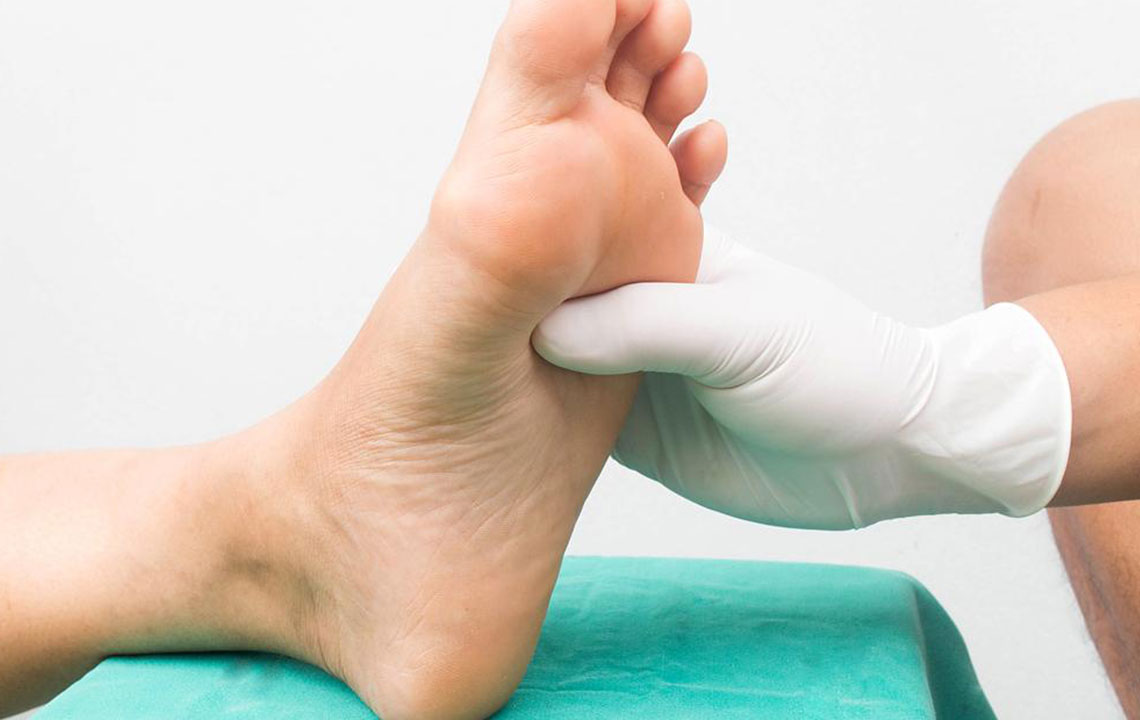
Peripheral Neuropathy: This is the most common form, primarily affecting the feet and legs, then progressing to the hands and arms. Patients may report symptoms such as tingling, burning, stabbing pain, numbness, or heightened sensitivity, which can interfere with daily activities and increase the risk of injuries due to loss of sensation. Preventive measures including proper foot care, moisturizing skin, and avoiding injuries are vital for managing peripheral neuropathy.
Autonomic Neuropathy: This type involves damage to the autonomic nerves that regulate vital involuntary functions like heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and sexual function. Symptoms may include dizziness upon standing, digestive disturbances such as nausea and diarrhea, urinary problems, and sexual dysfunction. Since autonomic nerves regulate essential body functions, ongoing management of blood sugar levels and regular medical checkups are indispensable for prevention and control.
Radiculoplexus Neuropathy: Also known as femoral or lumbosacral plexus neuropathy, this form impacts nerves in the thighs, hips, or buttocks, leading to pain, weakness, and muscle wasting. It usually manifests as sudden or gradual pain in the lower limbs, accompanied by difficulty in movement. Early medical consultation and physical therapy are crucial in preventing long-term disability.
Mononeuropathy: This involves localized damage to a single nerve, resulting in symptoms such as sharp pain, weakness, or numbness confined to the affected area. Commonly impacted nerves include those responsible for ocular movements or facial sensation. Prompt diagnosis and targeted treatment can help reduce nerve damage and restore function.
Effective Management and Prevention Strategies
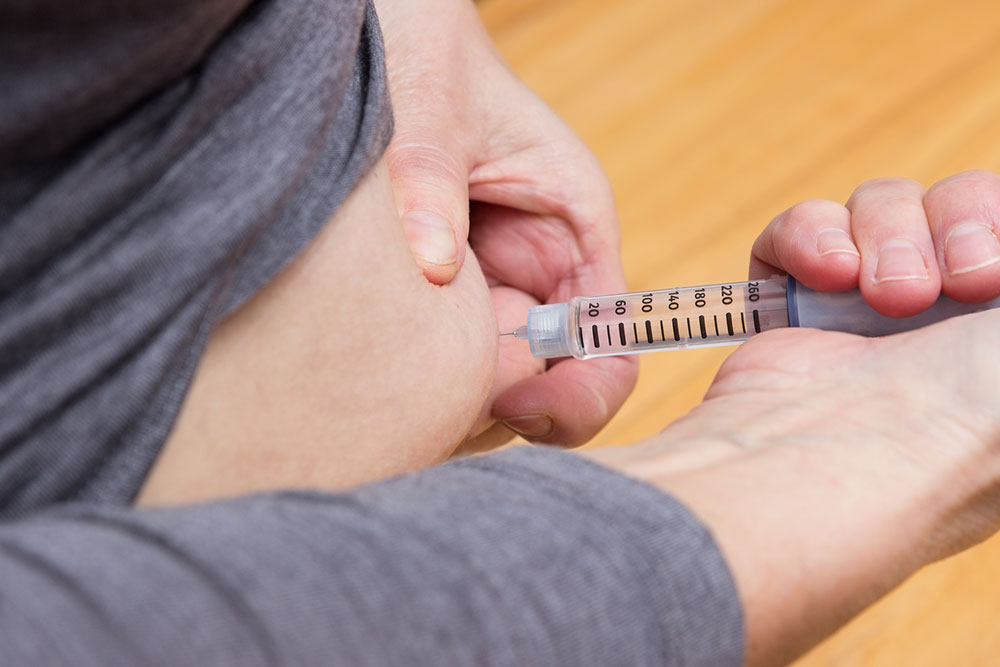
Managing diabetic neuropathy effectively involves a multifaceted approach focusing on blood sugar control, lifestyle changes, and symptomatic relief. Maintaining optimal blood glucose levels is the cornerstone of prevention and management. This can be achieved through a combination of medication adherence, dietary modifications, and regular physical activity.
Adopting a healthy, balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats supports metabolic health and nerve repair. Regular exercise enhances blood circulation, helps control weight, lowers blood sugar levels, and boosts overall well-being. Incorporating aerobic activities, strength training, and flexibility exercises into daily routines can significantly slow neuropathy progression.
Sleep hygiene is equally important, as poor sleep can negatively impact blood sugar control and nerve health. Establishing consistent sleep schedules, reducing stimulant intake before bedtime, and creating a comfortable sleeping environment are recommended.
In addition to lifestyle modifications, medications may be prescribed to manage pain or other specific symptoms associated with neuropathy. Over-the-counter pain relievers, topical treatments, antidepressants, or anticonvulsants are often employed depending on the severity and type of nerve damage.
Regular Monitoring and Medical Interventions
Early diagnosis through routine screening and neurological assessments is critical in preventing permanent nerve damage. Healthcare providers might perform nerve conduction studies, blood tests, and physical examinations to evaluate nerve function and identify early signs of neuropathy. Patients should report any new or worsening symptoms promptly to facilitate timely intervention.
In some cases, advanced therapies such as nerve blocks, physical therapy, or surgical procedures may be needed for severe nerve damage. Additionally, managing related health conditions like hypertension and high cholesterol further reduces the risk of neuropathy worsening.
Living Well with Diabetic Neuropathy
Living with diabetic nerve damage can be challenging, but proactive management and a comprehensive care plan can significantly improve quality of life. Patients are encouraged to engage with healthcare providers, stay vigilant about symptoms, and adhere to prescribed treatments and lifestyle recommendations. Support groups and educational resources are also beneficial in coping with this chronic condition.
Preventive care, early diagnosis, and a holistic approach to health are key components in controlling diabetic neuropathy and avoiding severe complications such as infections, ulcers, or amputations. By understanding their condition and taking proactive steps, individuals living with diabetes can maintain nerve health and enjoy a more active, fulfilling life.