Understanding the Main Causes of Blepharitis: Essential Information You Need to Know
Blepharitis is an eyelid inflammation caused by various factors including dry eyes, allergies, blocked oil glands, and rosacea. Recognizing these causes and seeking early treatment from an eye specialist can effectively manage symptoms, prevent complications, and enhance eye health. Proper hygiene practices and medical care are key to controlling this common yet uncomfortable condition.
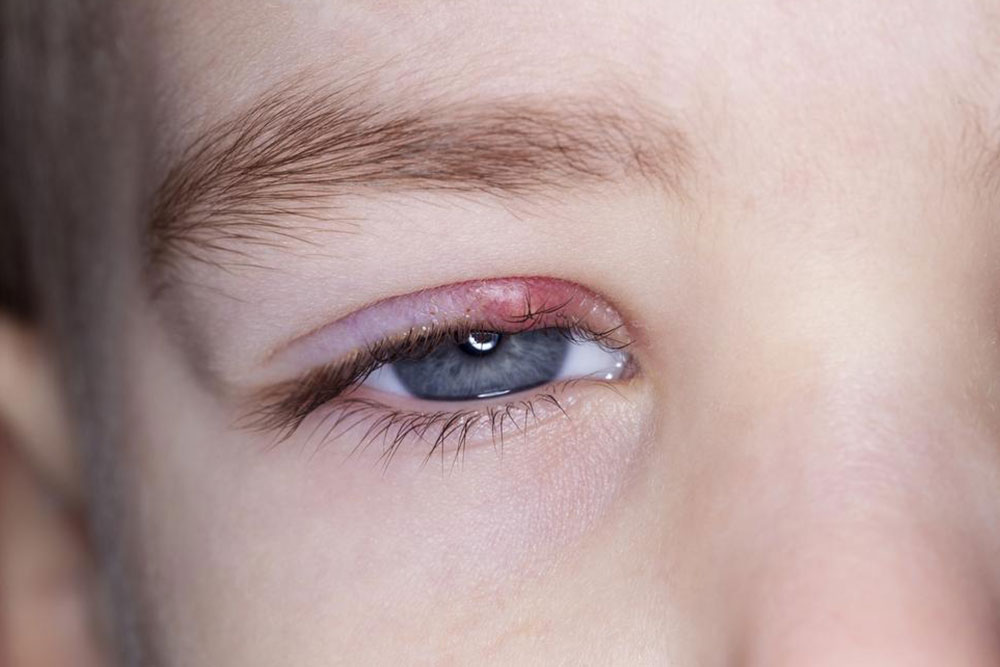
Key Factors That Lead to Blepharitis Development
Blepharitis is a common ophthalmic condition characterized by inflammation of the eyelids, particularly along the margins where eyelashes grow. This condition is often associated with discomfort, irritation, and noticeable changes in eyelid appearance. Individuals affected by blepharitis frequently report symptoms such as persistent itching, burning sensations, and the presence of flaky scales resembling dandruff along the eyelid edges. Although it is not contagious and can affect people of all ages, if left untreated or if symptoms worsen, blepharitis may predispose individuals to secondary infections, including bacterial conjunctivitis or other ocular issues. Proper understanding, early diagnosis, and effective management are crucial to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
While a precise single cause of blepharitis remains unidentified, multiple contributing factors have been identified through research and clinical observations. These factors are often interconnected, creating a cycle that exacerbates eyelid inflammation. Broadly, blepharitis can be classified into ulcerative and non-ulcerative types, each with its own set of underlying causes. The following are the primary triggers that have been widely recognized:
Dry Eyes: One of the leading causes, dry eye syndrome, plays a significant role in the development of blepharitis. Insufficient tear production or poor tear quality results in dry, irritated eyes that can promote bacterial proliferation along the eyelid margins. The decreased moisture hampers normal eyelid hygiene and creates an environment conducive to microbial overgrowth, leading to inflammation.
Eye Allergies: Allergic reactions triggered by environmental allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or certain chemicals can cause allergic conjunctivitis and eyelid inflammation. These allergic responses often manifest as redness, swelling, and itching around the eyes, which can exacerbate blepharitis symptoms. Patients with a history of allergies are at increased risk, especially during peak allergy seasons.
Blocked Oil Glands: The eyelids contain tiny sebaceous glands known as Meibomian glands, which produce oils essential for maintaining a healthy tear film and preventing evaporation. When these glands become blocked due to debris, inflammation, or dysfunction, it results in abnormal oil secretion and bacterial growth. The stagnation of oils and bacteria facilitates inflammation, bacterial colonization, and eyelid irritation, contributing significantly to blepharitis development.
Rosacea: This chronic skin condition marked by facial redness and visible blood vessels, especially on the cheeks and nose, has been linked to ocular surface diseases, including blepharitis. Ocular rosacea causes abnormal blood vessel dilation and inflammation, which can extend to eyelid margins, leading to persistent eyelid inflammation. Although the exact connection requires further study, many patients with rosacea also present with blepharitis symptoms.
For individuals experiencing symptoms of blepharitis, it is essential to seek consultation with an eye care professional. Accurate diagnosis often involves a comprehensive eye examination, including eyelid inspection and possibly microscopy. Treatment strategies involve maintaining meticulous eyelid hygiene, such as warm compresses, eyelid scrubs, and avoiding potential irritants like eye makeup and contact lenses during flare-ups. Medical interventions may include topical antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, or oral antibiotics in severe cases. Preventative measures, such as managing underlying conditions like dry eye syndrome or rosacea, are equally important in the overall management plan. Early intervention can prevent the progression of symptoms, reduce the risk of secondary infections, and restore normal eyelid function.