Understanding the Major Causes and Risks of Developing Tongue Cancer
Tongue cancer, primarily affecting the front of the tongue, is influenced by lifestyle choices such as tobacco use, heavy drinking, and HPV infection. This comprehensive guide discusses major causes, including tobacco, alcohol, HPV, and mouthwash effects, emphasizing prevention and early detection strategies. Quitting harmful habits and regular screenings are key to reducing risks of developing this serious oral cancer. Awareness and lifestyle modifications can significantly improve health outcomes, making understanding these factors vital for protecting oral health and preventing tongue cancer.

Understanding the Major Causes and Risks of Developing Tongue Cancer
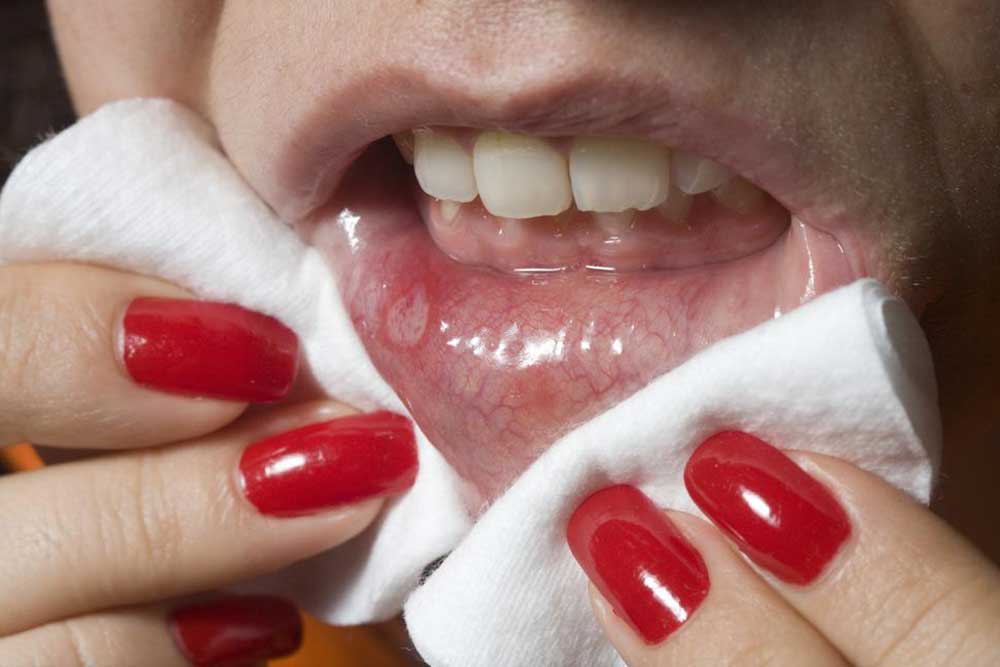
Tongue cancer is a serious form of oral malignancy that manifests when abnormal cells in the tongue's tissues grow uncontrollably. This cancer typically affects the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, which is the part most often visible and accessible for detection. While cancers in the back part of the tongue are classified under head and neck cancers, the front part's cancer is specifically known as tongue cancer. Recognizing the symptoms and being aware of various risk factors associated with this disease is essential for early detection and prevention. This detailed guide explores the primary reasons behind tongue cancer development and emphasizes the importance of awareness and proactive health measures.
Tongue cancer shares many symptoms with other oral cancers, such as persistent sore spots, difficulty swallowing, pain, or lumps in the mouth or neck. However, understanding the addressable risk factors can significantly improve preventive strategies. These factors include lifestyle choices, viral infections, and environmental exposures, all of which can influence the likelihood of developing this serious condition. Below, we analyze each major cause and the associated risks in detail to provide a comprehensive understanding of how tongue cancer forms and how to reduce one’s risk effectively.
Major Causes and Contributing Factors for Tongue Cancer
Knowledge about the causes and risks of tongue cancer is crucial for effective prevention and early intervention. Several well-documented factors contribute to the development of this disease. Understanding these can help individuals make informed decisions about their lifestyle, health management, and when to seek medical advice.
Tobacco Use and Smoking
One of the most significant risk factors for tongue cancer is the use of tobacco products, including cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and smokeless tobacco like chewing tobacco or snuff. These products contain carcinogenic chemicals that directly damage the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue. The harmful substances cause genetic mutations in the cells lining the mouth, which can eventually lead to malignant transformation and tumor formation.
Extensive research has demonstrated that individuals who smoke or use smokeless tobacco are markedly more susceptible to developing tongue cancer compared to non-users. The risk correlates with the duration and intensity of tobacco use. Quitting tobacco not only decreases this risk but can also result in significant health improvements even after years of use. The sooner a person ceases tobacco consumption, the higher their chances of preventing or mitigating tongue cancer growth. Health professionals strongly recommend cessation programs, counseling, and support networks to assist individuals in quitting tobacco for good.
Alcohol Consumption
Heavy alcohol intake is another prominent risk factor associated with tongue cancer. Regular consumption of large quantities of alcohol, especially hard liquor and spirits, can cause significant damage to the mucosal tissues inside the mouth. Alcohol acts as an irritant and solvent, making oral tissues more permeable to carcinogens like those found in tobacco. This combination further amplifies the risk of cellular mutations leading to cancer.
Studies have shown that individuals who combine heavy drinking with tobacco use are at an even greater risk of developing tongue cancer than those who only consume one of these substances. Moderating alcohol intake is a crucial preventive strategy. Routine dental check-ups and oral examinations can help identify suspicious changes early on. Public health campaigns promoting responsible drinking and awareness about the risks of alcohol-related oral cancers are vital tools in reducing the incidence of tongue cancer caused by alcohol consumption.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
The role of viral infections, notably Human Papillomavirus (HPV), in oral cancers, including tongue cancer, has garnered increasing scientific attention. HPV is a common sexually transmitted virus, and certain high-risk strains are linked to various cancers, particularly cervical cancer. Recent research indicates that HPV can infect the oral cavity during oral sex, leading to persistent infections that might promote carcinogenesis in the mucosal tissues of the tongue.
Experts project that HPV may surpass tobacco and alcohol as the leading cause of oral cancers in the coming years, primarily due to changing sexual behaviors and increased transmission rates. While many HPV infections resolve spontaneously without causing health issues, persistent infections with high-risk strains pose a significant danger. These infections can induce genetic alterations in oral epithelial cells, setting the stage for malignant transformation. The development of HPV vaccines has been a promising step in reducing the risk, but awareness and regular screenings remain essential for early detection and intervention.
Use of Mouthwash
The potential link between mouthwash ingredients and tongue cancer has been a topic of debate among scientists and healthcare professionals. Some studies suggest that mouthwashes containing high levels of alcohol might increase the risk of oral cancers because alcohol can act as an irritant and solvent, facilitating the absorption of carcinogens into oral tissues.
Although the evidence remains inconclusive, experts recommend moderation in mouthwash use, limiting it to no more than two times per day. Alternatives such as alcohol-free mouthwashes may pose lower risks. Maintaining good oral hygiene, regular dental visits, and avoiding harsh chemicals can contribute to overall oral health and reduce cancer risk. Consumers are advised to read product labels carefully and choose oral care products thoughtfully.
Preventive Measures and Early Detection
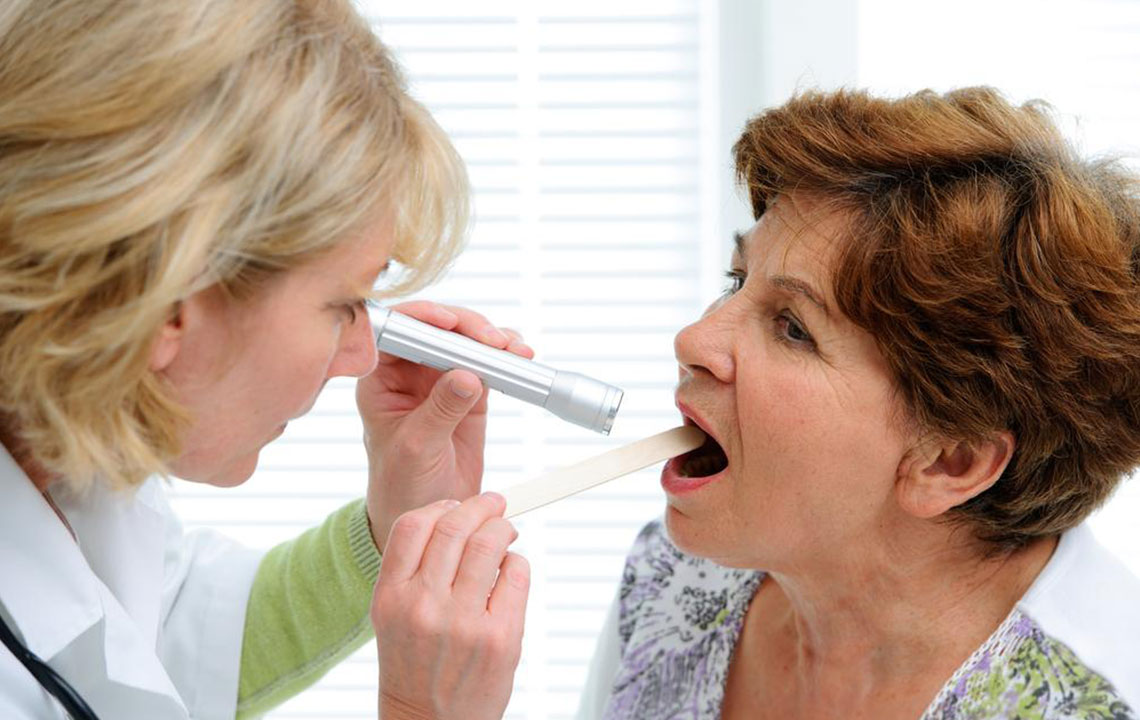
Prevention is the most effective approach to combating tongue cancer. Lifestyle modifications like quitting tobacco, reducing alcohol consumption, and practicing safe sexual behaviors can significantly decrease risk factors. Regular oral exams, both routine and scheduled with dental or medical professionals, are critical in detecting early abnormal changes that could signal the onset of cancer.
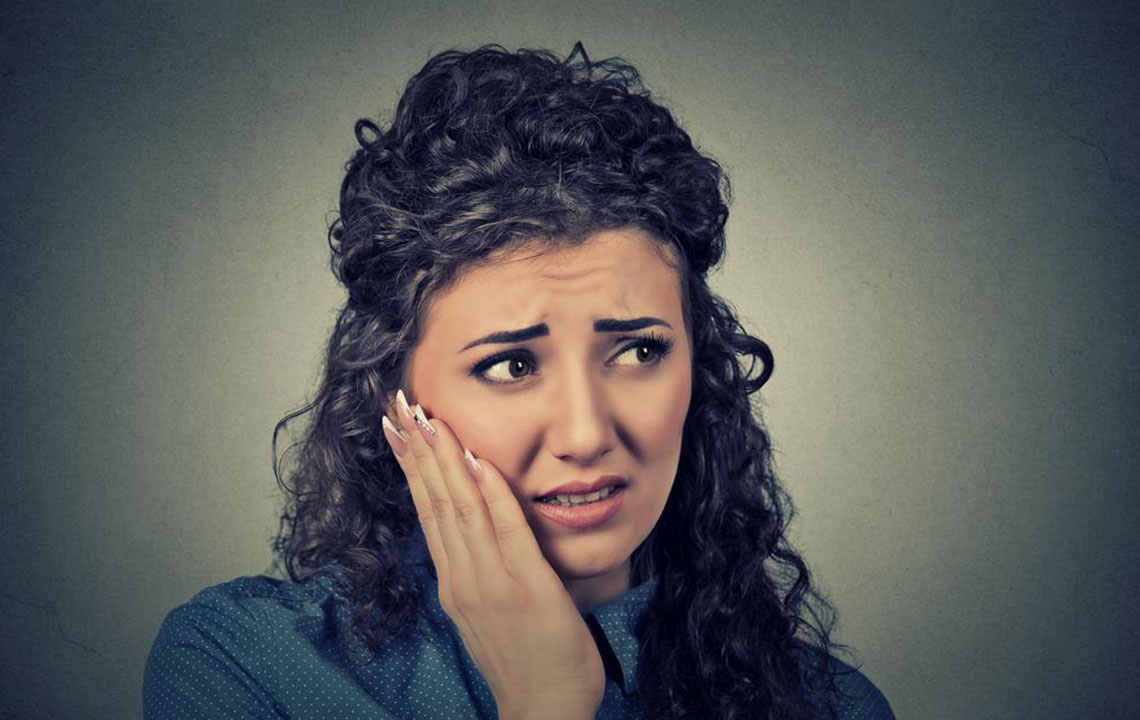
Individuals should be vigilant about persistent mouth sores, unexplained pain, lumps, or patches in the mouth or on the tongue, and seek medical advice promptly if any symptoms persist beyond two weeks. Such early detection increases the chances of successful treatment and improves overall prognosis. Public health education campaigns play a vital role in spreading awareness about the importance of oral health and early diagnosis.
Overall, understanding the causes and risks of tongue cancer empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards prevention. By eliminating or reducing exposure to known carcinogens and maintaining good oral hygiene, people can markedly lower their chances of developing this potentially life-threatening disease.