Comprehensive Guide to Risk Factors and Prevention of Oral Metastatic Cancer
This comprehensive article explores the critical risk factors and preventive strategies for oral metastatic cancer. It underscores the importance of early detection, lifestyle modifications, and regular dental check-ups to reduce the risk. With detailed insights into genetic factors, behaviors like tobacco and alcohol use, and environmental influences, the guide offers valuable tips for maintaining oral health and preventing the progression to metastatic disease. Early intervention remains key to improving survival rates and health outcomes in oral cancer cases.
Comprehensive Guide to Risk Factors and Prevention of Oral Metastatic Cancer
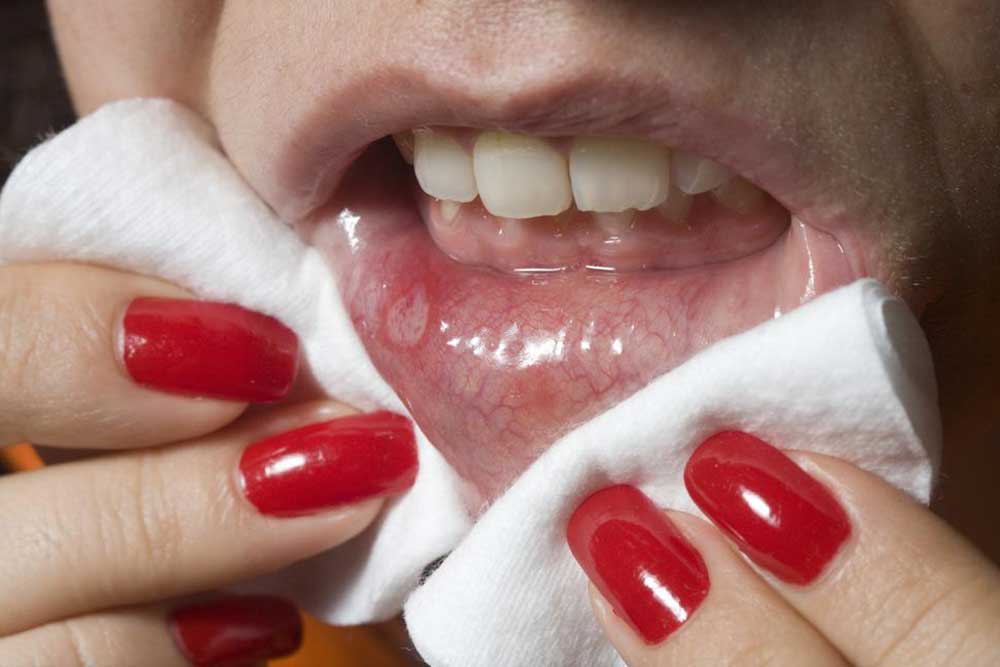
Oral cancer is a serious health concern that originates from the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in various parts of the mouth, including the lips, gums, tongue, cheeks, roof of the mouth, and floor of the mouth. These abnormal cells develop due to genetic mutations or changes, which lead to rapid cell proliferation and, eventually, tumor formation. Understanding the intricate mechanisms that drive the development and progression of oral cancer is crucial for early detection, effective treatment, and implementation of preventive measures.
Genetic alterations within mouth tissues play a pivotal role in the onset of oral cancer. These genetic changes might be influenced by environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and inherited predispositions. As the disease advances, it can invade neighboring tissues and spread to distant organs through the blood and lymphatic systems, a process known as metastasis. When oral cancer metastasizes, it becomes significantly more challenging to treat and manage, often leading to a decline in the patient’s overall prognosis.
Metastatic oral cancer is typically associated with aggressive behavior, rapid progression, and limited therapeutic options. Early diagnosis is vital, yet the exact causes leading to the genetic mutations that cause metastatic behavior remain complex and not fully understood. Often, the disease is diagnosed at an advanced stage, which adversely impacts survival rates. This highlights the importance of understanding risk factors and adopting preventive strategies to combat this potentially deadly disease.
The severity of oral cancer worsens with metastasis, emphasizing the need for early detection and intervention. Despite ongoing research, the precise mechanisms and causes of the genetic mutations that lead to metastatic oral cancer remain elusive, often resulting in late diagnoses and poor treatment outcomes.
Key Risk Factors Influencing Oral Cancer Development Include:
Weakened Immune System: A compromised immune system fails to effectively control abnormal cell growth, increasing susceptibility to cancers, including those in the mouth.
Overexposure to Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation: Particularly affecting the lips, excessive sun exposure without protection can damage skin cells, leading to mutations that may develop into cancer.
Tobacco Use and Alcohol Consumption: Both are among the most significant risk factors. Smoking cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and chewing tobacco expose tissues to carcinogenic substances. Heavy alcohol use acts synergistically with tobacco, exacerbating the risk of developing oral malignancies.
Prevention is the most effective approach to reducing the incidence of oral metastatic cancer. Several strategies can significantly diminish your risk and promote overall oral health:
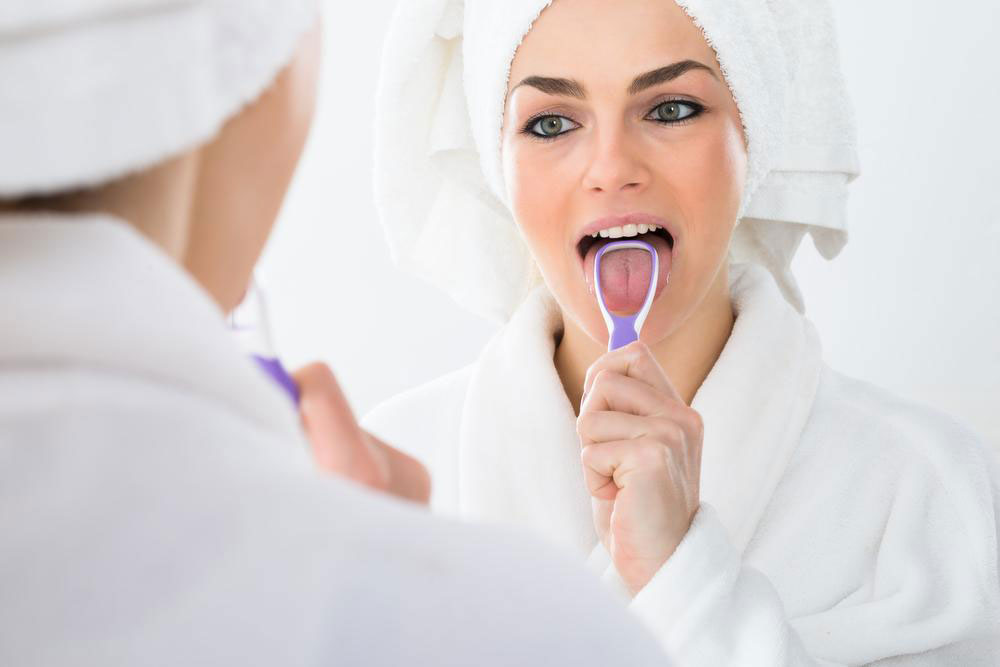
Regular Dental Check-Ups: Routine examinations by dental professionals can help detect early signs of abnormal tissue changes, lumps, discoloration, or other anomalies. Early detection facilitates prompt intervention, improving treatment outcomes and survival rates.
Limit Alcohol Intake: Reducing alcohol consumption is crucial. For moderate drinkers, it is advisable to restrict intake to no more than one drink per day for men and two for women. Abstaining altogether if possible provides the best protection against oral cancers.
Eliminate or Reduce Tobacco Products: Ceasing smoking and tobacco chewing not only decreases the risk of oral cancer but also benefits overall health. Support systems, counseling, and cessation aids can assist individuals in quitting tobacco use effectively.
Additional preventive measures include maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding excessive sun exposure by using lip balms with SPF, and avoiding irritants like rough or abrasive foods that can damage oral tissues. Public education campaigns are essential to increase awareness about oral cancer risks and encourage early screening and preventive care.
Implementing these strategies can significantly lower the risk of developing oral metastatic cancer and contribute to better health outcomes. As research continues, understanding individual risk factors and adopting early detection protocols remain vital components in combating this disease. If you notice persistent mouth sores, unusual lumps, or other concerning symptoms, seeking prompt medical or dental consultation is crucial for early diagnosis.