Early Signs and Symptoms of Oral Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide for Prevention and Detection
This comprehensive guide highlights the critical early signs of oral cancer, emphasizing the importance of awareness for timely diagnosis. It discusses common symptoms, risk factors like tobacco and alcohol use, and preventive measures. Recognizing subtle early indicators such as mouth ulcers, lumps, and patches can significantly improve treatment success rates. Regular dental checkups and healthy lifestyle choices are essential in reducing risk. The article aims to educate the public and healthcare professionals on early detection strategies, ultimately saving lives through prompt medical intervention.

Understanding the Early Signs and Symptoms of Oral Cancer
Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, represents a serious health concern affecting millions worldwide. As a subset of head and neck malignancies, it can manifest in various regions within the oral cavity, including the lips, tongue, inner cheeks, gums, and the roof or floor of the mouth. Due to its often subtle early signs, many cases are diagnosed at advanced stages, which reduces the chances of successful treatment. Therefore, recognizing the early indicators of oral cancer is essential for timely medical intervention and improving overall prognosis.
Statistics from 2016 reveal that nearly 50,000 new cases of oral cancer were diagnosed across the nation, underscoring its prevalence as a significant health threat. Tragically, over 9,000 individuals succumbed to this disease that year alone. Early detection plays a vital role in improving survival rates, as treatment options are more effective when the cancer is identified at an initial stage.
Most individuals impacted by oral cancer are typically in their mid to late 40s. Men are more susceptible to developing the disease than women, possibly due to higher rates of tobacco and alcohol use. In its early phase, oral cancer often presents with subtle, nonspecific symptoms that can easily be overlooked or mistaken for benign conditions. As a result, awareness about these signs is crucial for both the general public and healthcare professionals.
Common early symptoms of oral cancer include:
Persistent jaw pain or stiffness
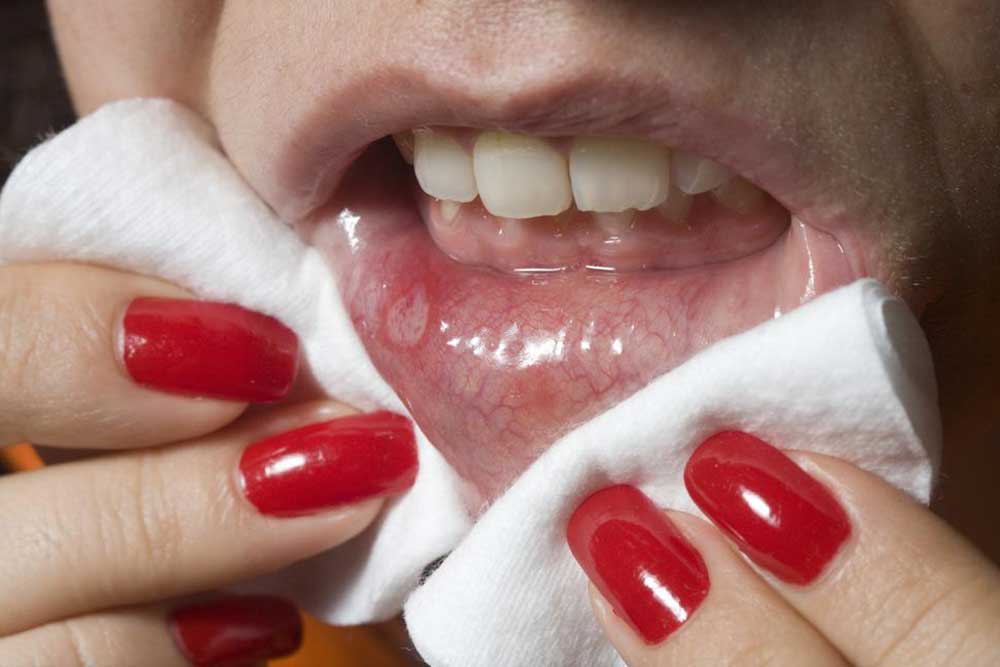
Non-healing mouth ulcers or sores that do not respond to typical treatments
Persistent swelling or lumps inside the mouth or neck
Thickened areas or unexplained lumps within the oral cavity
Pain or difficulty while swallowing (dysphagia)
Sore throat or a persistent sensation of something stuck in the throat
Tongue soreness or discomfort that doesn’t fade
Hoarseness or changes in voice quality
Neck pain or enlarged lymph nodes
Unexplained loose teeth or mobility of teeth without apparent dental disease
Presence of red (erythroplakia) or white patches (leukoplakia) in the mouth or throat area
Unintentional weight loss over a short period
Unpleasant foul breath (halitosis)
Unusual bleeding from the mouth or gums
It is important to note that while not all these symptoms imply cancer, experiencing more than two of these signs warrants prompt medical evaluation. Many benign conditions, such as fungal infections, can cause similar oral patches, but early professional assessment is essential to distinguish benign from malignant lesions. Early diagnosis significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and survival.
Though the exact causes of oral cancer remain somewhat unclear, several risk factors have been identified. These include tobacco use—whether through smoking cigars, cigarettes, or using smokeless tobacco—and heavy alcohol consumption. The synergistic combination of tobacco and alcohol dramatically increases the risk of developing oral cancer. Additionally, poor nutrition, aging, and unhealthy lifestyle choices are significant contributors. Approximately 90% of diagnosed cases have a history of tobacco use, highlighting its critical role in disease development.
Other risk factors encompass poor oral hygiene, chronic irritation from rough dental appliances or sharp teeth, exposure to certain viruses like human papillomavirus (HPV), and dietary deficiencies lacking in fruits and vegetables. A diet low in crucial nutrients and antioxidants weakens the immune system, making tissues more vulnerable to malignant changes. As people age, cellular repair mechanisms diminish, further elevating the risk of cancerous transformations in the mouth tissues.
Preventive measures are vital in reducing the risk of oral cancer. These include quitting tobacco and alcohol, maintaining excellent oral hygiene, consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and regular dental checkups. Routine oral examinations by dental professionals can help identify suspicious lesions early, especially in high-risk populations. Public awareness campaigns emphasizing early signs and the importance of prompt medical consultation are key strategies to curb the incidence of this potentially deadly disease.
In summary, understanding and recognizing the early symptoms of oral cancer can save lives. If you notice any persistent mouth sores, unexplained lumps, or red and white patches, seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and intervention remain the most effective ways to ensure successful treatment outcomes and improve survival rates for those afflicted by this disease.