Complete Guide to Tongue Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Preventive Measures
This comprehensive guide explores tongue cancer, detailing its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and preventive strategies. Early detection is vital for effective treatment, and awareness can help reduce risks and improve prognosis. Learn about the latest treatment options and how lifestyle choices impact tongue cancer risk.

Complete Guide to Tongue Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Preventive Measures
Tongue cancer is a serious health condition that originates in the cells of the tongue, often manifesting as noticeable lesions, persistent ulcers, or tumors in the oral cavity. It is classified among head and neck cancers, which collectively encompass a variety of malignancies affecting parts of the head and neck region. If diagnosed early, tongue cancer can be effectively managed, but if overlooked or untreated, it can lead to severe physical disabilities and psychological distress. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the causes, symptoms, risk factors, and preventive strategies associated with tongue cancer to promote awareness and early detection.
Understanding what tongue cancer is
Cancer occurs when normal, healthy cells in the body undergo genetic mutations, leading to uncontrolled growth and division. These abnormal cells accumulate to form malignant tumors that interfere with the body's normal functions. Specifically, in tongue cancer, the primary cells involved are the squamous epithelial cells that line the tongue's surface. The most common type of tongue cancer is squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). This cancer can develop in different parts of the tongue—namely, the anterior or front section (oral tongue) or near the base of the tongue, close to the throat, known as the oropharynx.
Early detection is crucial, as symptoms can be subtle and easily overlooked. Recognizing early signs can significantly improve treatment success rates.
Identifying the causes and risk factors associated with tongue cancer can be challenging because multiple factors are involved. However, understanding these risks can help individuals adopt preventive measures and seek medical advice promptly.
Key risk factors linked to tongue cancer include:
Family Medical History: Individuals with a family history of head and neck cancers, especially in close relatives, are at increased risk, particularly men over the age of 55. Genetic predispositions can make certain individuals more susceptible to developing malignancies in the oral cavity.
Lifestyle Choices and Habits: Unhealthy lifestyle choices play a significant role. Consuming processed foods high in preservatives, red meats, sugary desserts, and ignoring oral hygiene can contribute to carcinogenesis in the mouth. Chewing tobacco or other harmful substances, such as betel quid and areca nuts, further elevates this risk.
Prolonged Exposure to Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation: Excessive sun exposure, particularly to the lips and surrounding facial areas, can increase the risk of lip and oral cavity cancers. Artificial UV light from tanning beds and salons is also a concern, especially for individuals with prolonged or frequent exposure.
Medical Conditions and Viral Infections: Certain medical conditions, notably infections by human papillomavirus (HPV), are associated with an increased risk of oral cancers. HPV is known to cause various cancers, including those affecting the mouth and throat. Regular screening for high-risk groups is essential to catch early changes.
Understanding these risk factors highlights the importance of adopting healthier lifestyles, maintaining good oral hygiene, and undergoing regular dental and medical check-ups.
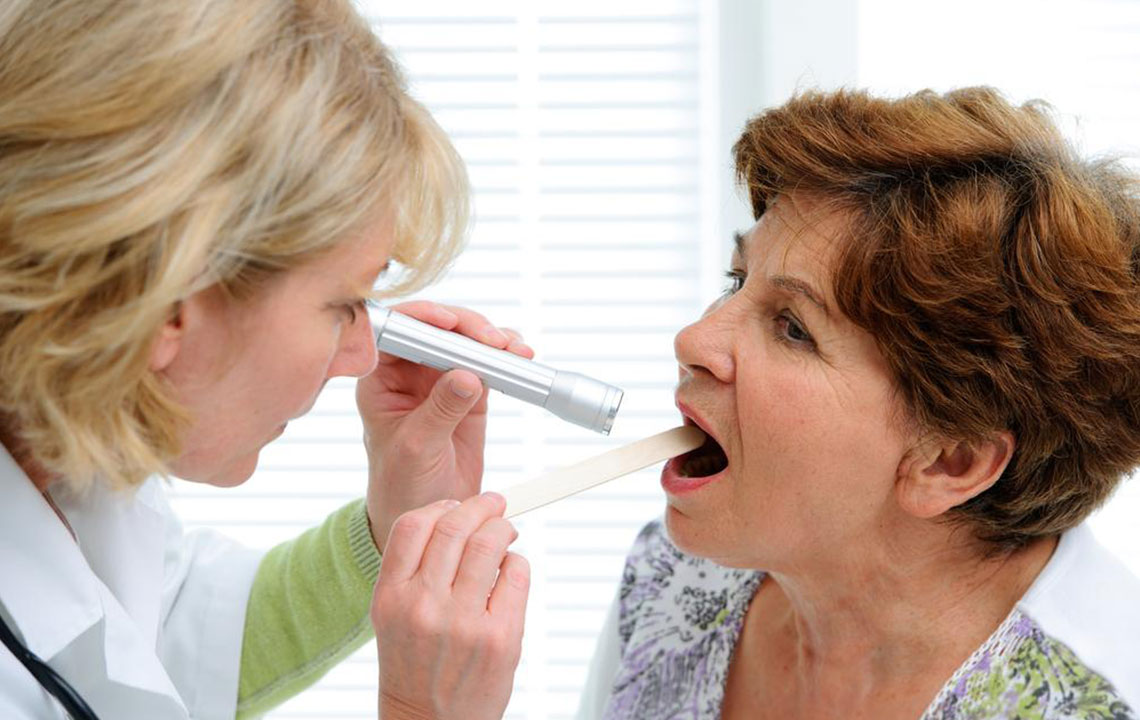
Trials and studies show that early detection can dramatically improve the prognosis of tongue cancer. The key symptoms to watch for include:
Lumps, thickening, or swelling on the tongue
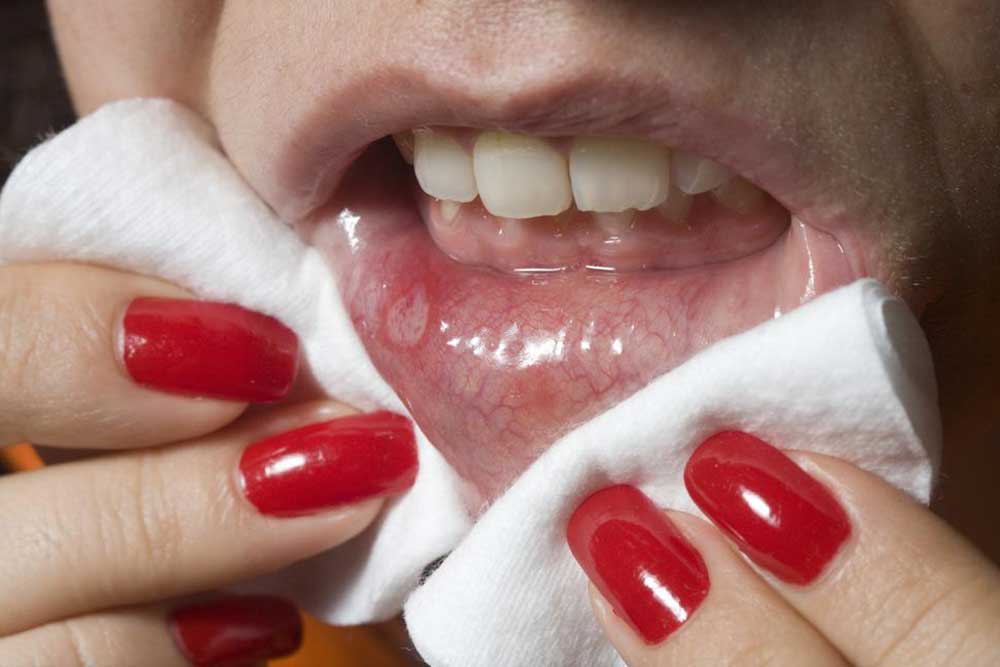
Persistent ulcers or sores that do not heal within two weeks
Blisters,red or white patches, or unusually discolored areas
Persistent pain or discomfort, especially when speaking or swallowing
Difficulty moving the tongue or jaw, hoarseness, or a sensation of fullness
Changes in the fit of dentures or loose teeth without clear reason
In some instances, symptoms remain subtle initially. Many patients may ignore or dismiss early signs, which underscores the importance of routine oral examinations. Additionally, systemic symptoms such as fatigue, unexplained weight loss, persistent night sweats, or general malaise can indicate advanced disease and warrant immediate medical attention.
Fortunately, recent advancements in medical treatments have bolstered the prognosis for tongue cancer patients. Innovative therapies like targeted chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and minimally invasive surgical options have improved survival rates and quality of life for many individuals. The key to successful management remains early diagnosis followed by appropriate medical intervention. Patients diagnosed at an early stage often respond well to treatment, enabling them to regain normal oral functions, retain their speech and swallowing abilities, and enjoy long-term remission.
In conclusion, understanding the causes, recognizing early symptoms, and seeking prompt medical care are essential steps in combating tongue cancer. Public awareness campaigns, regular dental visits, and avoiding known risk factors can significantly reduce the incidence and improve outcomes of this potentially life-threatening disease.