Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing the Early Signs and Symptoms of Tongue Cancer
This comprehensive article explores the early signs and symptoms of tongue cancer, emphasizing the importance of awareness for early detection. It details risk factors, early warning signs, diagnostic methods, and treatment options to help readers recognize and respond promptly to this serious condition. Understanding these indicators can improve outcomes through timely medical intervention and prevention strategies.

Understanding the Key Indicators and Symptoms of Tongue Cancer
Cancer is characterized by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells within tissues, and it can originate in virtually any part of the body. One of the less discussed but significant types is oral cancer, which includes cancers affecting the tongue, lips, inner cheeks, and throat. Globally, oral cancer ranks as the 15th most common cancer, with thousands of new diagnoses each year. In the United States alone, approximately 50,000 individuals received an oral cancer diagnosis in 2018. This disease not only impacts patients physically but can also have profound psychological and social effects, emphasizing the importance of early detection and awareness.
Men are statistically twice as likely as women to develop tongue cancer, making gender a relevant risk factor. Several parts of the mouth are vulnerable to cancer development, with the tongue being one of the most common sites. The primary causes and risk factors include lifestyle choices such as smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, and infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). Extensive research indicates that about 90% of oral cancer cases are linked directly or indirectly to tobacco and alcohol use. Understanding these risk factors is essential for preventative strategies and early intervention.
Tongue cancer most often develops in the squamous cells that make up the lining of the tongue, which is why it is classified as a squamous cell carcinoma in many cases. The primary risk factors include tobacco use—whether through smoking cigarettes, cigars, or chewed tobacco—and high alcohol consumption levels. Additionally, infection with HPV acquired through sexual contact significantly increases the risk, especially in younger populations.
Detecting tongue cancer in its early stages can be challenging because initial symptoms tend to be subtle, painless, and easily overlooked. Nevertheless, awareness of certain early signs can prompt timely medical consultation, potentially improving outcomes. Early symptoms to watch for include:
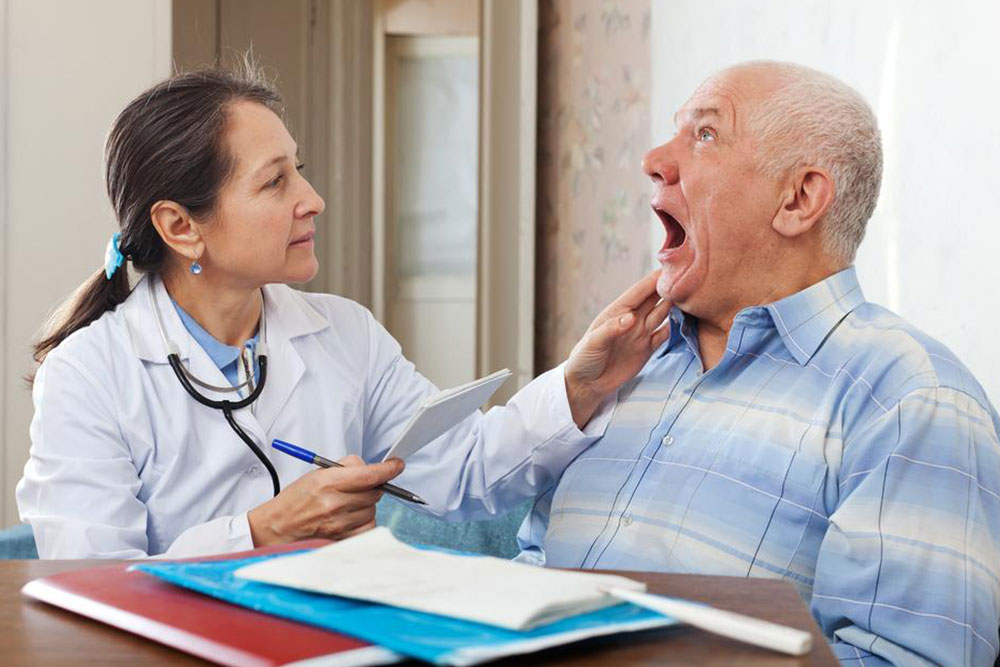
The appearance of red and white patches on the surface of the tongue, which are often painless but persistent.
The presence of a lump or ulcer on the tongue that does not heal over weeks or months.
Unexplained sore throat that persists despite usual treatments.
Pain during swallowing, which may feel like discomfort or a burning sensation.
Unexplained bleeding from the mouth or tongue, not caused by injury or ulcers.
Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, indicating possible metastasis, along with numbness or tingling sensation in the tongue.
In older adults who wear dentures, swelling of the jaw or sudden changes in denture fit can serve as early warning signs. As the tumor progresses, patients may also experience severe ear pain, often without any apparent cause. Due to the hidden nature of early symptoms, tongue cancer is often diagnosed in advanced stages, making it more difficult to treat effectively. Healthcare providers may utilize various imaging techniques such as PET scans, CT scans, or MRI to assist in confirming the diagnosis and determining the extent of spread. Advances in treatment—including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted biological agents—offer hope for better prognosis. In advanced cases, reconstructive surgeries may be necessary to restore speech, swallowing, and appearance, highlighting the importance of early detection for less invasive treatment options.