Comprehensive Guide to Effectively Managing Excessive Sweating
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies and medical treatments for hyperhidrosis, a condition characterized by excessive sweating. It covers natural remedies, lifestyle changes, and advanced procedures such as Botox, Miradry, laser therapy, and surgery. The article provides valuable insights for those seeking relief from social discomfort and daily challenges caused by uncontrollable sweating, emphasizing the importance of personalized treatment and professional medical advice to achieve optimal results and improve quality of life.
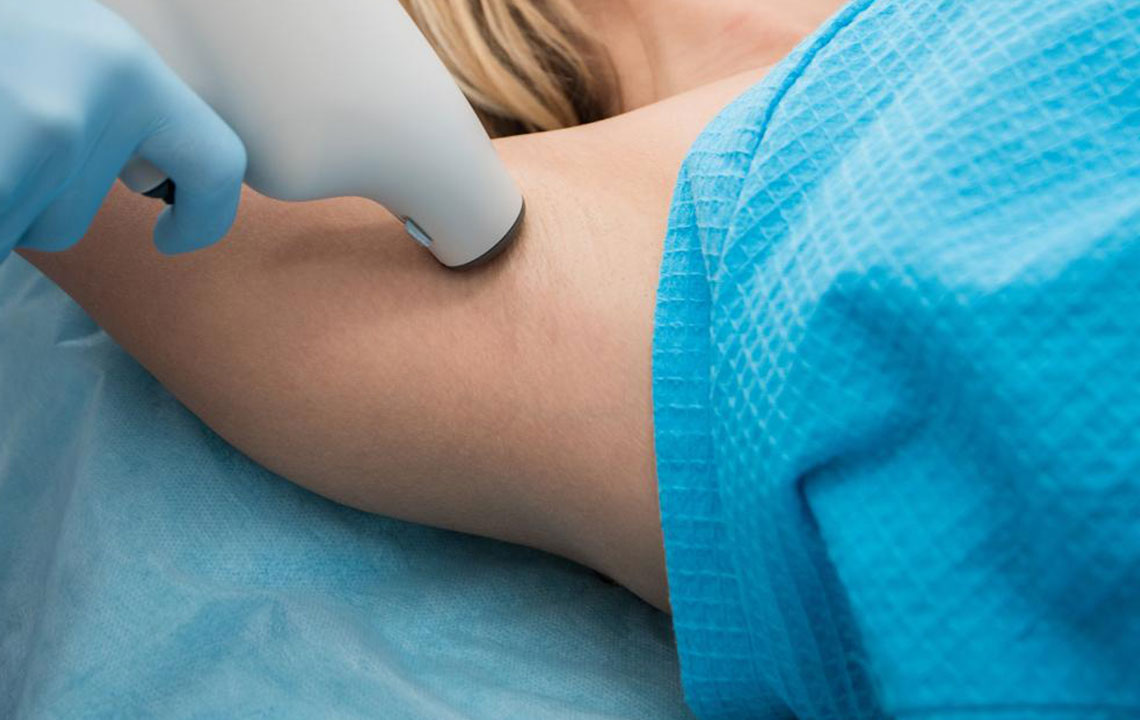
Effective Strategies to Manage Excessive Sweating
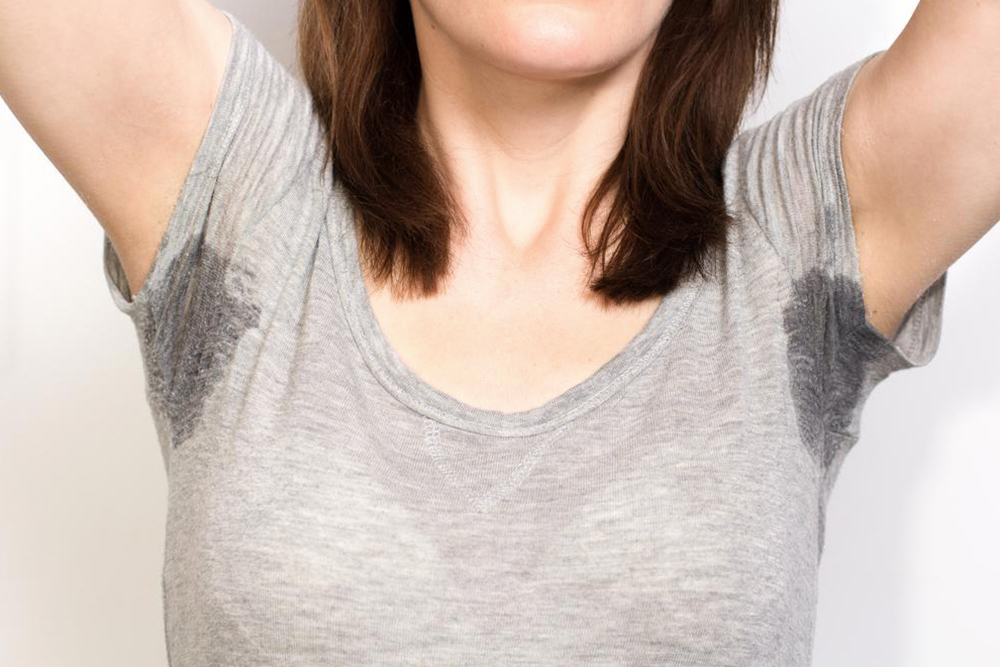
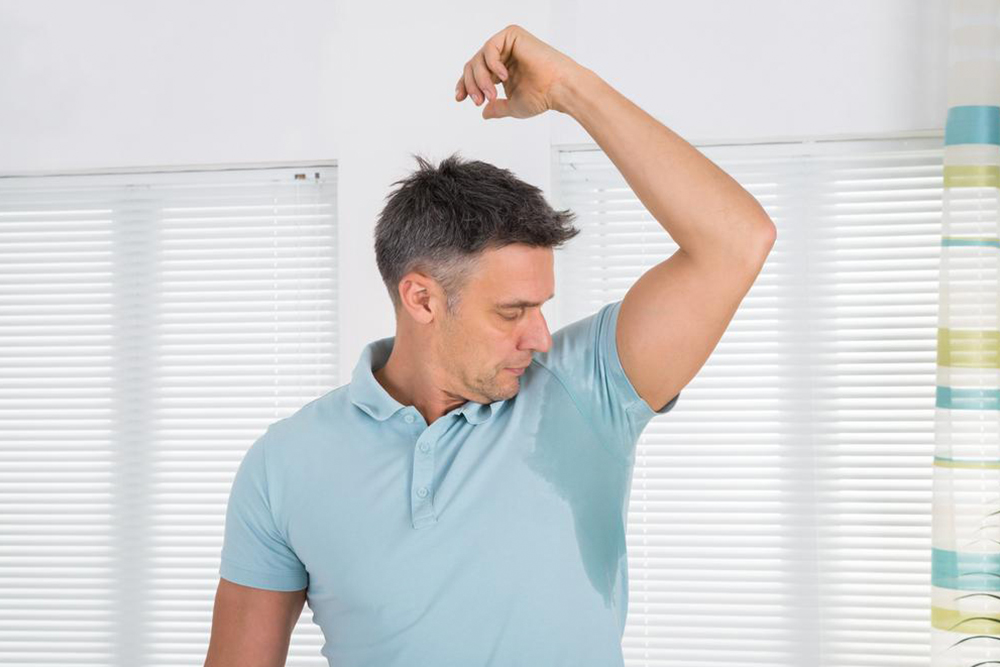
Excessive sweating, medically known as hyperhidrosis, is a condition where the sweat glands produce sweat beyond what is necessary to regulate body temperature. This condition can manifest in various parts of the body, most commonly affecting the palms, soles, and underarm areas. When hyperhidrosis is localized to specific regions, it is referred to as focal hyperhidrosis; however, when sweating is widespread across larger areas or the entire body, it is termed generalized hyperhidrosis. Individuals experiencing generalized symptoms should seek professional medical evaluation to explore suitable treatment options tailored to their needs.
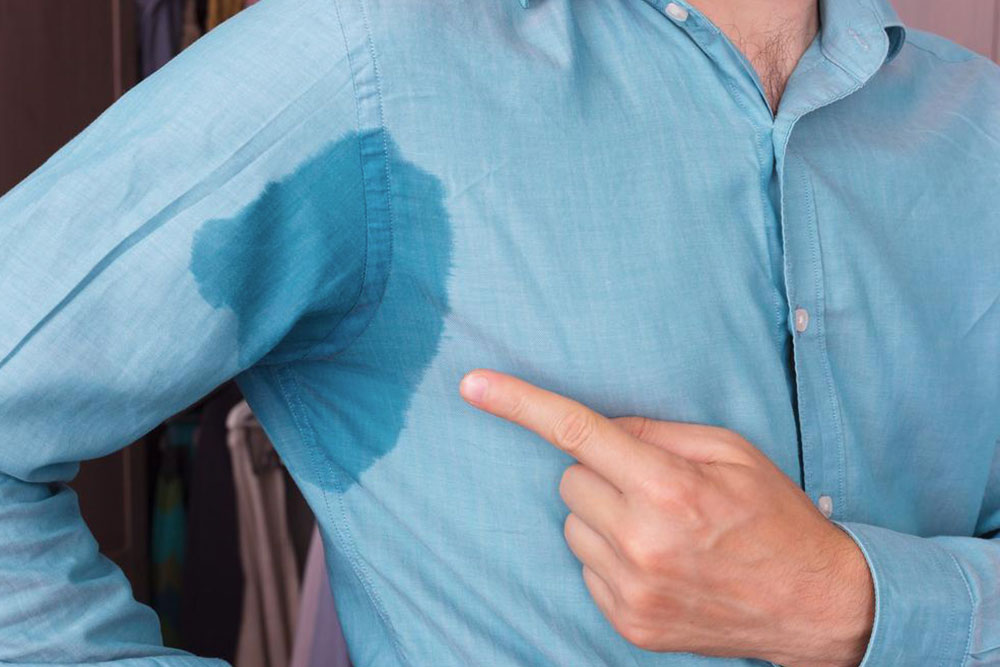
While hyperhidrosis is not life-threatening, it can significantly impact a person's quality of life. The persistent sweat can lead to social embarrassment, emotional distress, and practical difficulties in daily activities. People with severe sweating often avoid handshakes at social gatherings, steer clear of intimate interactions, or become reluctant to wear certain clothing that traps sweat, all due to the fear of embarrassment and odor. Social withdrawal and lowered self-esteem are common among those affected.
Managing hyperhidrosis involves a combination of natural remedies, lifestyle adjustments, and medical interventions, especially for severe cases. The degree of sweating varies enormously among individuals, so initial management typically starts with non-invasive methods such as deodorants, antiperspirants, and powders designed to reduce sweat and odor. When these options prove insufficient, more advanced medical treatments become necessary. While these treatments tend to be more effective, they are also more invasive and should be considered after consulting with a healthcare professional. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of various strategies and treatments available for managing excessive sweating effectively.
Antiperspirants
Antiperspirants are the first line of defense against excessive sweating. These products work by temporarily blocking sweat glands, thereby reducing sweat production and neutralizing odor. Over-the-counter (OTC) antiperspirants are widely available and can be used daily—usually applied during the night to ensure maximum absorption and effectiveness for the following day. However, individuals with severe hyperhidrosis might require prescription-strength formulations containing higher concentrations of aluminum salts, which should be used under medical supervision. Consulting a dermatologist can help determine the most suitable antiperspirant for your condition, especially if OTC options are insufficient.
Anticholinergic Medications
For individuals needing more targeted relief, anticholinergic drugs are prescribed to temporarily reduce sweat production. These medications work by blocking the nerve signals that stimulate sweat glands. They can be particularly effective during specific events or for managing unpredictable episodes of excessive sweating. Nonetheless, long-term use of anticholinergics is associated with potential side effects such as dry mouth, urinary retention, dizziness, and blurred vision, so they should only be used under strict medical guidance. Your healthcare provider can evaluate the risks and benefits based on your health profile.
Iontophoresis
Iontophoresis is a non-invasive treatment primarily used to control excessive sweating of the hands and feet. It involves immersing the affected areas into water and passing a mild electrical current through the water, which helps inhibit sweat gland activity. This procedure usually requires multiple sessions spaced over days or weeks for optimal results. It is generally deemed safe but contraindicated for individuals with certain health conditions such as heart disorders, epilepsy, or pregnant women. Regular treatments can significantly improve quality of life by reducing distress caused by excessive hand and foot sweating.
Botox (Botulinum Toxin) Injections
Botox is widely known for its cosmetic applications but also proves highly effective in treating hyperhidrosis. Botox injections work by blocking the nerve signals that activate sweat glands, leading to a substantial reduction in sweating in targeted areas. It is especially effective for axillary (underarm), palm, and plantar (foot) hyperhidrosis. Typically, multiple injections are required per session, with results lasting for several months. While generally safe, the procedure should be performed by trained medical professionals to minimize risks and ensure optimal results. Many patients enjoy a dramatic decrease in sweating and improved confidence following treatment.
Miradry System
Miradry is a non-invasive, FDA-approved treatment specifically designed for underarm hyperhidrosis. It utilizes electromagnetic energy to target and eliminate sweat and odor glands in the underarm region. The procedure involves minimal discomfort, with most patients experiencing a temporary sensation of heat. Multiple treatment sessions are usually necessary, but the results can be long-lasting, often permanently reducing sweating in the treated area. Miradry is considered a safe and effective option for individuals seeking a non-surgical solution to their underarm hyperhidrosis.
Laser Therapy
Laser-based treatments offer a minimally invasive approach for removing sweat glands. During laser therapy, targeted laser beams are used to precisely destroy overactive sweat glands beneath the skin without damaging surrounding tissues. This procedure is suitable for mild to severe cases and can lead to significant reduction in sweat production. It offers the advantage of quick recovery times and minimal scarring. As with all treatments, laser therapy should be performed by qualified dermatologists or specialists experienced in laser procedures.
Thoracic Sympathectomy
When less invasive treatments fail, surgical intervention such as thoracic sympathectomy may be considered. This procedure involves cutting or clipping the nerves responsible for activating sweat glands, primarily in the chest area. It is usually reserved for severe, resistant cases of hyperhidrosis. While highly effective, this surgery can have side effects—including the possibility of compensatory sweating in other parts of the body—and requires thorough medical consultation. Post-surgery, most patients experience a marked reduction in armpit sweating, but must weigh the benefits against potential risks and side effects.
Local Surgical Options
For localized hyperhidrosis, targeted surgical procedures such as sweat gland excision or curettage provide effective and less invasive options. These procedures involve removing or destroying sweat glands in specific areas and are associated with lower risks compared to extensive surgeries. Local surgery is typically performed under local anesthesia and offers a quicker recovery with satisfactory results. It is particularly suitable for individuals with focal hyperhidrosis confined to limited regions.
In conclusion, managing hyperhidrosis effectively involves a personalized approach based on the severity, affected areas, and individual health considerations. Consultation with a healthcare provider or dermatologist can help determine the most appropriate treatment plan suited to your condition. Whether starting with natural remedies or opting for advanced medical interventions, effective management can significantly improve your comfort, confidence, and overall quality of life.





