Effective Strategies for Managing Excessive Sweating (Hyperhidrosis)
Discover comprehensive strategies to effectively manage hyperhidrosis, a condition characterized by excessive sweating. Learn about treatment options ranging from over-the-counter antiperspirants to advanced medical procedures, and understand how personalized treatment plans can improve comfort and confidence. This guide emphasizes the importance of professional consultation for severe cases, offering practical solutions to enhance quality of life for those affected by excess sweat.

Effective Strategies for Managing Excessive Sweating (Hyperhidrosis)
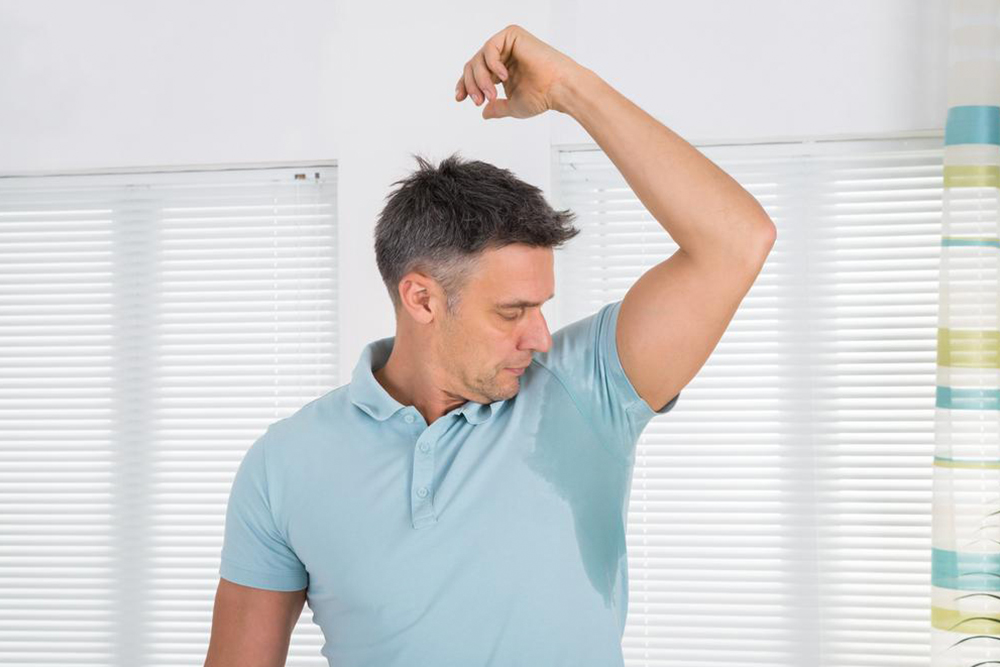
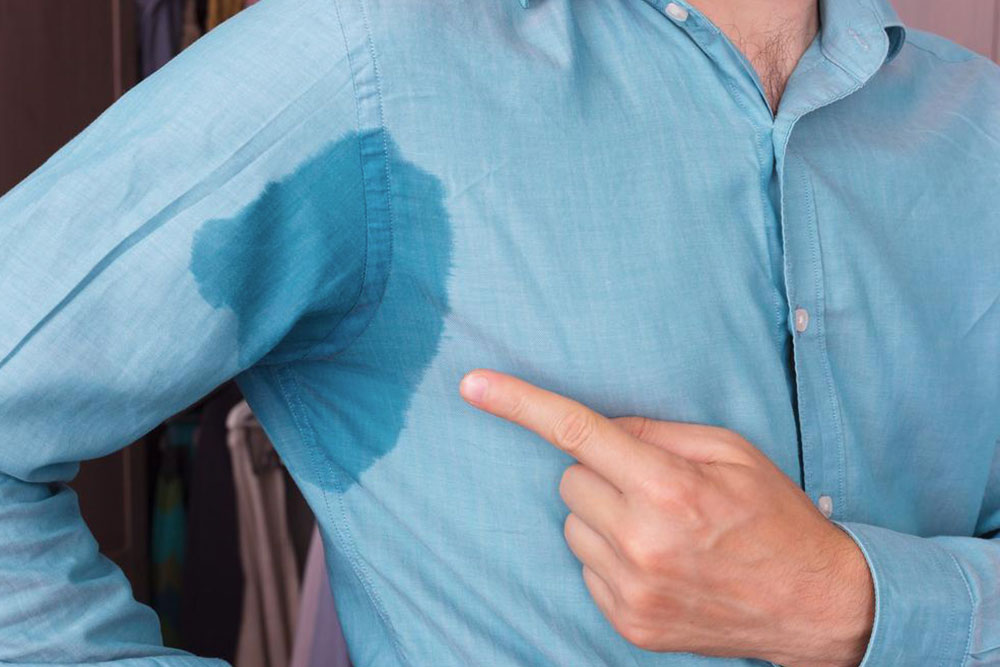
Everyone experiences sweating as a natural bodily function, primarily to regulate internal temperature and maintain homeostasis. Sweating helps cool the body by releasing heat through the evaporation of sweat from the skin surface. This process is especially important in hot or humid weather conditions, where the body needs to dissipate excess heat efficiently. However, for some individuals, sweating becomes an overwhelming issue, leading to significant discomfort and social embarrassment. This phenomenon, known as hyperhidrosis, affects nearly 3% of the American population and can profoundly impact daily life and emotional wellbeing.
Hyperhidrosis is characterized by excessive sweating that often occurs without any identifiable trigger or reason. Unlike typical sweating, which is proportional to temperature or physical exertion, hyperhidrosis can happen spontaneously or in response to only mild stimuli, such as stress or anxiety. This condition can affect various parts of the body, including the palms, soles, face, and underarms, leading to wet clothes, constant dampness, and a significant decrease in quality of life. Many individuals suffering from hyperhidrosis experience social anxiety, low self-esteem, and even depression due to their condition.
Understanding the treatment options available is essential for managing hyperhidrosis effectively. Mild cases often respond well to over-the-counter antiperspirants containing aluminum salts, which work by blocking sweat glands temporarily. The most common active ingredient is aluminum chloride, which, when applied correctly, can substantially reduce sweating episodes. For more persistent or severe cases, prescription-strength antiperspirants containing higher concentrations of aluminum chloride hexahydrate are recommended. These are typically applied at night over consecutive days, allowing the active ingredients to work while the skin is less prone to irritation. Proper skin care before application can help minimize skin irritation, which is a common side effect.
In cases where topical treatments are insufficient, healthcare professionals may recommend additional interventions. These include iontophoresis, Botox injections, or medications that help regulate excessive sweating. Iontophoresis involves passing a mild electrical current through the skin to block sweat glands temporarily. Botox, or botulinum toxin, can be injected into affected areas to paralyze sweat glands and reduce secretion for several months. When conservative methods fail, more advanced options like surgical removal of sweat glands or sympathectomy (a procedure to cut nerve pathways responsible for sweating) might be considered.
Despite the variety of available treatments, managing hyperhidrosis requires a personalized approach. Consulting with a dermatologist or a healthcare professional specializing in sweat disorders is crucial to determine the most effective and safe treatment plan. Proper diagnosis and tailored interventions can significantly increase comfort, restore confidence, and improve social interactions. Living with hyperhidrosis can be challenging, but effective management strategies and professional guidance can transform the quality of life for sufferers.