Comprehensive Dietary Approaches to Managing Excessive Sweating (Hyperhidrosis)
Discover comprehensive dietary strategies to manage hyperhidrosis effectively. Learn which foods to incorporate, including hydrating fruits, calcium-rich options, magnesium sources, and healthy fats, to help regulate body temperature and reduce excessive sweating episodes. Combining these dietary tips with proper hydration and medical treatments can improve quality of life for hyperhidrosis sufferers. This detailed guide provides practical advice backed by nutritional science to support optimal health and comfort.

Effective Nutrition Strategies to Alleviate Excessive Sweating
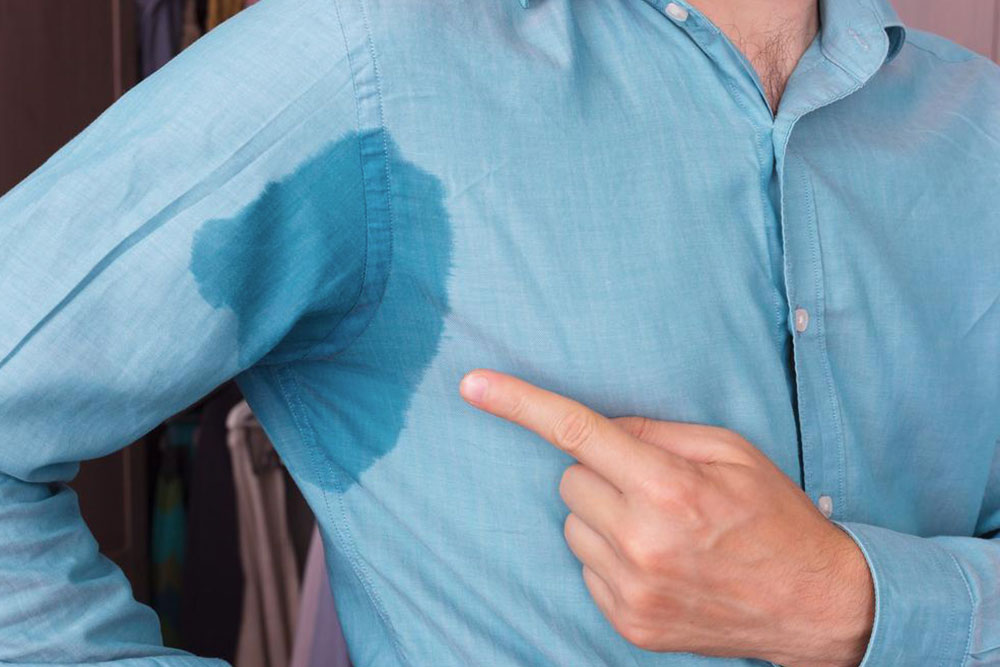
Excessive sweating, medically known as hyperhidrosis, is a condition characterized by abnormally high perspiration levels that can significantly impact daily life. While factors such as hormonal imbalances, metabolic disorders, infections, and stress contribute to hyperhidrosis, one of the most manageable aspects is dietary habits. Maintaining a balanced, nutrient-dense diet can play a crucial role in controlling this condition, improving overall health, and enhancing quality of life. This comprehensive guide explores dietary modifications and specific food choices that can help manage hyperhidrosis effectively.
Understanding Hyperhidrosis and Its Triggers
Hyperhidrosis affects millions worldwide and can be localized (affecting specific body parts) or generalized (affecting the entire body). The underlying causes are often linked to overactive sweat glands, hormonal fluctuations, or nervous system overactivity. Certain lifestyle factors, including diet, may influence sweat production, either exacerbating or alleviating symptoms.
Addressing dietary habits is a vital component of an integrated approach, enabling affected individuals to reduce episodes of excessive sweating and improve overall comfort.
Key Dietary Tips for Hyperhidrosis Management
Prioritize hydrating fruits and vegetables with high water content
Incorporate calcium-rich foods to support thermoregulation
Choose decaffeinated herbal teas over caffeinated beverages
Eat magnesium-rich foods to prevent deficiencies that may worsen symptoms
Use healthy fats like olive oil to promote metabolic health
Maintain proper hydration throughout the day
Consume vitamin B sources to boost metabolism and nerve health
Each of these strategies plays a pivotal role in minimizing sweat episodes by balancing body temperature and supporting overall bodily functions. Let's delve into each aspect in detail, explaining how specific foods and habits contribute to better management of hyperhidrosis.
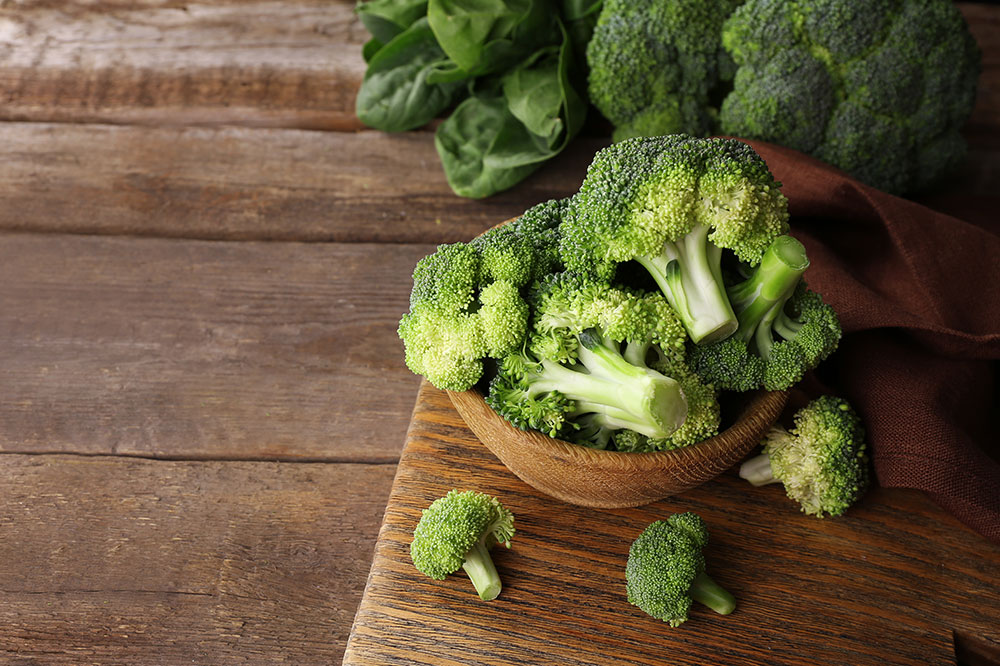
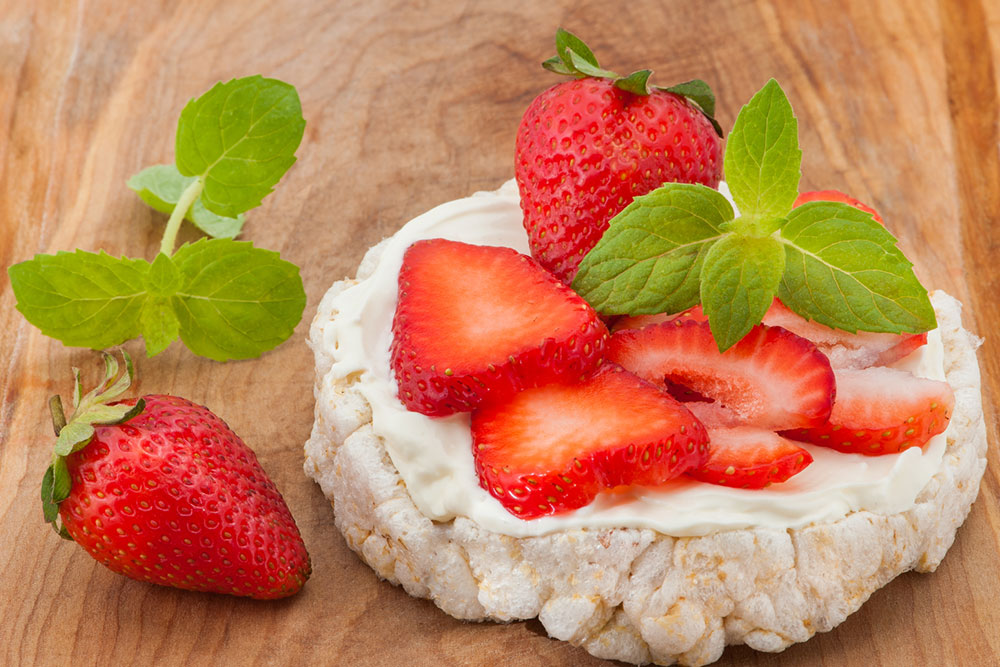
Hydrating Fruits and Vegetables
One of the most effective ways to control excessive sweating is through proper hydration. Consuming fruits and vegetables with high water content helps regulate body temperature naturally. Incorporate a variety of hydrating produce like watermelons, cantaloupes, oranges, strawberries, peaches, pineapple, apples, and grapes into your daily diet. Leafy greens such as spinach, romaine lettuce, and kale, along with vegetables like cucumbers, bell peppers, celery, eggplant, and red cabbage, are excellent choices. These foods not only help keep you cooled but also provide essential vitamins and minerals vital for overall health. Staying well-hydrated by drinking water is equally important, especially in hot environments or during physical activities.
Calcium-Rich Foods and Their Role in Thermoregulation
Calcium plays a significant role in body's heat regulation processes. Including calcium-rich foods such as skim milk, low-fat cheese, yogurt, and dark leafy greens like kale and collard greens can support the body's ability to maintain a stable core temperature. These foods are beneficial because they help prevent metabolic stress and reduce the likelihood of excessive sweating triggered by elevated internal temperatures. For individuals looking to reduce fat intake, opting for low-fat dairy products is advisable. Incorporating adequate calcium intake not only promotes skeletal health but can also contribute to better management of hyperhidrosis symptoms.
Benefits of Decaffeinated Green Tea
Switching from caffeinated drinks such as coffee to decaffeinated green tea can have cooling effects on the body and promote relaxation. Green tea contains antioxidants that combat oxidative stress, which may contribute to excessive sweating. Additionally, green tea helps soothe nerve activity, potentially reducing nervous-induced sweating episodes. The decaffeinated variety is preferable, especially for sensitive individuals or those prone to stress and anxiety. Regular consumption of green tea can be a calming, hydrating, and sweat-reducing addition to your diet.
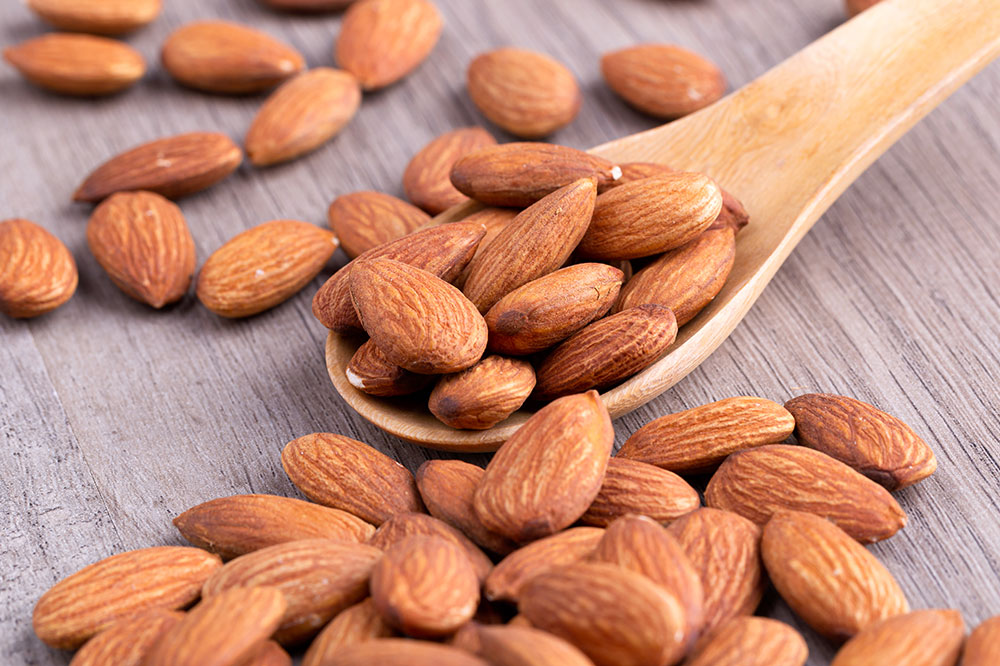
Magnesium-Rich Foods for Nervous System Support
Magnesium is essential for nerve function, immune health, and metabolic regulation. A deficiency in magnesium can heighten the sensitivity of sweat glands or intensify stress responses that lead to hyperhidrosis. To prevent this, incorporate foods rich in magnesium such as almonds, cashews, pumpkin seeds, dark chocolate, soy-based products, and leafy greens like spinach. Adequate magnesium intake helps relax the nervous system, stabilize mood, and support metabolic efficiency, which may collectively help reduce excessive sweating episodes.
Healthy Fats from Olive Oil
Olive oil is renowned for its antioxidant properties and healthy monounsaturated fats. Including olive oil in your diet supports metabolism, digestion, and immune health—all of which can influence sweat production. Its anti-inflammatory effects may also aid in managing stress-related sweating. Use olive oil as a primary cooking fat or drizzling over salads and vegetables to enhance flavor and health benefits.
Maintaining Adequate Hydration
Proper hydration is the cornerstone of body temperature regulation and overall health. Carry a reusable water bottle throughout the day and sip fluids regularly, especially in hot weather or during exercise. Adjust fluid intake based on activity level and environmental conditions to prevent dehydration, which can paradoxically trigger more sweating to cool the body. Besides water, herbal teas and electrolyte-balanced beverages can help maintain hydration and electrolyte levels.
Incorporating Vitamin B-Rich Foods
Vitamin B complex nutrients, found in foods like salmon, lean beef, eggs, and green vegetables, are vital for energy metabolism and nerve health. Enhancing metabolic efficiency can help mitigate excessive sweating, especially in individuals with sluggish digestion or metabolic issues. Including these foods in your diet ensures optimal nerve function and supports the body's natural ability to regulate temperature and sweat production.
While dietary modifications can significantly alleviate hyperhidrosis symptoms, some cases may require medical intervention. Treatments like Botox injections, which temporarily block nerve signals responsible for stimulating sweat glands, offer effective relief but should be administered by qualified healthcare providers. Prior consultation with medical professionals is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to individual needs and health conditions.
various strategies, including diet, hydration, and medical treatments, can collectively improve quality of life for people suffering from hyperhidrosis. Achieving optimal results often involves integrating these approaches under professional guidance to ensure safety and effectiveness. Taking control of your diet is a proactive step towards reducing excessive sweating and feeling more comfortable every day.