Comprehensive Dietary Approaches to Managing Excessive Sweating
Managing excessive sweating, or hyperhidrosis, can be naturally supported through strategic dietary choices. Incorporating hydrating fruits and vegetables, calcium-rich foods, green tea, magnesium sources, olive oil, and maintaining proper hydration can significantly reduce episodes of uncontrollable sweating. This comprehensive guide highlights vital nutrients and lifestyle strategies to help regulate body temperature, promote nerve health, and improve overall comfort for those affected by hyperhidrosis, emphasizing the importance of personalized medical consultation for persistent cases.

Strategic Nutrition Tips to Reduce Unnecessary Sweating
While sweating is an essential physiological process that helps regulate body temperature and eliminate toxins, some individuals experience uncontrolled excessive sweating, medically termed hyperhidrosis. This condition can significantly impact quality of life and may be linked to underlying health issues such as diabetes, hormonal changes during menopause, infections, or other medical conditions. Fortunately, adjusting one's diet can be a natural and effective way to manage and reduce episodes of hyperhidrosis. By incorporating specific nutrient-rich foods and hydration strategies into daily routines, individuals can help control excess sweating and improve their overall comfort.
Key Dietary Interventions
Incorporating Hydrating Fruits and Vegetables
One of the foundational strategies for controlling excessive sweating involves maintaining optimal hydration levels. Consuming foods with high water content not only nourishes your body but also helps regulate internal temperature effectively. Hydrating fruits such as watermelon, oranges, peaches, pineapples, strawberries, grapes, apples, and cucumbers are excellent choices. Leafy greens like spinach, lettuce, and kale, along with vegetables like celery, bell peppers, eggplant, and red cabbage, can be integrated into meals to promote hydration. These foods support cooling the body from within and can reduce the body's need to sweat excessively in response to overheating. Remember, complementing these with low-sugar, natural beverages like herbal teas and infused waters amplifies hydration benefits.
Boosting Calcium Intake for Thermoregulation
Calcium plays a crucial role in controlling body temperature and sustaining nerve functions that influence sweating. Including calcium-rich foods such as low-fat dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt can aid in stabilizing internal temperature and reducing hyperhidrosis symptoms. Additionally, green leafy vegetables including kale, collard greens, and bok choy serve as excellent non-dairy calcium sources. Opting for low-fat options supports overall health without adding metabolic burden, which could otherwise aggravate sweating episodes. Proper calcium levels contribute to optimal muscle function and may help prevent over-activation of sweat glands during hot conditions or emotional stress.
Switching to Green Tea for Natural Cooling
Decaffeinated green tea offers numerous benefits for managing hyperhidrosis. Known for its cooling and calming properties, green tea contains antioxidants that help soothe nerves and potentially reduce sweating. Replacing caffeinated beverages like coffee or energy drinks with green tea is a healthful alternative that supports body temperature regulation and stress reduction. The gentle diuretic effect of green tea also aids in hydration, which is vital for controlling excess sweating.
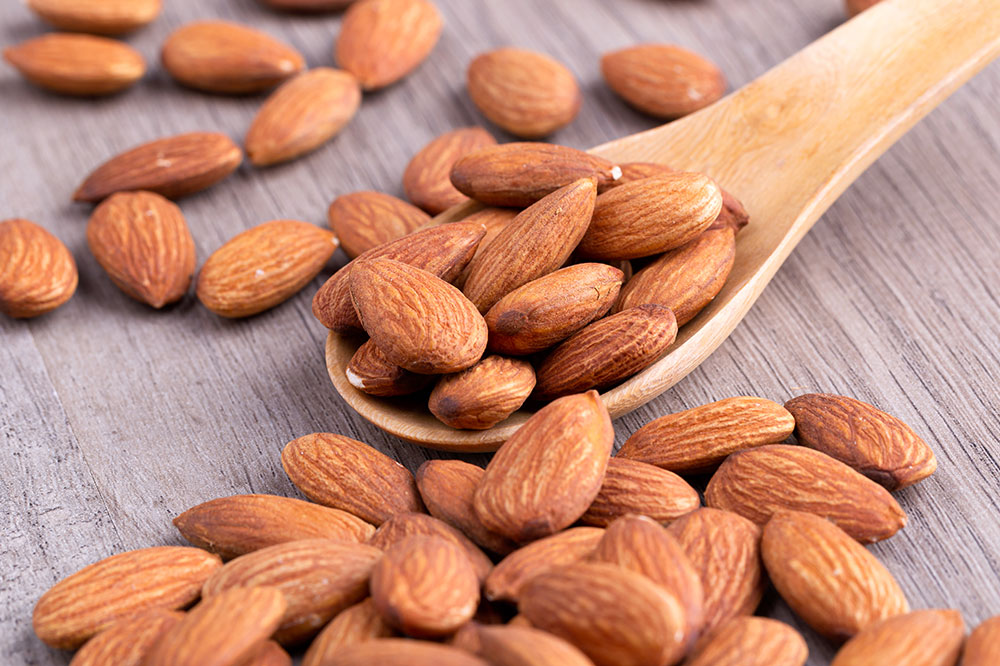
Foods Rich in Magnesium
Magnesium deficiency has been linked to increased sweating and hyperhidrosis. Incorporating magnesium-rich foods such as almonds, cashews, pumpkin seeds, dark chocolate, spinach, and soy products can help bolster nerve function and immune health. These foods support relaxation of nerve signals, thus potentially decreasing excessive sweat production. Additionally, magnesium plays a role in energy production and metabolic health, which are crucial for maintaining a balanced internal environment.
Using Olive Oil to Support Sweat Regulation
Olive oil is renowned for its antioxidant properties and health benefits. Its inclusion in the daily diet can help lower sweat production by supporting metabolic processes and reducing inflammation. Extra virgin olive oil, rich in monounsaturated fats, not only enhances flavor but also contributes to overall cardiovascular and metabolic health. Its antioxidant components help combat oxidative stress, which can exacerbate sweating issues in susceptible individuals.
Maintaining Adequate Hydration
Proper hydration is a cornerstone of managing hyperhidrosis. Drinking at least eight glasses of water daily helps regulate body temperature and prevent dehydration, which can trigger excessive sweating. Hydration needs may vary based on activity level, climate, and individual physiology. Carrying a reusable water bottle and sipping fluids throughout the day promotes consistent hydration and helps keep the body's thermoregulatory mechanisms functioning optimally.
Ensuring Sufficient Vitamin B in Your Diet
Vitamin B complex vitamins, especially B6 and B12, are vital for healthy metabolism and nerve function. Consuming foods like salmon, lean meats, eggs, and leafy greens supplies these essential nutrients. Individuals with slower digestion or metabolic issues might experience heightened sweating due to impaired thermoregulation. Incorporating these foods can aid in metabolic efficiency, thus reducing the likelihood of excessive sweating triggered by internal imbalances.
For persistent hyperhidrosis, medical interventions such as Botox injections are available and have been approved by the FDA for underarm hyperhidrosis. Botox works by blocking nerve signals that activate sweat glands, providing relief for many patients. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most suitable treatment plan, which might include medication, therapy, or lifestyle changes, in addition to dietary adjustments.