Comprehensive Guide to Common Bacterial Skin Infections and Effective Treatment Strategies
This comprehensive article explores common bacterial skin infections like folliculitis, cellulitis, impetigo, and boils. It covers their causes, symptoms, risk factors, prevention tips, and effective treatment options, emphasizing early diagnosis and proper hygiene to maintain healthy skin and prevent complications.

Bacterial skin infections are a prevalent health concern affecting millions globally. These infections, primarily caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, can manifest in various forms, each with distinct characteristics, causes, and treatment options. Understanding the different types of bacterial skin infections, their symptoms, preventive measures, and treatment strategies is crucial for anyone looking to maintain healthy skin and avoid complications stemming from these infections. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the most common bacterial skin infections, their causes, signs, prevention tips, and available treatments to equip readers with valuable knowledge.
Many bacterial skin infections are attributed to the widespread presence of Staphylococcus and Streptococcus bacteria, which are naturally present on the skin and in the environment. Under certain conditions, these bacteria can invade the skin barrier and cause infection. The following infections are among the most frequently encountered:
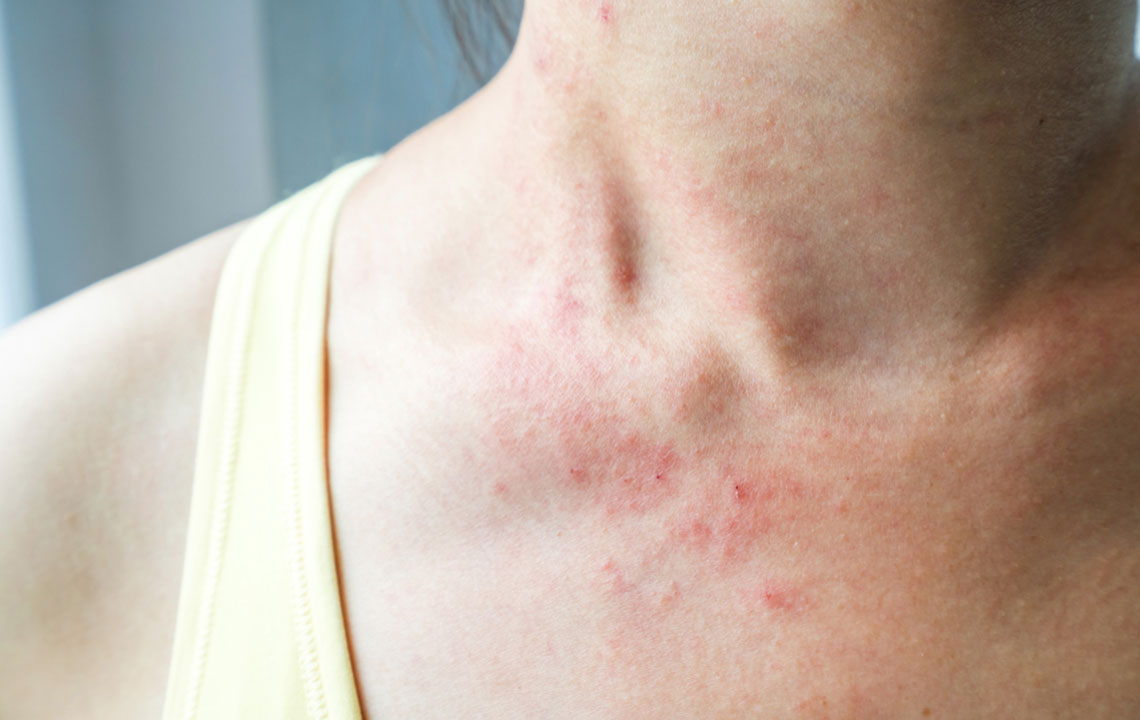
Folliculitis: This condition occurs when hair follicles become inflamed due to bacterial invasion. It manifests as small, red, pus-filled bumps that resemble acne. Folliculitis often appears after exposure to contaminated hot tubs, swimming pools, or from shaving irritations. People with compromised immune systems or those who have prolonged sweating are also more susceptible.
Cellulitis: A serious bacterial skin infection that affects the deeper layers of the skin and underlying tissues. It commonly affects the legs but can occur anywhere on the body. Cellulitis causes redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness, sometimes accompanied by fever and chills. If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications such as abscesses or systemic infection.
Impetigo: An highly contagious infection primarily affecting children but also seen in adults. Impetigo can present as either bullous, with large blisters, or non-bullous, characterized by crusted, yellowish sores. It often affects the face and hands and spreads easily through contact or shared objects.
Boils (Furuncles): These are deep, tender, red lumps originating from infected hair follicles. Boils develop over days and can grow larger, sometimes forming abscesses filled with pus. They often occur in areas with hair or sweat glands, such as the neck, face, armpits, or groin.
Several factors increase the risk of developing bacterial skin infections, including skin injuries like cuts, scrapes, or sunburns, which provide bacteria a portal of entry. Poor hygiene, excessive sweating, skin conditions like dermatitis, and immunosuppression are additional risk factors. Preventive measures are vital in reducing infection likelihood:
Maintaining good personal hygiene by washing hands regularly with soap and water.
Cleaning wounds thoroughly with water and mild soap to remove bacteria and debris.
Covering cuts and abrasions with sterile dressings to prevent bacterial intrusion.
Avoiding sharing personal items such as towels, razors, or clothing that may harbor bacteria.
Managing skin conditions promptly to minimize skin barrier disruption.
Keeping skin dry and cool, especially in hot and humid weather, to prevent bacterial proliferation.
Most minor bacterial skin infections can be managed effectively at home with proper hygiene and care. However, recognizing when to seek medical attention is crucial. Larger or more severe infections may require medical intervention, including antibiotics or drainage procedures performed by healthcare professionals. Antibiotics can be topical or oral, depending on the infection's extent and severity. In cases of abscess formation, surgical drainage might be necessary to remove pus accumulation and facilitate healing.
Timely treatment is essential to prevent complications such as the spread of bacteria, tissue destruction, or systemic infections. If symptoms like increasing redness, swelling, pain, fever, or signs of spreading infection occur, consulting a healthcare provider promptly is recommended. Through awareness and preventive practices, maintaining healthy skin and avoiding bacterial infections is achievable for everyone.