Comprehensive Guide to Bacterial Skin Infections: Types, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive article explores bacterial skin infections, including boils, carbuncles, impetigo, erythrasma, and hidradenitis suppurativa. It covers symptoms, risk factors, and essential prevention methods. Understanding these common infections helps in early detection and effective treatment, reducing complications and promoting healthy, infection-free skin. Maintaining proper hygiene, timely medical care, and awareness are key to managing and preventing bacterial skin conditions effectively.

Exploring Various Bacterial Skin Infections and How to Protect Yourself
Bacterial skin infections represent a broad spectrum of conditions caused by different bacteria infiltrating the skin layers. These infections vary in terms of their severity, appearance, and affected areas. Commonly diagnosed conditions like boils, carbuncles, and impetigo are frequently associated with bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus species. Understanding these infections, recognizing their symptoms, and knowing how to prevent them are crucial steps in maintaining healthy skin and reducing the risk of complications.
What Are Furuncles (Boils)?
Furuncles, commonly known as boils, originate from hair follicles and extend deeper into the skin, involving the sebaceous (oil) glands as well.
They usually appear on areas with dense hair growth or where friction occurs, such as on the neck, face, armpits, and buttocks.
The initial stage presents as a small, red, tender bump resembling a pimple, which gradually enlarges, becomes more painful, and often develops a central white or yellow head filled with pus.
Most boils resolve naturally by draining the pus on their own, but some may require medical intervention.
Factors increasing risk include obesity, diabetes, immunosuppression, steroid therapy, and blood disorders which impair the body's ability to fight infection.
Understanding Caruncles (Carbuncles)
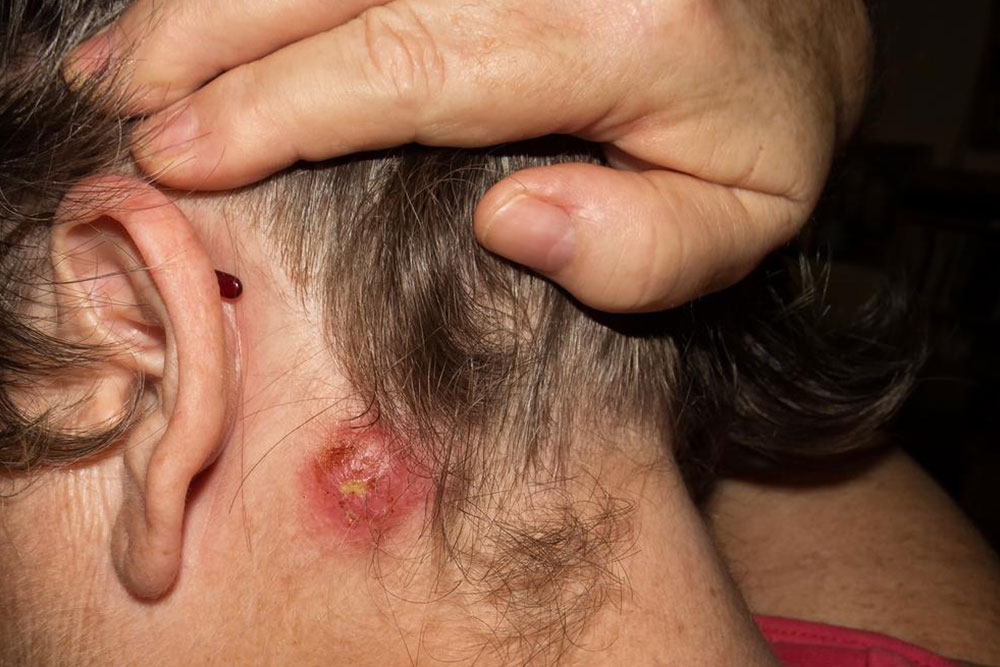
Carbuncles are large, painful skin infections made up of multiple interconnected boils or abscesses affecting several hair follicles simultaneously.
They form deep beneath the skin, creating swollen, red, tender lumps that may rupture and drain pus through multiple channels or sinus tracts.
Associated symptoms often include fever, chills, malaise, and general discomfort, indicating systemic infection.
Severe cases necessitate prompt medical treatment, usually with systemic antibiotics, and sometimes incision and drainage procedures.
Signs and Symptoms of Impetigo
This contagious bacterial skin infection predominantly affects children, especially those in preschool or early school age, but can occur in all age groups.
It typically manifests at sites of skin injury, cuts, or insect bites as honey-colored crusted sores that can spread rapidly.
Commonly seen around the nostrils and mouth, particularly if accompanied by a runny nose or nasal congestion.
If left untreated, impetigo can spread across the body, causing intense itching and increasing the risk of further bacterial invasion.
The bullous form of impetigo develops larger blisters that rupture easily, leading to raw, moist sores.
What Is Erythrasma?
Erythrasma is caused by bacterial colonization with Corynebacterium minutissimum and primarily affects moist, warm areas of the skin.
Common sites include between toes, underarms, groin, and beneath the breasts—areas prone to trapped moisture and friction.
It is more prevalent among obese, diabetic, and elderly individuals living in hot and humid climates.
The initial presentation involves pink or red patches with sharply defined borders, often with a fine scale or wrinkled appearance, gradually darkening over time to brown or rust-colored patches.
Key Preventive Measures Against Bacterial Skin Infections
Practicing good skin hygiene by washing regularly and thoroughly to remove bacteria and dirt.
Avoiding skin trauma by carefully cleaning and covering cuts, abrasions, or insect bites with sterile dressings to prevent bacterial ingress.
Limiting unnecessary use of antibiotics for minor injuries to prevent antibiotic resistance and hypersensitivity.
Maintaining good personal hygiene and prompt treatment of skin injuries helps reduce the risk of infection spread.
Understanding Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic, recurrent bacterial infection affecting certain sweat glands, notably in the armpits, groin, buttocks, and sometimes the scalp.
This condition typically occurs in post-adolescent individuals and tends to worsen over time without proper management.
Patients experience painful bumps or nodules that may open, release pus, develop foul odors, and create tunnels or sinus tracts under the skin surface, leading to abscesses.
The exact cause remains uncertain, but factors like genetics, obesity, hormonal influences, and smoking are considered contributory.
Bacterial skin infections are common yet manageable with timely medical intervention and good hygiene practices. Recognizing early symptoms, avoiding skin trauma, and seeking medical advice for appropriate antibiotics are vital for effective treatment and prevention. Maintaining clean skin and addressing infections promptly can significantly reduce complications and improve quality of life.