Identifying Early Signs and Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn to identify early signs of rheumatoid arthritis, including joint pain, swelling, and fatigue. Recognizing these symptoms early enables timely diagnosis and treatment, reducing the risk of joint damage. This comprehensive guide explains the causes, symptoms, and importance of early detection of RA, helping individuals seek medical attention promptly and improve their quality of life.

Understanding the Early Indicators and Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects millions worldwide, with over 1.5 million Americans diagnosed every year. This disease predominantly occurs in women and is more common among middle-aged and older adults, though it can develop at any age. Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management. Early detection can significantly prevent irreversible joint damage, improve quality of life, and reduce long-term disability. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the key signs to watch for and the importance of early intervention.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system, which normally protects the body from infections and injuries, mistakenly targets the joints and surrounding tissues. This misguided immune response leads to inflammation, swelling, pain, and eventual joint destruction if left untreated. Unlike osteoarthritis, which typically results from wear and tear, RA is systemic and can affect multiple joints symmetrically, often impacting the hands, wrists, elbows, shoulders, knees, and ankles.
The hallmark of rheumatoid arthritis is inflammation of the synovium, the tissue lining the joints that produces synovial fluid, essential for smooth joint movement. Persistent inflammation damages surrounding cartilage, bones, ligaments, and tendons, leading to joint instability, deformity, and severe pain. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to controlling the disease progression and preserving joint function. Recognizing early symptoms allows patients to seek medical attention promptly, reducing the risk of irreversible joint damage and improving their overall prognosis.
Below are detailed descriptions of common early symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis to help you identify potential signs of this condition:
Persistent Fatigue: Many individuals with early RA report ongoing fatigue and exhaustion that doesn’t improve with rest. This fatigue is often caused by systemic inflammation, disrupted sleep patterns resulting from joint pain or discomfort, side effects from medications, and anemia, which is common in autoimmune conditions. Persistent tiredness can negatively impact mood, appetite, concentration, and daily activity levels, serving as an early warning sign.
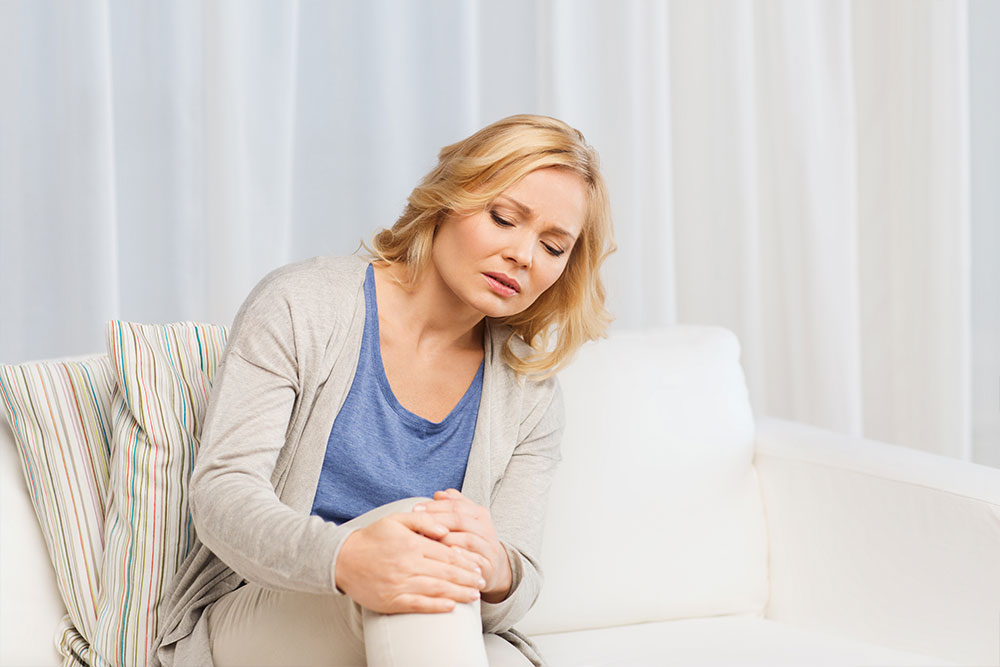
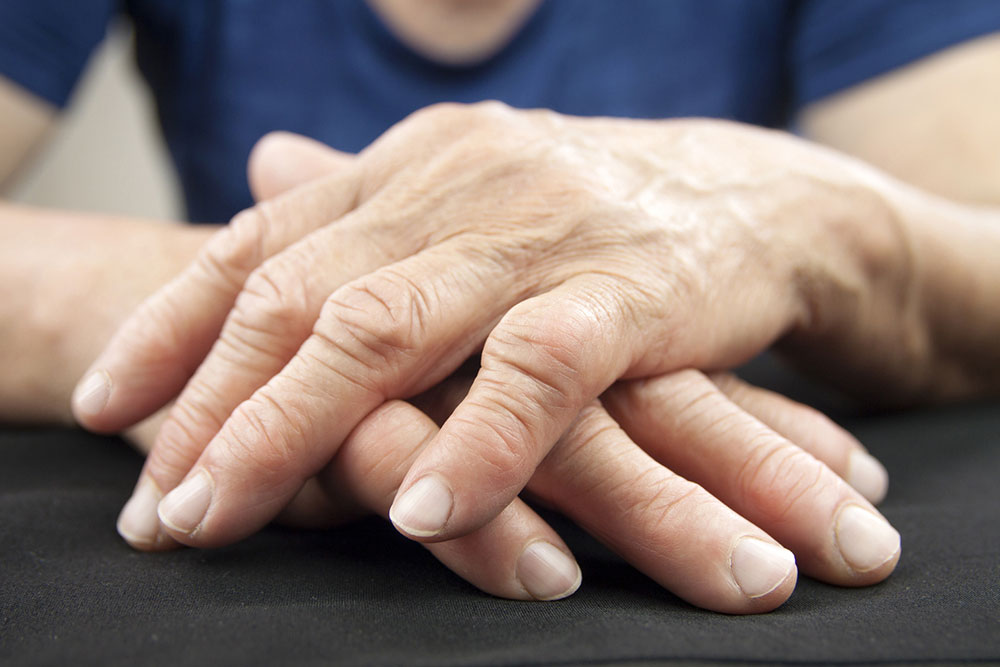
Joint Pain: One of the most noticeable symptoms is joint soreness and pain, which often worsens during periods of active inflammation. The pain may be constant or intermittent and might be more severe in the morning or after periods of inactivity. Over time, persistent joint pain can become debilitating, affecting mobility and quality of life. Notably, joint pain due to RA can persist even after the inflammation subsides or due to cumulative joint damage.
Joint Tenderness: Tenderness is a common early symptom, where joints become sensitive to touch. Swollen tissues can irritate nearby nerves, causing pain when pressure is applied. This tenderness often worsens at night or during certain activities, interfering with sleep and daily routines.
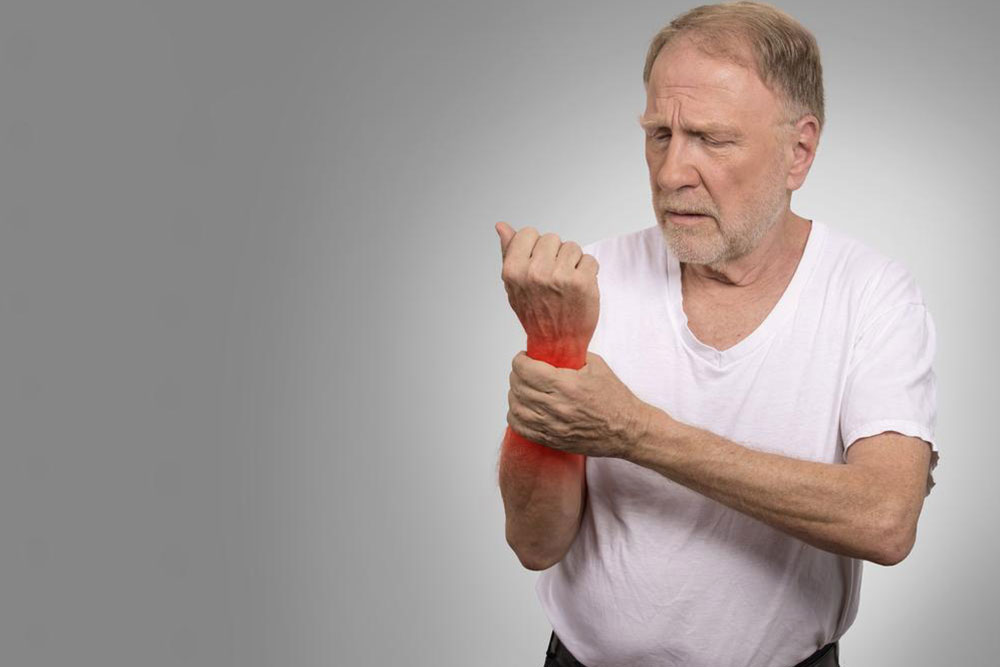
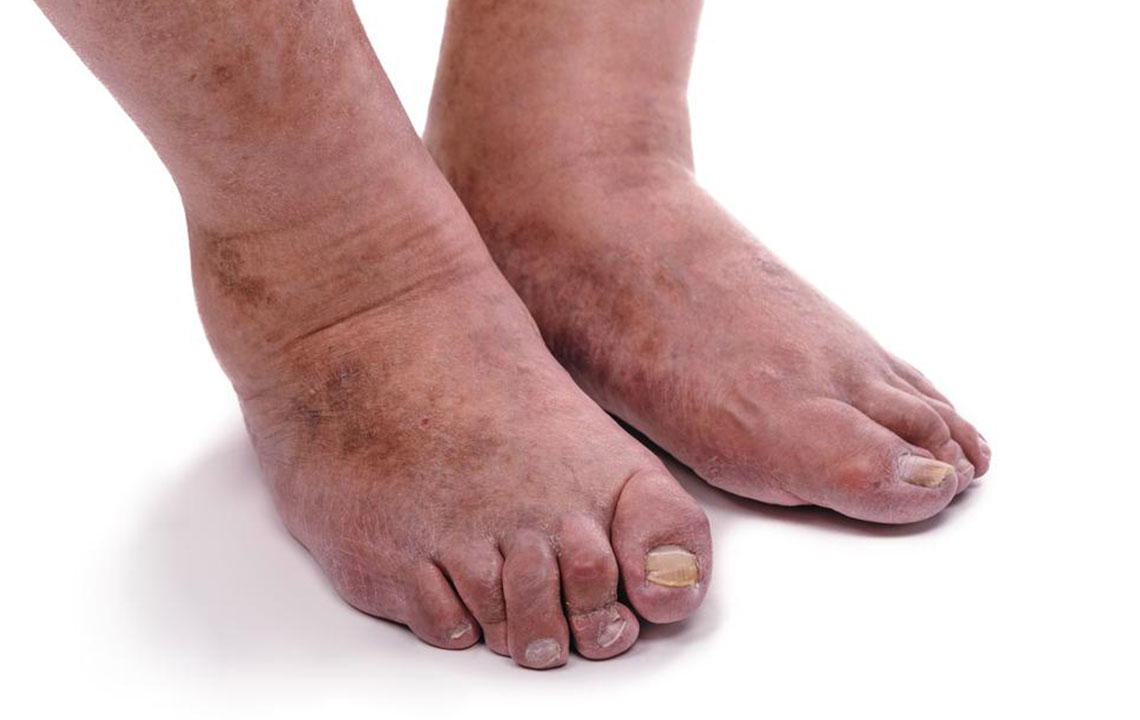
Swelling in the Joints: Visible swelling is a hallmark sign of inflammation. Joints affected by RA often look enlarged and feel warm or firm to the touch. Swelling can limit movement, making simple tasks like opening jars, removing rings, or walking difficult. Early recognition of swelling allows timely management to prevent joint deformities.
Redness and Warmth: Inflammatory processes increase blood flow to the affected areas, leading to redness and warmth over the joint surface. These signs are clear indicators of active inflammation and usually fluctuate with disease activity. Effective treatment often reduces redness and warmth over time.
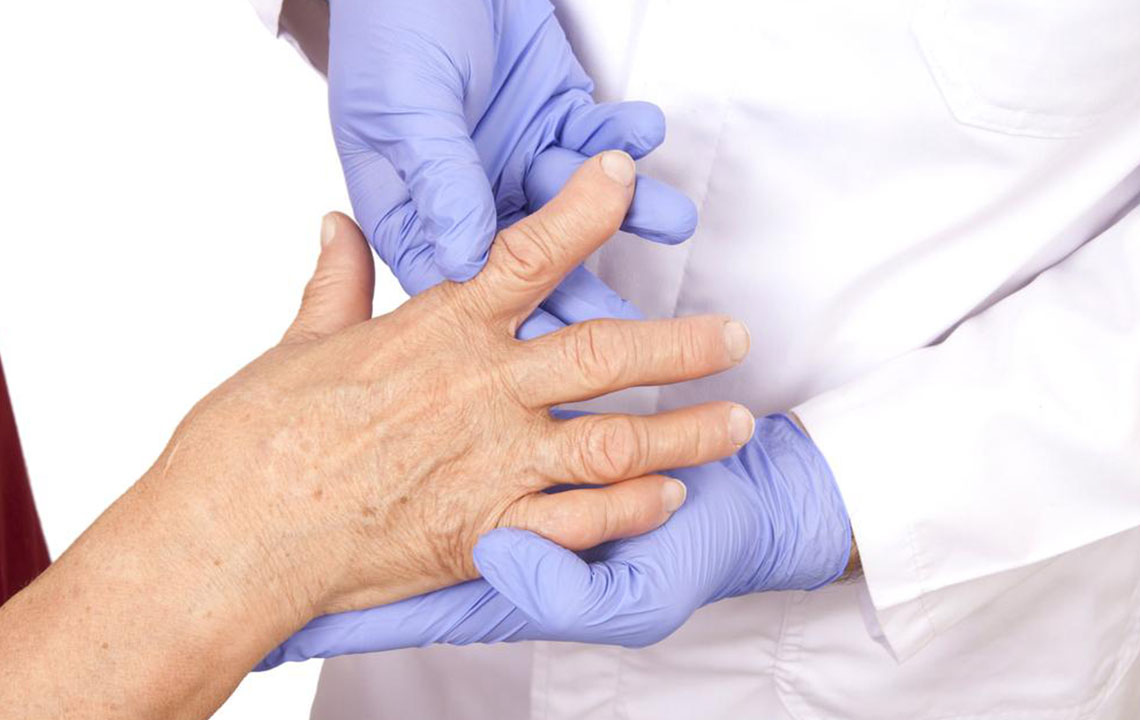
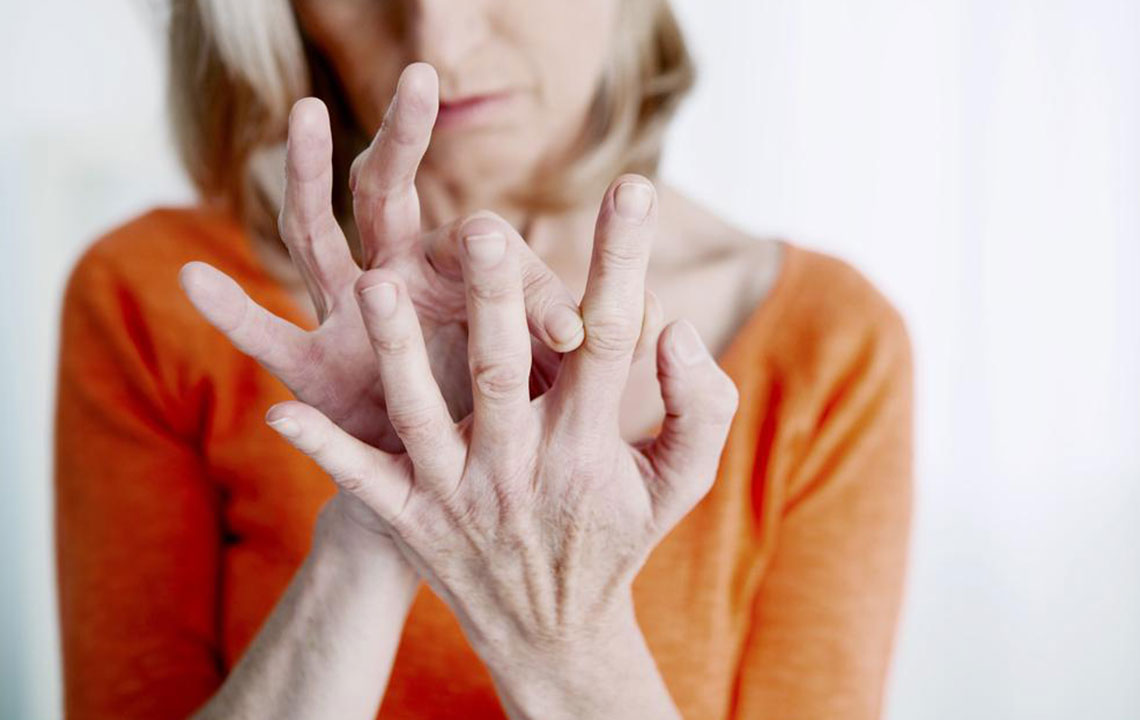
Limited Range of Motion: Swelling, pain, and tissue damage restrict joint mobility. In the early stages, movement may be painful or stiff, especially after periods of inactivity, such as mornings. If untreated, joint stiffness can become chronic and lead to permanent deformities.
Joint Deformation: Over time, persistent inflammation can cause structural changes, including ligament laxity and joint misalignment. Early deformities such as ulnar deviation of the fingers or swan neck deformities are signs of advanced RA and require prompt treatment to halt progression.
Numbness and Tingling: Inflamed blood vessels or nerve impingement due to swelling can cause neurological symptoms like tingling, numbness, or a pins-and-needles sensation, particularly in the extremities such as wrists, elbows, ankles, and toes. Recognizing these neurological signs early helps in diagnosing the disease and managing complications.
If you experience any combination of these symptoms, it is imperative to seek medical advice promptly. Early intervention with medications and lifestyle changes can effectively control inflammation, relieve symptoms, and prevent permanent joint damage. Regular check-ups, blood tests, and imaging studies are essential components of diagnosis and ongoing management.