Early Detection of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Key Symptoms and When to Seek Medical Help
This comprehensive guide explores the early symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, highlighting the importance of early detection. Recognizing signs like joint tenderness, swelling, and morning stiffness can lead to prompt medical intervention, significantly improving outcomes. The article emphasizes the need for awareness and timely diagnosis to prevent joint damage and maintain quality of life. Learn about RA's causes, common symptoms, and the critical steps to take if you suspect early signs, ensuring you get appropriate treatment before irreversible damage occurs.

Early Detection of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Key Symptoms and When to Seek Medical Help
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common and serious autoimmune disorder that predominantly targets the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and potential joint destruction. It affects millions worldwide and can significantly impair daily functioning if not diagnosed and treated promptly. Recognizing the initial signs of RA is essential for early intervention, which can drastically reduce the risk of irreversible joint damage and disability. Although there is currently no cure for RA, timely diagnosis and management are vital for controlling symptoms and maintaining quality of life.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues, resulting in chronic inflammation. Unlike wear-and-tear arthritis, RA often affects joints symmetrically—meaning both sides of the body—such as both wrists or knees. Over time, the persistent inflammation can lead to cartilage erosion, bone damage, and joint deformity if not properly managed. The exact cause of RA remains unknown, but genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors are believed to play roles in its development. Early recognition of symptoms is the cornerstone of effective RA management.
While there is no definitive cure for rheumatoid arthritis, early detection combined with appropriate treatment can significantly improve patient outcomes. Ignoring early warning signs often leads to progressive joint damage, cartilage loss, and decreased mobility. Recognizing key early symptoms such as persistent fatigue, joint tenderness, swelling, stiffness, redness, and mild fever is critical. Consulting a healthcare professional promptly upon noticing these symptoms increases the chances of initiating effective treatment early, which can slow disease progression and preserve joint function.
Common Early Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Persistent Fatigue: Often one of the earliest symptoms, fatigue in RA results from systemic inflammation, anemia, disrupted sleep, or side effects of medication. Patients frequently report feeling unusually tired, which affects their mood and everyday activities.
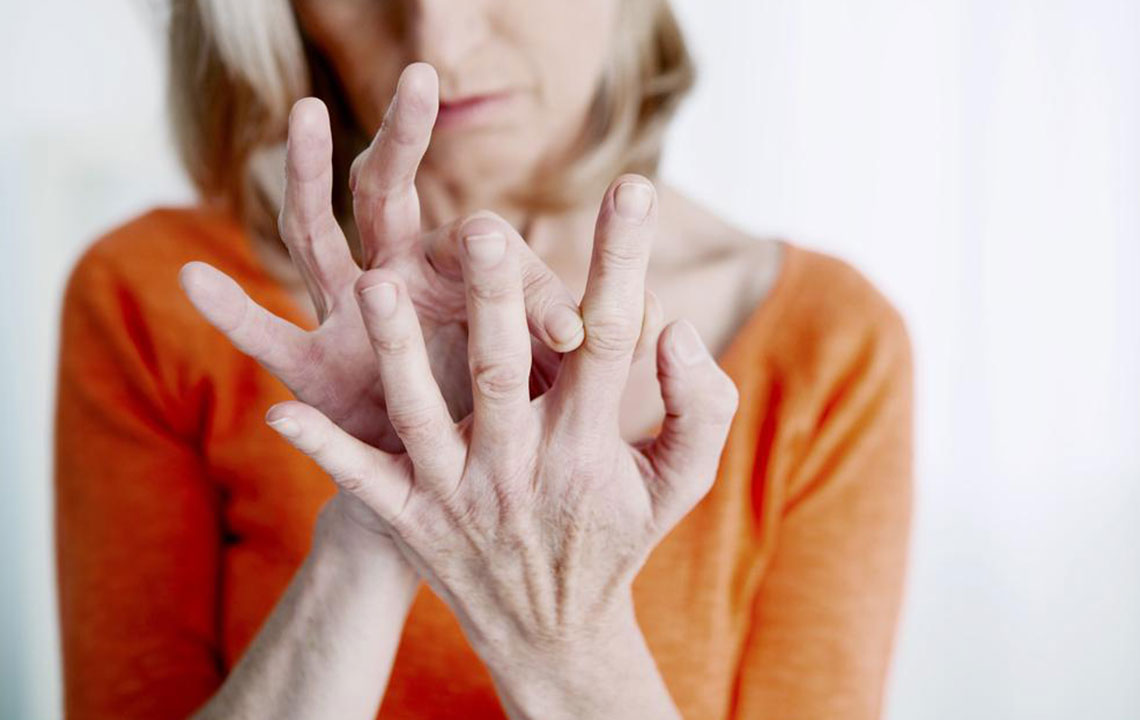
Joint Tenderness: This manifests as sensitivity or pain when applying gentle pressure to affected joints. Tenderness occurs because the joint lining tissues, called synovium, become inflamed and irritated, making the slightest touch uncomfortable.
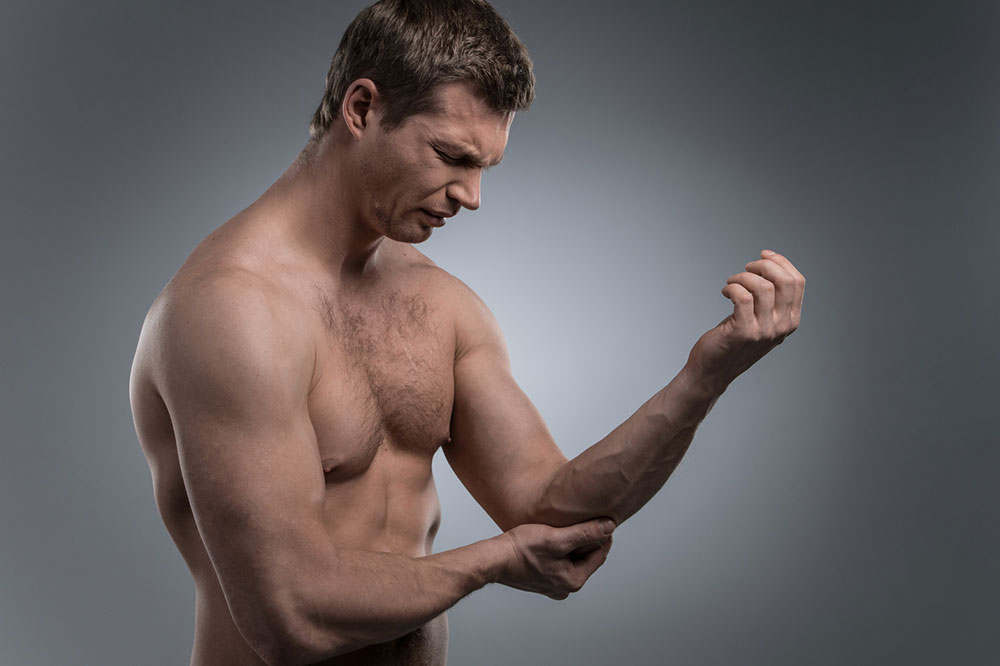
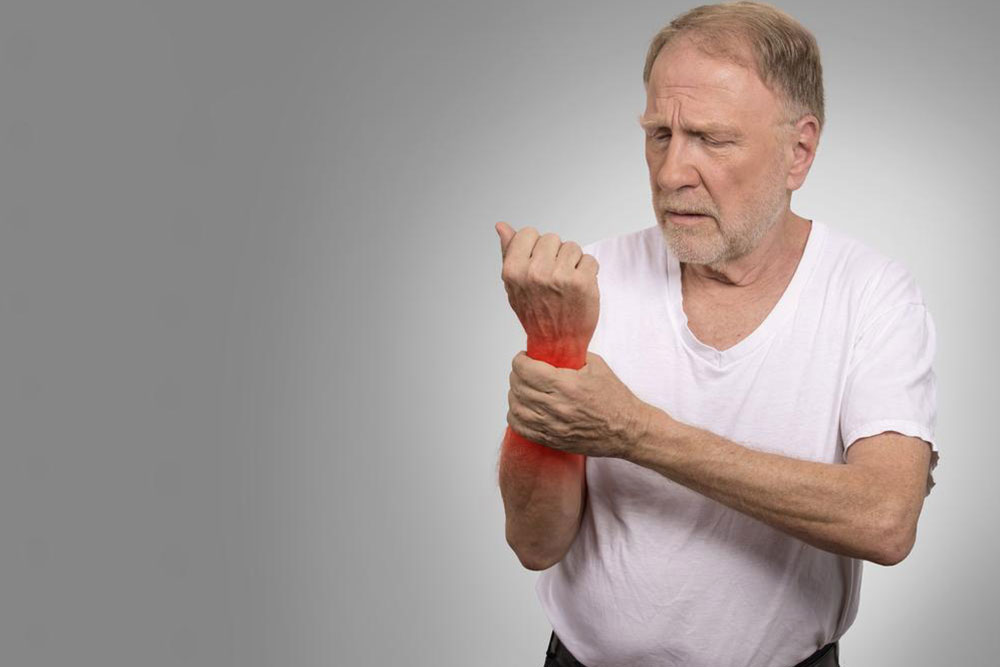
Chronic Joint Pain: Continuous joint pain, especially during or after activity, indicates ongoing inflammation and tissue damage. Pain may be worse in the mornings or after periods of inactivity, then gradually improve with movement.
Swelling: Swollen joints are a hallmark feature, caused by excess synovial fluid and inflammatory cell infiltration. Swelling can be subtle or prominent, sometimes detectable by the patient's observation or through physical examination.
Morning Stiffness: Experiencing stiffness in the joints that lasts longer than 30 minutes after waking is a classic early sign. This stiffness results from joint inflammation and edema, often improving with movement but persisting for weeks or months if untreated.
Redness and Warmth: The affected joints may appear reddish and feel warm due to increased blood flow and inflammation.
Mild Fever: Some patients experience slight fever or chills caused by systemic inflammatory responses, which may accompany joint symptoms.
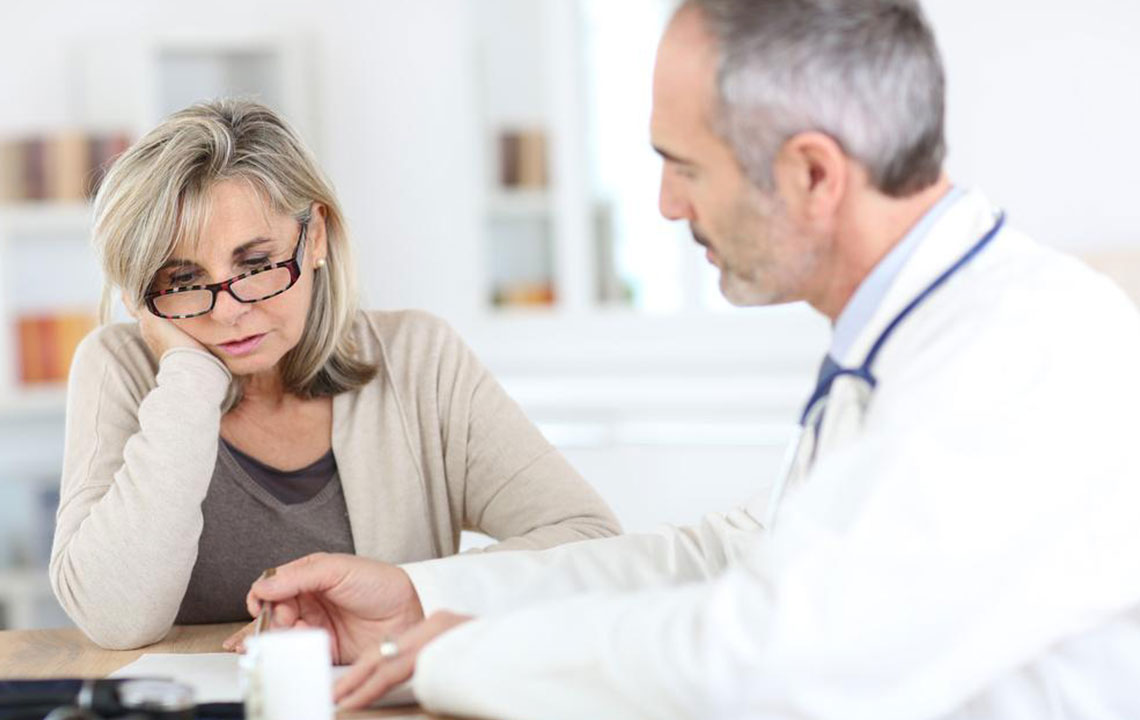
Recognizing these early indicators and seeking medical advice promptly can make a significant difference. Early diagnosis allows for tailored treatment plans that can effectively control inflammation, reduce symptoms, and prevent joint deformities. During consultation, healthcare providers may perform blood tests (such as rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP antibodies), imaging studies, and physical examinations to confirm the diagnosis and assess disease severity.
In conclusion, staying vigilant for initial signs of rheumatoid arthritis facilitates earlier intervention and better long-term outcomes. While RA remains a chronic condition without a cure, modern treatments—such as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologics, and lifestyle adjustments—offer hope for managing symptoms and maintaining a functional, pain-free life. Recognizing symptoms early is the key to preserving joint health and achieving optimal disease control.