Comprehensive Guide to Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores eczema's causes, symptoms, and management strategies. It covers hereditary factors, environmental triggers, and various treatment options including home remedies and medical therapies. By understanding eczema's complexities, individuals can better control flare-ups, reduce discomfort, and improve skin health through proactive skincare practices.

Comprehensive Guide to Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a prevalent chronic skin condition that affects millions worldwide. Despite its widespread nature, many individuals remain unaware of its causes, symptoms, and effective ways to manage and control flare-ups. This extensive guide aims to provide in-depth insights into eczema, covering its types, causes, triggers, symptoms, and proven treatment options. Whether you or your loved ones are affected by eczema, understanding this condition can empower you to take proactive steps toward healthier skin and improved quality of life.
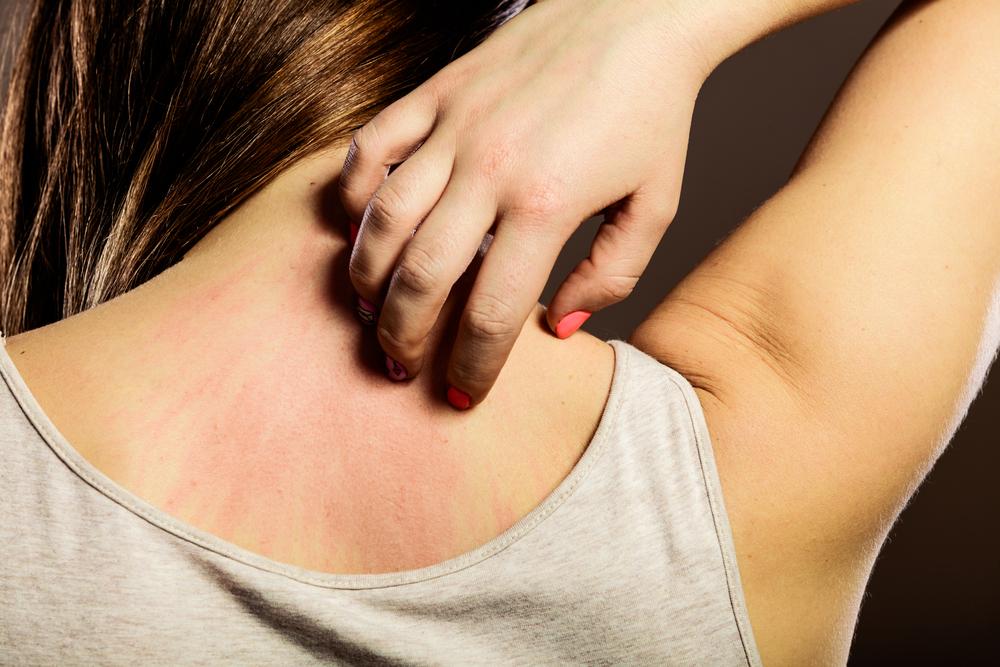
Eczema is characterized by inflammation, redness, intense itching, and skin irritation, which can severely disrupt daily activities, sleep, and emotional well-being. Although it is not contagious, eczema can cause discomfort and often fluctuates in severity over time. Recognizing its symptoms early and adopting appropriate management strategies can significantly reduce flare-ups and promote skin healing.
Understanding the Causes of Eczema Eczema's development is influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It often runs in families, indicating a hereditary component. Individuals with a family history of eczema, asthma, or allergies are at higher risk of developing the condition themselves. The genetic predisposition affects the skin's ability to retain moisture and defend against irritants, leading to increased vulnerability.
External factors play a significant role in triggering or worsening eczema symptoms. Common triggers include exposure to irritants and allergens such as synthetic fabrics, jewelry containing nickel, pollen, microbes, certain foods, and harsh soaps. Skin irritation can also result from prolonged contact with wool or other rough textiles. Environmental influences are equally impactful, with extreme weather conditions like cold, dry air or hot, humid climates aggravating skin dryness and inflammation. Sudden temperature changes, humidity fluctuations, and sweating can also provoke flare-ups, thereby making the management of triggers essential for controlling eczema.
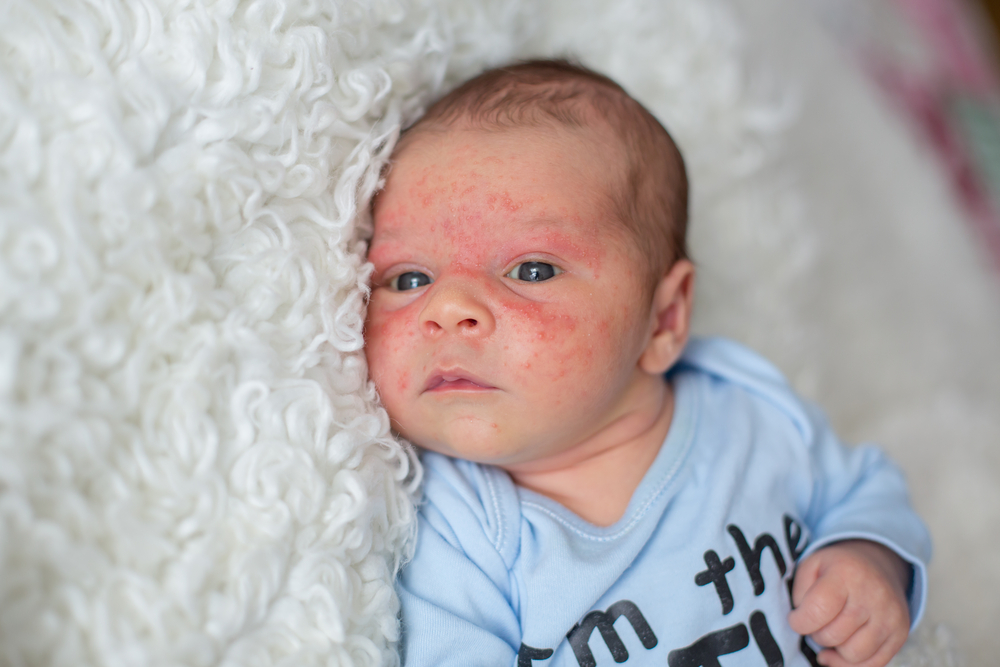
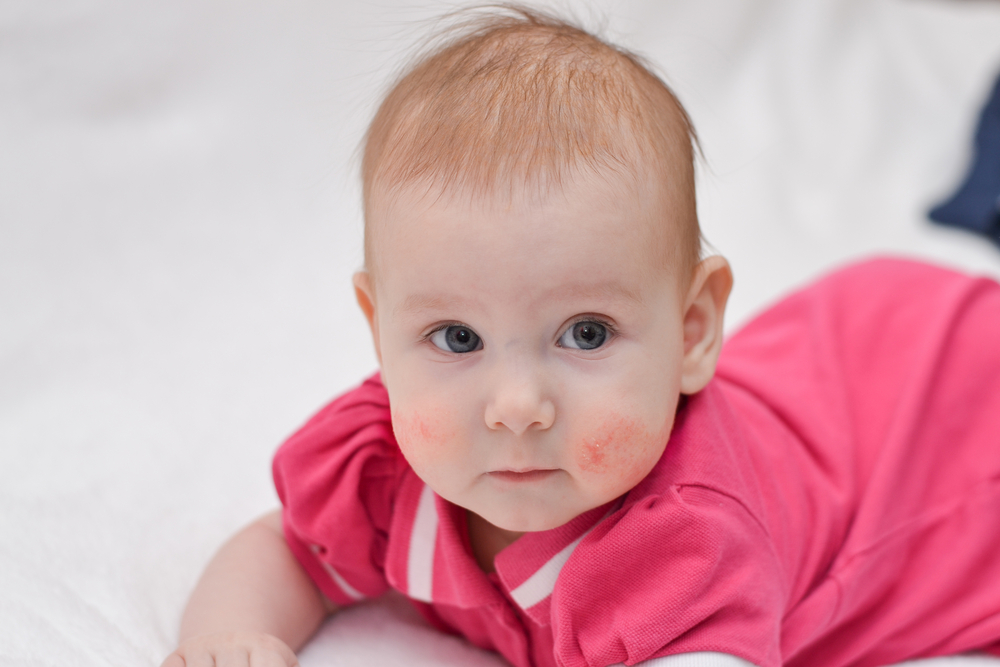
Recognizing the Symptoms of Eczema Eczema manifests differently across age groups, with varied symptoms that require careful observation. In infants under two years old, symptoms typically include red, inflamed patches on the cheeks, scalp, and neck, often accompanied by oozing and intense itching. These symptoms can interfere with sleep and feeding, and scratching may lead to secondary bacterial infections.
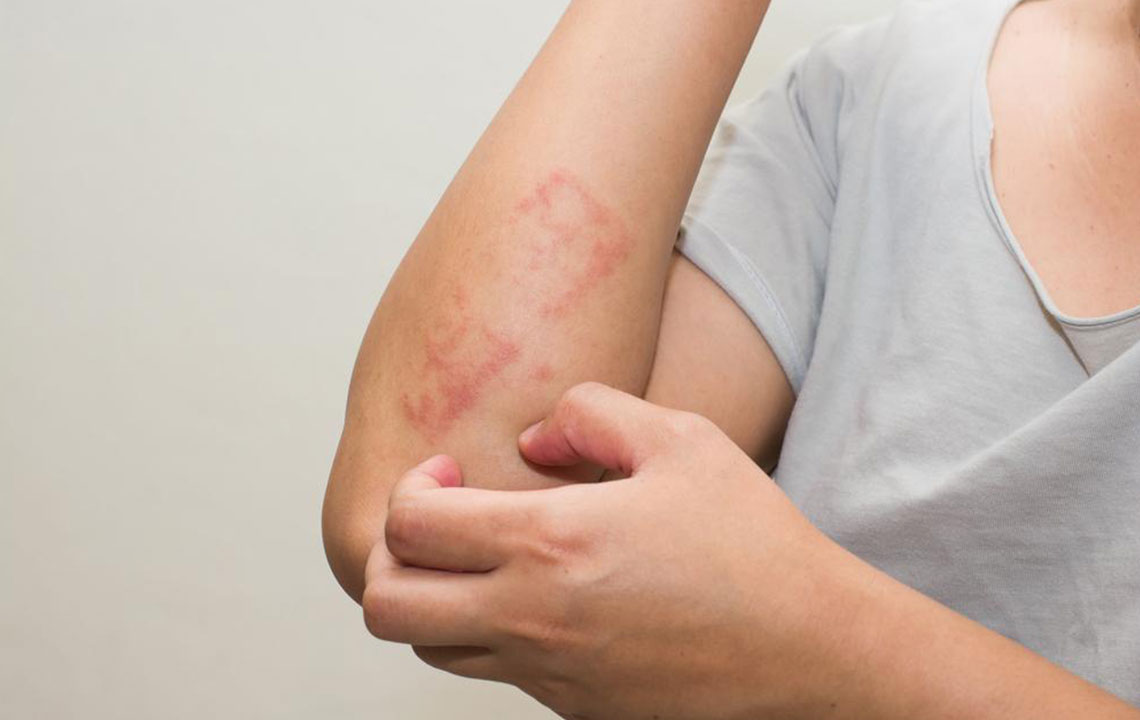
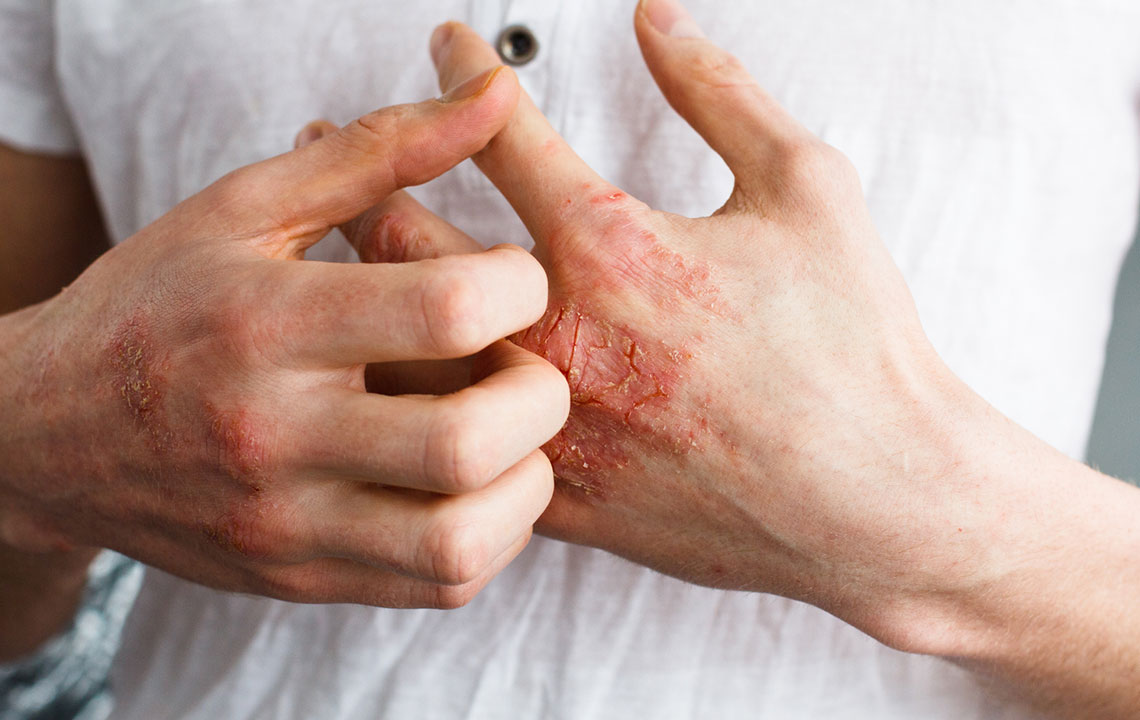
In older children and adults, eczema commonly appears as dry, cracked, and inflamed skin on areas such as the elbows, knees, wrists, ankles, neck, and creases of the arms and legs. Persistent scratching can hyperpigment or darken the affected skin areas and cause skin thickening, a condition known as lichenification. Other distinctive types of eczema include:
Atopic Dermatitis: Characterized by itchy, inflamed, and thickened skin, primarily affecting the flexural areas like elbows and knees.
Contact Dermatitis: Results from direct contact with irritants, leading to redness, burning sensation, blisters, and crusts.
Dyshidrotic Eczema: Presents as small, itchy blisters on palms, soles, and fingers, often resulting in peeling skin.
Hand Eczema: Manifested as dry, cracked, or blistered hands, often due to repeated exposure to irritants.
Neurodermatitis: Shows as thickened patches that are intensely itchy, usually during periods of rest.
Nummular Eczema: Features coin-shaped patches that are itchy and covered with scales.
Effective Management and Treatment Options for Eczema Proper management of eczema hinges on an accurate identification of triggers and a tailored approach to skincare. Home remedies and lifestyle modifications can significantly alleviate symptoms and reduce the frequency of flare-ups.
Basic home strategies include taking lukewarm baths infused with gentle moisturizers or colloidal oatmeal, avoiding hot water that can dry out the skin further, and gently patting the skin dry instead of rubbing. Applying fragrance-free emollients immediately after bathing helps lock in moisture, creating a protective barrier. Wearing loose, breathable clothing made of soft fabrics such as cotton minimizes skin irritation, while avoiding irritants like synthetic fibers, harsh chemicals, and known allergens is crucial.
In addition to lifestyle changes, medical treatments are often necessary for managing severe eczema. Topical corticosteroids are the mainstay for reducing inflammation during flare-ups. For persistent or severe cases, healthcare professionals might prescribe antihistamines to control itching, antifungal creams if infections occur, or immunosuppressants for resistant cases. Newer therapies like personalized biologic drugs are emerging as effective options for chronic and severe eczema.
It is vital to consult a healthcare professional before starting any treatment. They can recommend the most suitable options based on individual conditions, age, and severity, ensuring safe and effective management. Regular follow-up and skin care routines are key to preventing future flare-ups and maintaining healthy skin.
In conclusion, eczema is a complex but manageable skin condition. With the right knowledge, trigger avoidance, proper skincare, and medical intervention, individuals can significantly minimize symptoms, prevent complications, and enjoy healthier, itch-free skin. Living with eczema demands ongoing attention and care, but modern treatments and skincare strategies offer hope for effective management and improved quality of life.