Comprehensive Guide to Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition affecting many individuals. This comprehensive guide covers the causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies, including medications, skincare routines, lifestyle changes, and environmental precautions. Early diagnosis and personalized treatment are crucial to controlling flare-ups and improving quality of life. While no permanent cure exists, modern advancements enable effective symptom management, helping sufferers stay comfortable and healthy. Learn how to identify triggers and implement holistic care approaches for long-term relief.
Comprehensive Guide to Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
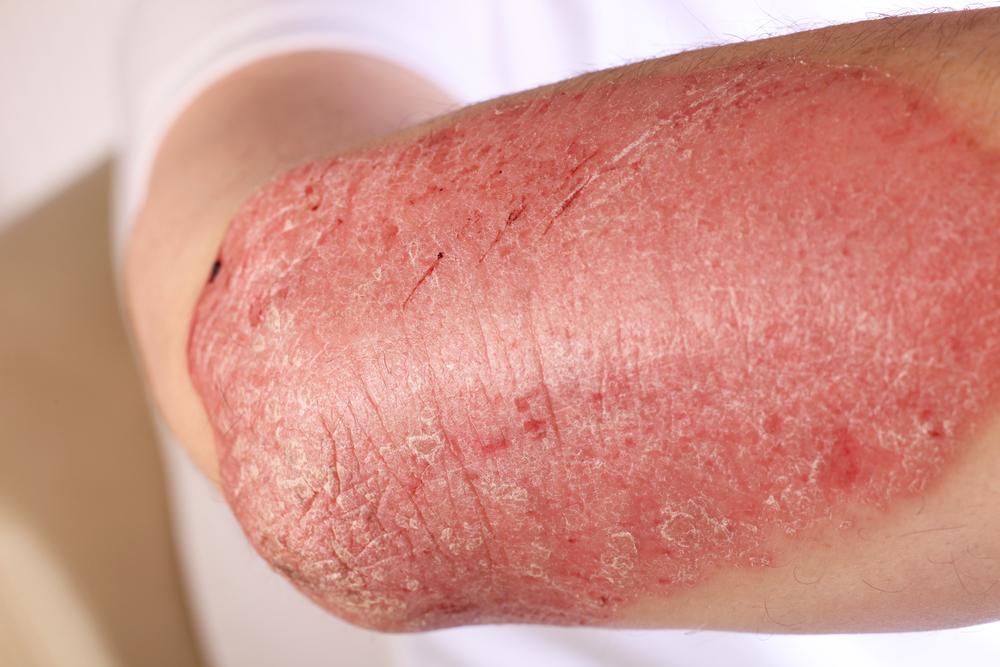
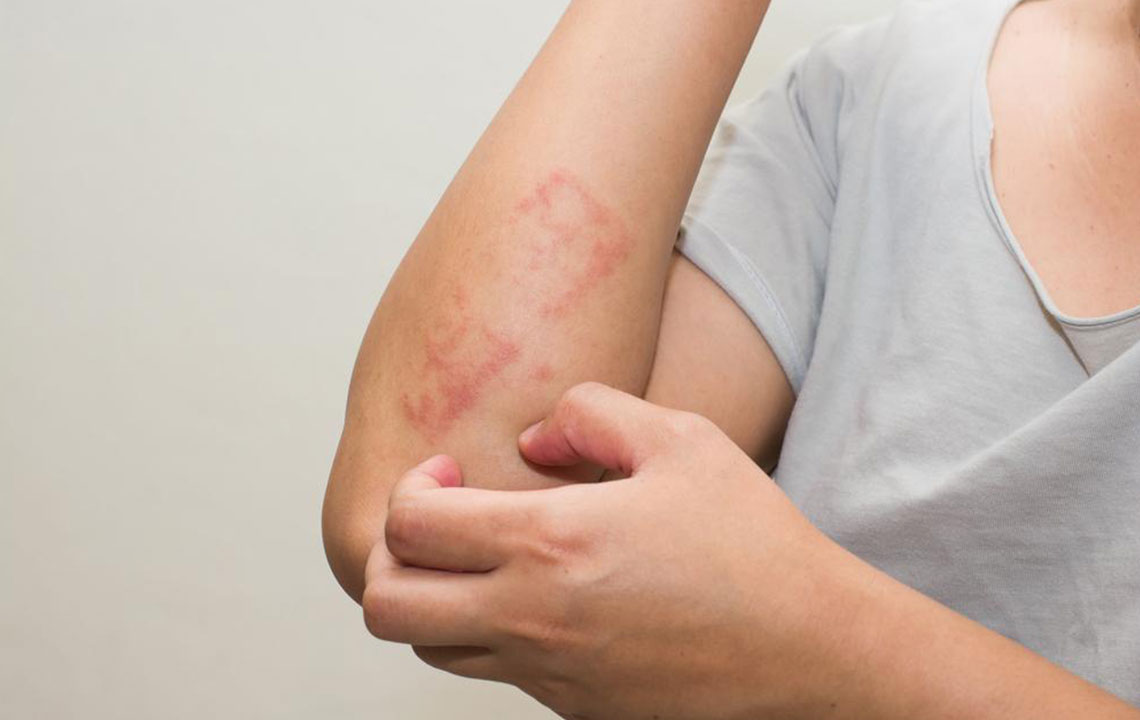
Are you experiencing persistent patches of itchy, inflamed skin that seem to come and go without clear reason? If yes, you might be dealing with eczema, also known scientifically as atopic dermatitis. Eczema is a prevalent skin condition that affects millions worldwide, often manifesting with dry, irritated skin that can fluctuate in severity over time. Recognizing the signs early and understanding the underlying causes can significantly improve quality of life through effective management and treatment options.
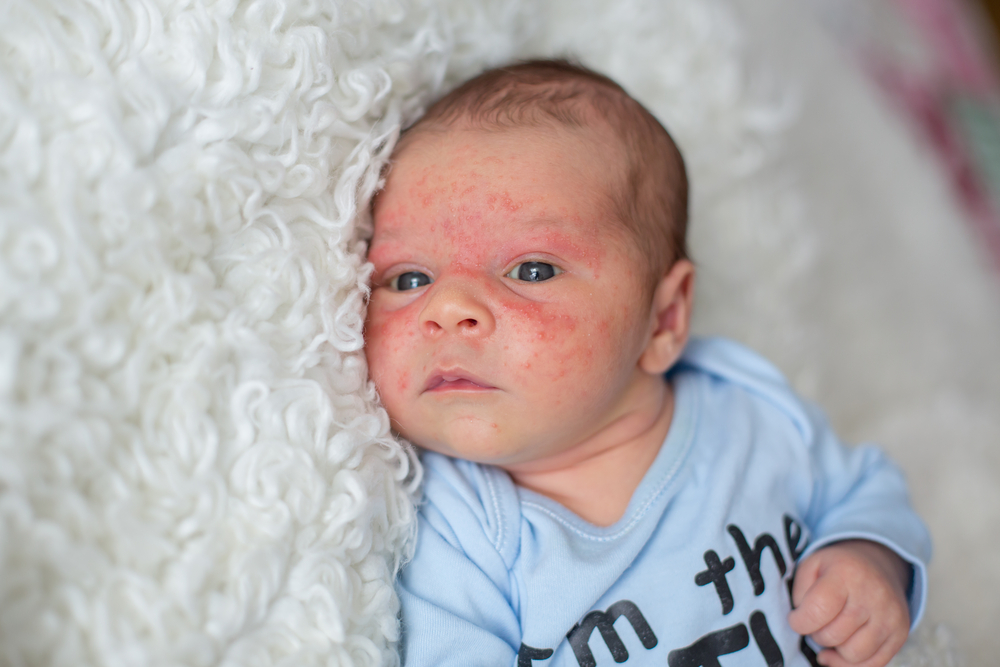
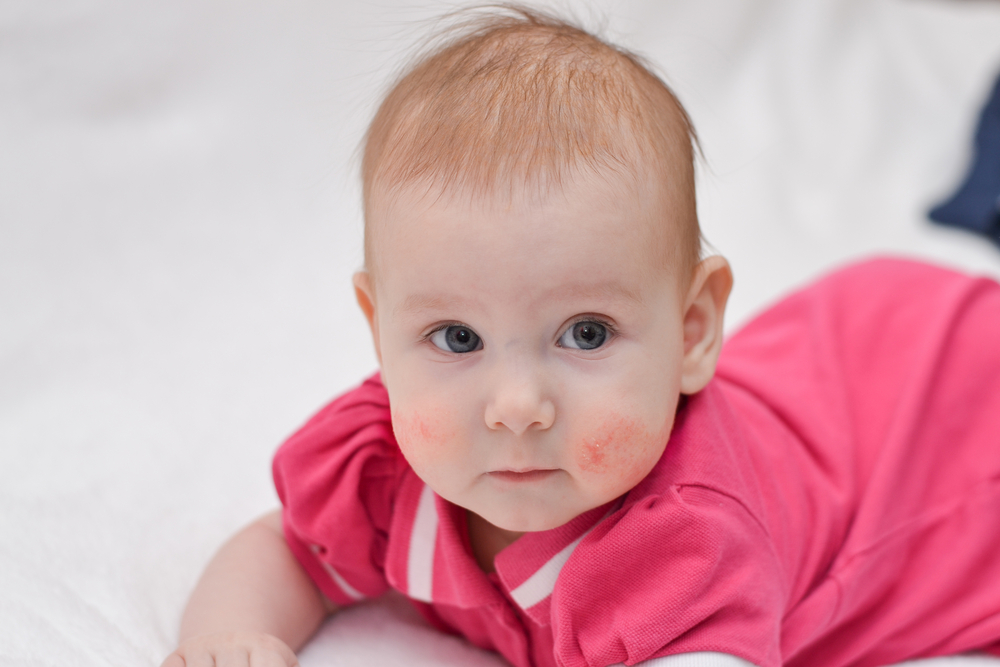
This skin condition can impact individuals of all ages but is particularly common among children and those with other allergic conditions. The lesions associated with eczema typically appear as dry, flaky patches and may be accompanied by itching, redness, and swelling—symptoms that often worsen with environmental triggers or stress. Although eczema itself is not contagious, it can lead to skin infections if scratched excessively or if broken skin becomes infected.
The origins of eczema remain complex and multifactorial. While no definitive cause has been identified, research suggests that a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors contribute to the development and exacerbation of this condition. Understanding these factors can now aid individuals in adopting better prevention and management strategies.
Several primary factors are associated with eczema:
Genetics: Family history plays a significant role; individuals with relatives who have eczema, allergies, or asthma are at higher risk.
Environmental Exposure: Factors such as dust, pollen, pet dander, or mold can act as triggers for flare-ups. Exposure to irritants like harsh soaps, chemicals, or fragrances can further aggravate symptoms.
Dietary Sensitivities: Certain foods, notably wheat, dairy, or nuts, might trigger or worsen eczema symptoms in some individuals.
Climate and Humidity: Dry, cold, or windy environments tend to dry out the skin, making it more susceptible to irritation. Conversely, humid weather can sometimes worsen symptoms for others.
Water Quality: Hard water, containing high levels of calcium and magnesium minerals, can strip the skin of natural oils, leading to dryness and increased irritation.
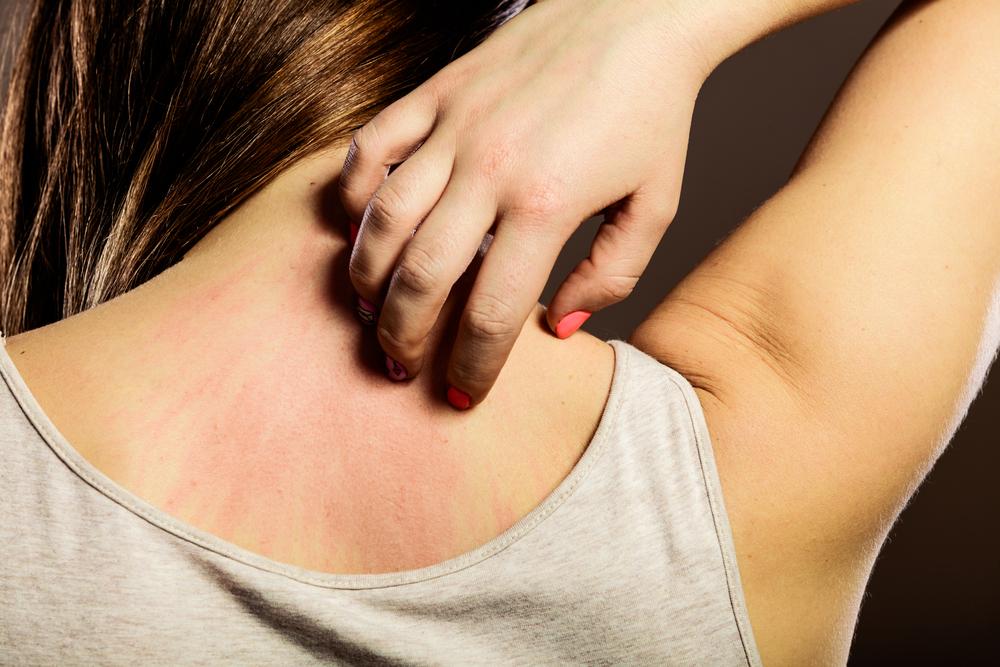
Recognizing the symptoms early is essential for managing eczema effectively. Typical signs include persistent dry, flaky skin, redness, swelling, and intense itching. Scratching not only causes discomfort but can also damage the skin barrier, leading to infections or chronic skin changes. Diagnosis is primarily based on clinical examination, although allergy testing or skin biopsies may be utilized to identify specific triggers or differentiate eczema from other dermatological conditions.
While a permanent cure for eczema still eludes scientists, many effective treatments and management strategies have been developed to control symptoms and prevent flare-ups. The goal is to restore skin barrier function, reduce inflammation, and avoid triggers.
Effective Treatment Options for Eczema
Management of eczema involves a comprehensive approach combining medications, skincare routines, lifestyle adjustments, and environmental modifications:
Medications: Topical corticosteroids remain the mainstay for reducing inflammation during flare-ups. For more resistant cases, non-steroidal options like pimecrolimus or crisaborole can be prescribed. Recent advances include biologic drugs like dupilumab, which target specific immune pathways and can be highly effective for severe cases.
Phototherapy: Controlled ultraviolet (UV) light exposure can help suppress immune responses in the skin, decreasing inflammation over the long term. This treatment requires supervision by a dermatologist due to potential side effects.
Systemic Therapies: For extensive or refractory eczema, immunosuppressants such as ciclosporin or methotrexate might be recommended under careful medical supervision.
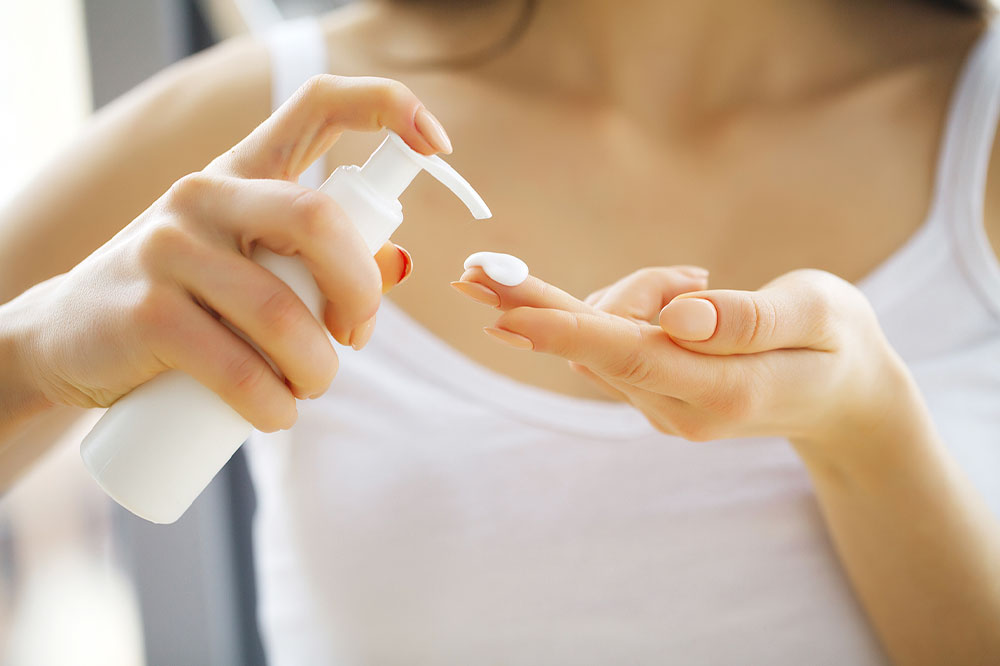
Skincare and Lifestyle: Daily use of gentle, fragrance-free moisturizers helps maintain hydration and skin barrier integrity. Avoiding harsh soaps, hot water, and irritants is crucial. In addition, wearing soft, breathable fabrics like cotton, staying well-hydrated, and maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins (especially vitamin D) can support skin health.
Stress Management and Behavioral Strategies: Since stress is a known trigger, practicing relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or mindfulness can reduce flare-ups. Recognizing early signs of exacerbation and acting promptly is vital for effective control.
Environmental Precautions: Protecting skin from extreme weather conditions by wearing appropriate clothing, using humidifiers during dry seasons, and avoiding known allergens can significantly reduce incidences of flare-ups.
Holistic Approach to Eczema Management
Effective control of eczema also involves managing associated allergies, such as asthma and hay fever, since these conditions share common immune system dysfunctions. Regular follow-up with dermatologists and allergists helps tailor treatment plans and makes necessary adjustments.
Children with eczema benefit greatly from early intervention to prevent the development of chronic skin issues or related allergic conditions. Early management also helps reduce psychological impacts, such as skin appearance concerns and emotional distress.
In conclusion, while eczema can be a challenging condition, modern medical advancements provide numerous options for effective management. Recognizing early signs, avoiding triggers, following personalized treatment plans, and maintaining healthy lifestyle habits are key to living comfortably with eczema. Always consult healthcare professionals for proper diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies tailored specifically to your condition.