Comprehensive Dietary Strategies to Manage Eczema: Foods to Include and Avoid
This comprehensive guide provides detailed dietary strategies for managing eczema, highlighting foods to include such as quercetin-rich produce, probiotics, and omega-3 fatty acids, while identifying common triggers like dairy, eggs, and gluten. Tailoring an eczema-friendly diet can help reduce flare-ups and improve skin health through inflammation control and immune support. Always consult healthcare professionals before making significant dietary adjustments for personalized eczema management.

Effective Dietary Approaches for Eczema Relief
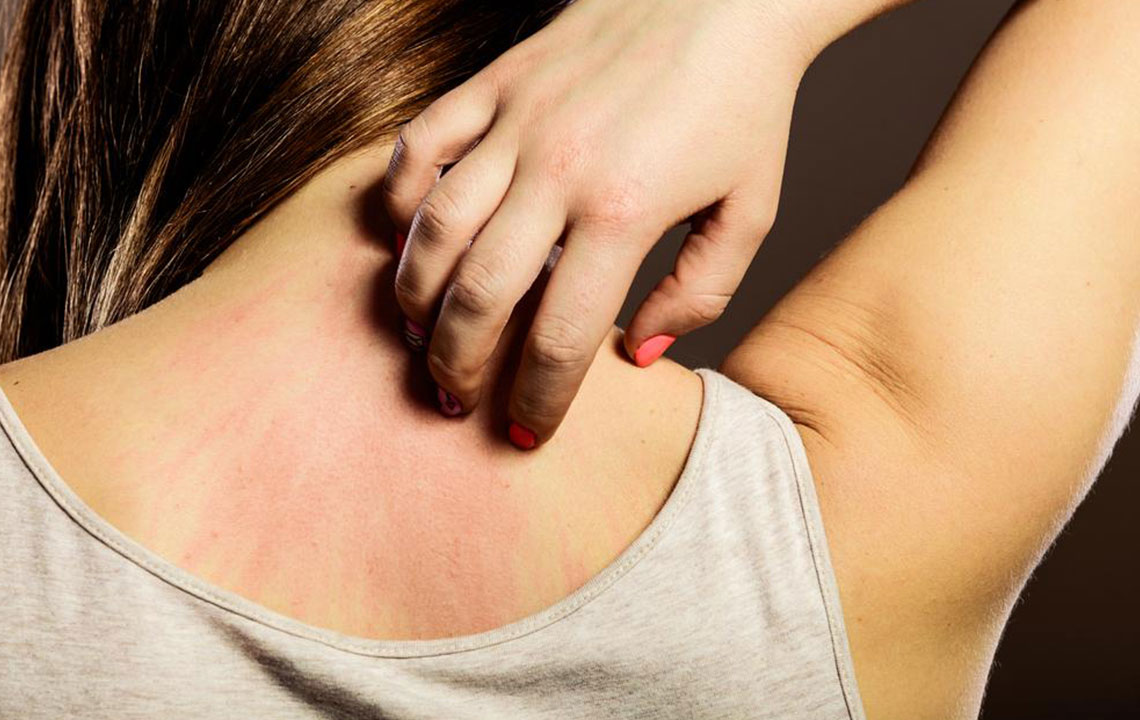
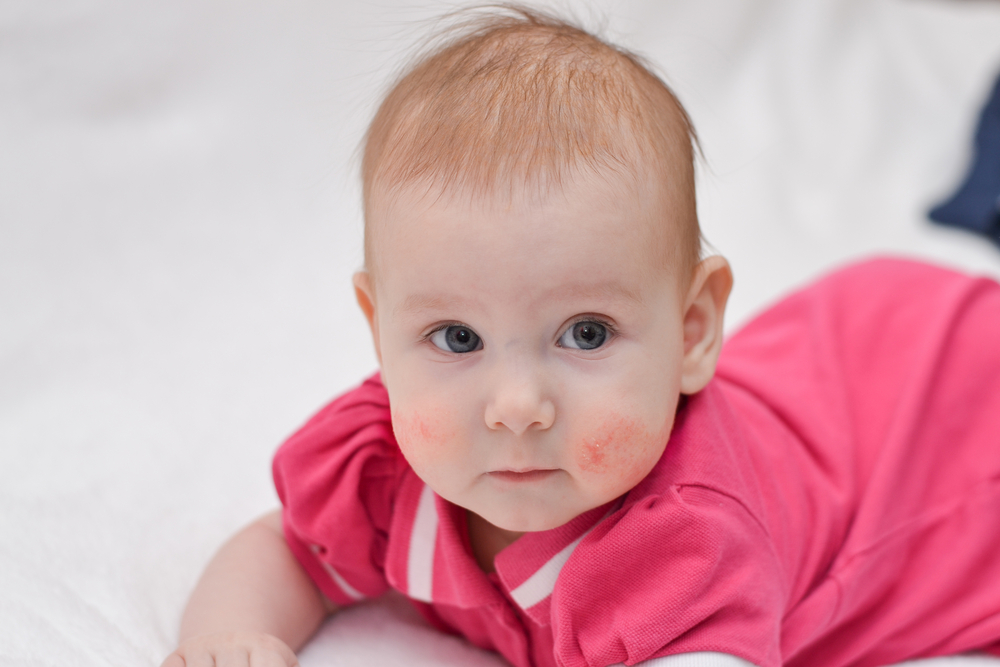
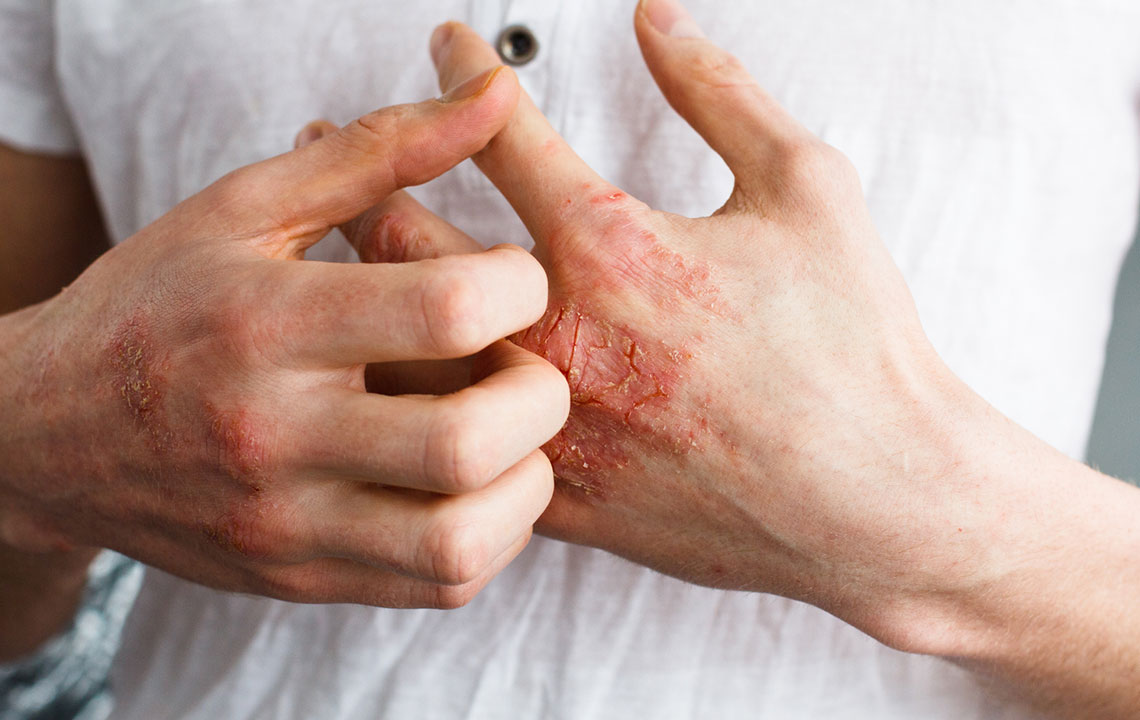
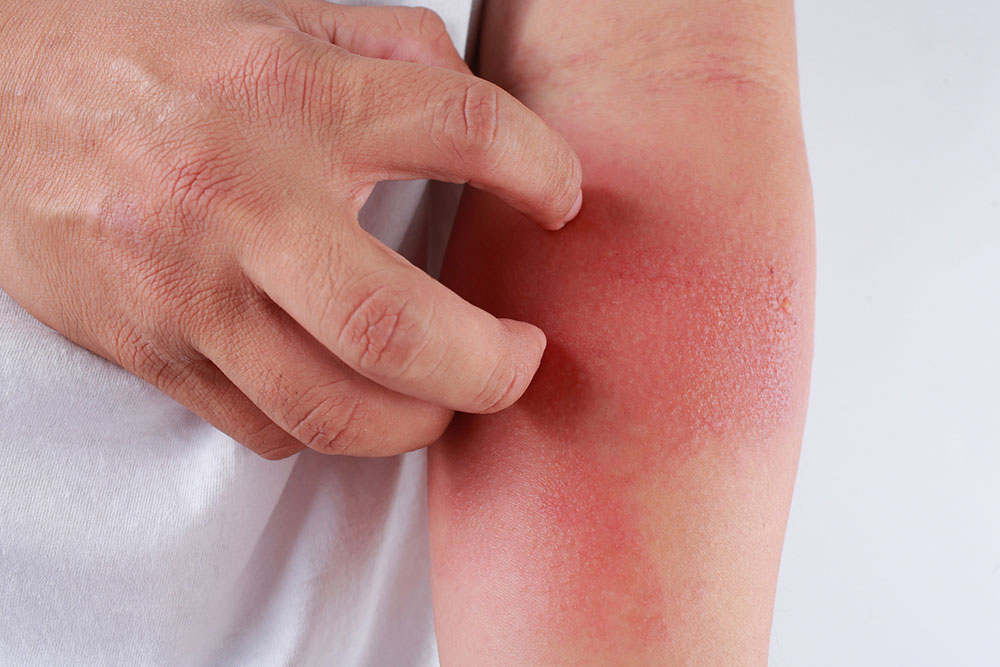
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that affects millions worldwide. Managing its symptoms requires a holistic approach that includes proper skincare, environmental control, and notably, mindful dietary habits. Diet plays a crucial role in either triggering flare-ups or helping to reduce inflammation and soothe irritated skin. An estimated 31.6 million people in the United States, representing approximately 10.1% of the population, are affected by eczema, making it a common concern across age groups.
Understanding the influence of diet on eczema is vital for creating an effective management plan. Certain foods can exacerbate the condition, while others may have protective anti-inflammatory properties that alleviate symptoms. This comprehensive guide explores which foods to prioritize and which to avoid, helping individuals tailor a personalized nutrition strategy for better skin health.
Incorporating Anti-Inflammatory Foods
To manage eczema effectively, focus on dietary choices that help reduce inflammation and strengthen the immune response. Here's a detailed look at specific foods beneficial for eczema sufferers:
Quercetin-rich fruits and vegetables: Quercetin, a natural plant flavonoid, acts as a potent antihistamine and antioxidant. Including a colorful array of fruits and vegetables in your diet can help mitigate allergic reactions and decrease the severity of flare-ups. Recommended options include apples, blueberries, cherries, and a variety of leafy greens like spinach, kale, and broccoli.
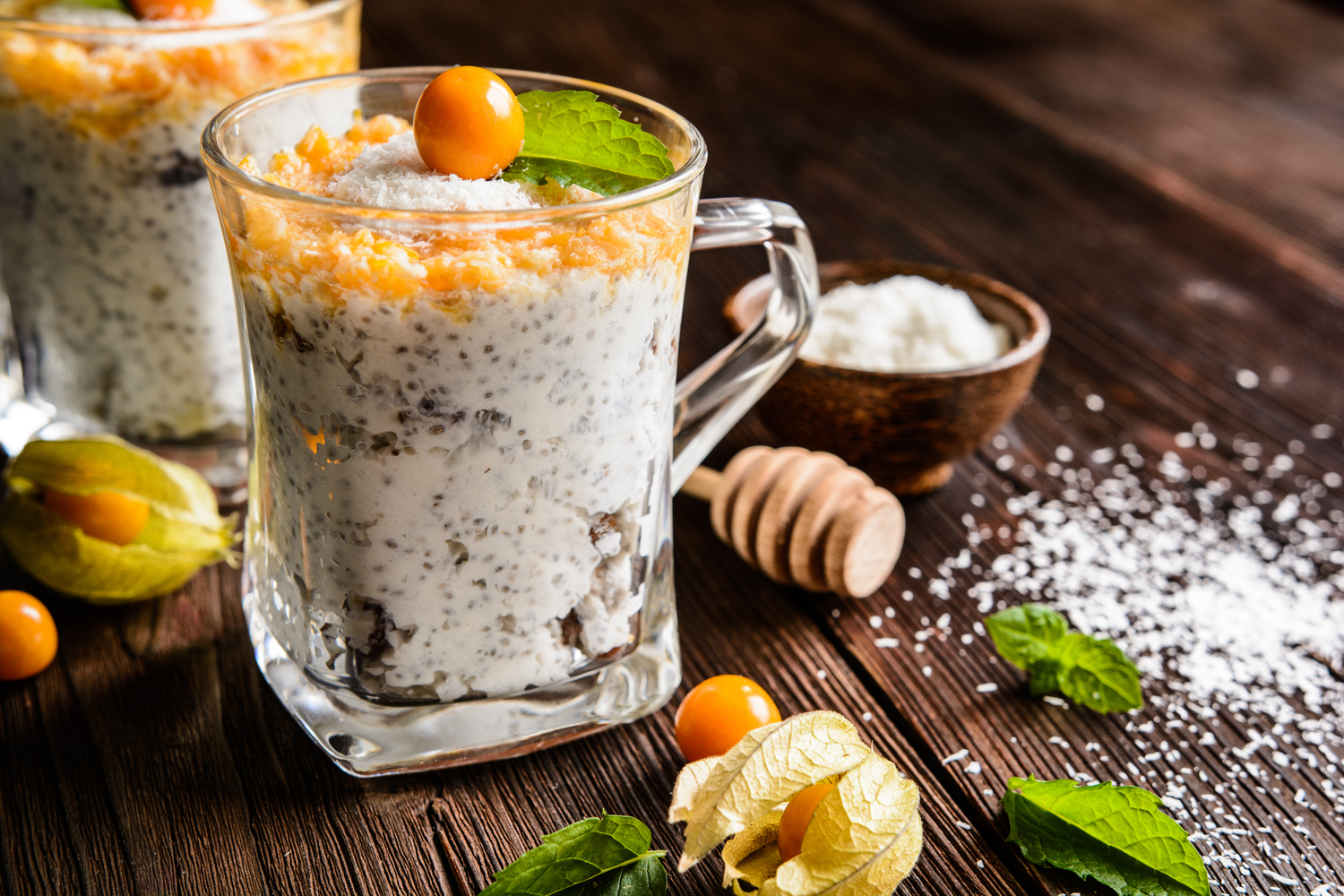
Probiotic-rich foods: Maintaining a healthy gut flora is essential for immune regulation and can potentially reduce eczema severity. Incorporate fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, miso, sauerkraut, kimchi, and sourdough bread. These contain beneficial bacteria that support gut health and may help decrease allergic responses and skin inflammation.
Omega-3 fatty acids from fatty fish: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, herring, and sardines are rich sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which are renowned for their anti-inflammatory effects. Regular consumption can help soothe irritated skin and reduce flare-ups. Fish oil supplements can also be considered after consulting with a healthcare professional.
Foods to Avoid for Eczema Management
Some dietary items have been found to aggravate eczema symptoms in certain individuals. The reaction can vary depending on personal sensitivities, so a systematic elimination diet can help identify triggers. Symptoms often appear within 6 to 24 hours after consuming problematic foods. Common culprits include:
Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt
Eggs
Citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits
Soy-based foods
Wheat and gluten-containing grains
Spices like cinnamon, cloves, and vanilla
Tomatoes and tomato-based products
Nuts and nut products
Implementing an elimination diet involves removing suspected foods one at a time and monitoring skin reactions over several weeks. If symptoms worsen upon reintroduction, that food should be permanently avoided. Conversely, if no reaction occurs, it's unlikely to be a trigger. For dyshidrotic eczema affecting the hands and feet, paying attention to nickel-rich foods such as canned meats, chocolate, beans, black tea, lentils, peas, soybeans, seeds, and shellfish is also recommended. Always seek guidance from a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes to ensure nutritional adequacy and safety.
In conclusion, diet is a powerful tool in managing eczema. By focusing on anti-inflammatory foods and avoiding known triggers, individuals can significantly reduce flare-ups and improve overall skin health. Personalization of dietary plans through careful observation and professional guidance remains the key to effective eczema management.