Comprehensive Guide to Eczema: Types, Symptoms, and Management Tips
This comprehensive article delves into various types of eczema, highlighting key symptoms, potential complications, and effective management strategies. It emphasizes the importance of visual aids for accurate diagnosis and offers insights into personalized treatment options to improve skin health and quality of life.

In-Depth Understanding of Eczema: Types, Symptoms, and Effective Management
Eczema refers to a broad range of chronic skin conditions characterized by inflammation, redness, dryness, scaling, and itchiness. These skin ailments impact millions of people worldwide, often leading to discomfort and skin damage if left unmanaged. Recognizing the different types of eczema is vital for appropriate treatment and relief. Accurate diagnosis can be challenging without visual cues, hence, the importance of images and detailed descriptions to differentiate among variants. Because eczema is a long-term condition, consistent care, lifestyle adjustments, and medical interventions are crucial for maintaining skin health and preventing flare-ups.
What are the primary types of eczema?
Understanding the distinct characteristics of each eczema type helps in effective management and treatment. Visual references, such as high-quality images, assist both patients and healthcare providers in identifying the specific form.
Atopic Dermatitis
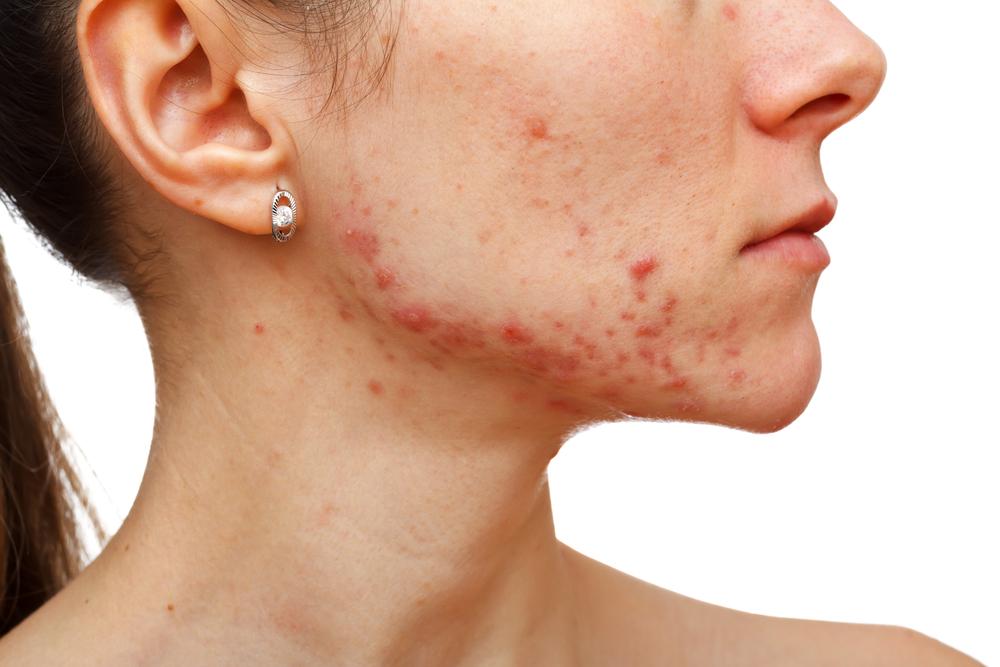
The most common form, predominantly affecting children but also seen in adults. It often runs in families with a history of allergies, asthma, or hay fever. Rashes predominantly appear on the cheeks, elbows, knees, neck, and ankles, exhibiting dryness, redness, and persistent itching. Atopic dermatitis tends to flare periodically, often triggered by environmental factors, stress, or allergens.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
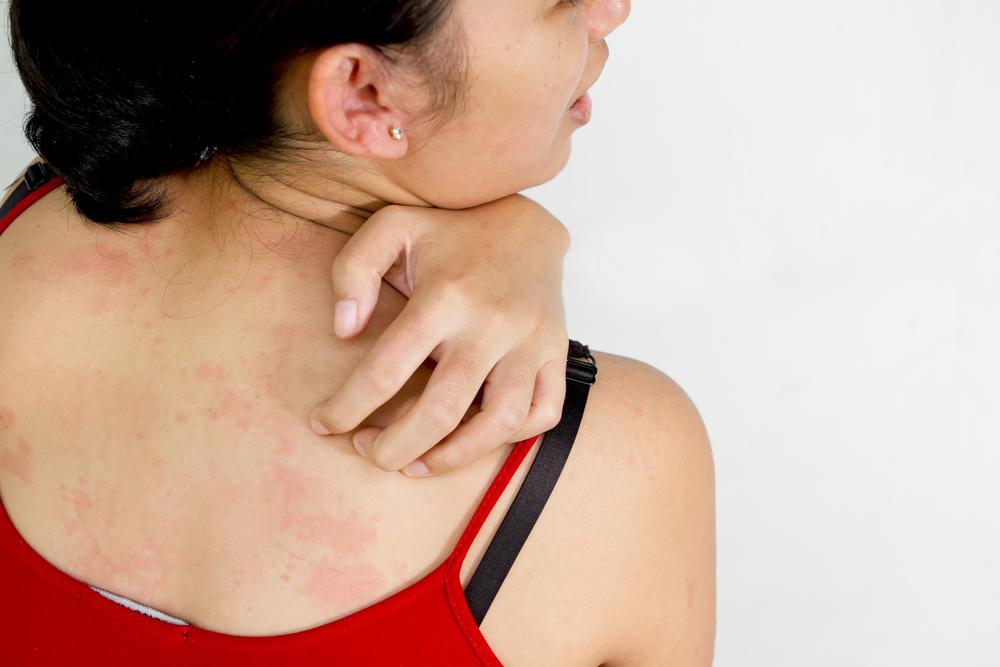
This type develops following repeated exposure to specific allergens or irritants such as cosmetics, metals, soaps, or plants like poison ivy. The immune system reacts to these substances, leading to dermatitis. Symptoms include redness, swelling, blistering, and itching at the contact site. Patch testing by dermatologists helps identify specific allergens involved.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Commonly found in infants (cradle cap) and adults, this form appears on oily areas of the skin, including the scalp, face (especially around the nose and eyebrows), ears, and sometimes the mid-chest. It manifests as greasy, yellowish scales or patches with redness. The condition can be recurrent and is often linked to fungal overgrowth, like Malassezia yeast.
Fungal Eczema
Caused by fungal infections, particularly by fungi like Candida or Malassezia, this type mimics other eczema forms but can be distinguished through laboratory tests, including microscopic examination or culture growth. Fungal eczema appears as persistent, itchy patches that may spread if untreated, often requiring antifungal medications.
Common symptoms associated with eczema include:
Skin Rashes
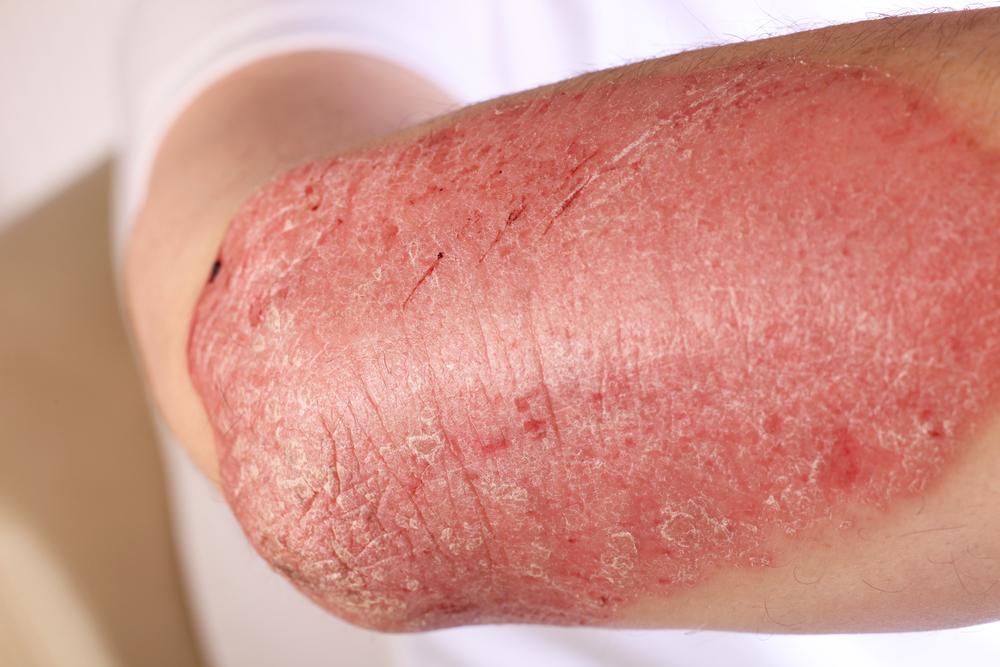
Rashes are hallmark signs with varying appearances depending on the eczema type. They can be oozing, crusted, dry, or scaly, with locations dispersed across different body parts. Visual aids can drastically assist in correct identification.
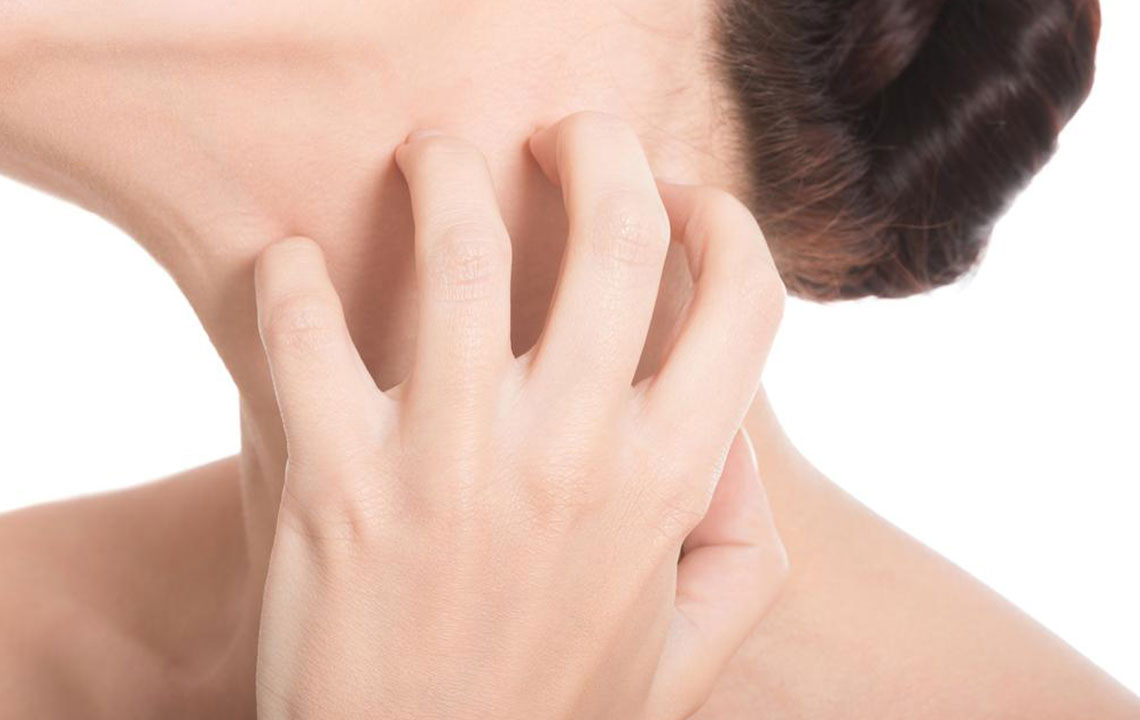
Intense Itching
Itching is almost universal among eczema sufferers. This sensation can be severe, leading to scratching that worsens skin damage and increases infection risk. It often worsens at night, disrupting sleep and daily life.
Potential complications stemming from eczema include:
Asthma and Allergic Rhinitis
Children with eczema are more prone to developing respiratory allergies such as asthma and hay fever later in life. The 'atopic march' describes this progression where skin and airway allergies coexist or follow each other.
Secondary Skin Infections
Continuous scratching can break the skin barrier, providing entry points for bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus or viruses including herpes simplex virus, resulting in impetigo or herpetic dermatitis.
Sleep and Quality of Life Issues
The persistent itch and discomfort compromise sleep quality, leading to fatigue, irritability, and stress, which may further exacerbate skin conditions.
How is eczema diagnosed?
No Need for Specific Laboratory Tests
Diagnosis primarily depends on visual examination by a dermatologist and evaluating patient history. Skin biopsies or allergy testing are reserved for uncertain cases or when identifying triggers is necessary.
Medical History Evaluation
Clinicians inquire about familial allergy history, environmental exposures, personal history of other allergic diseases, and previous skin conditions to determine the eczema type and possible triggers. Understanding these factors guides personalized treatment approaches.
In summary, eczema is a complex, multifaceted skin disorder demanding a comprehensive understanding for effective management. Recognizing the different types, identifying symptoms, and understanding potential complications are essential steps for patients and caregivers. Proper diagnosis based on visual cues and medical history helps tailor appropriate therapies ranging from topical treatments to lifestyle modifications. By actively managing eczema, individuals can significantly improve their skin condition, reduce flare-ups, and enhance their overall quality of life.