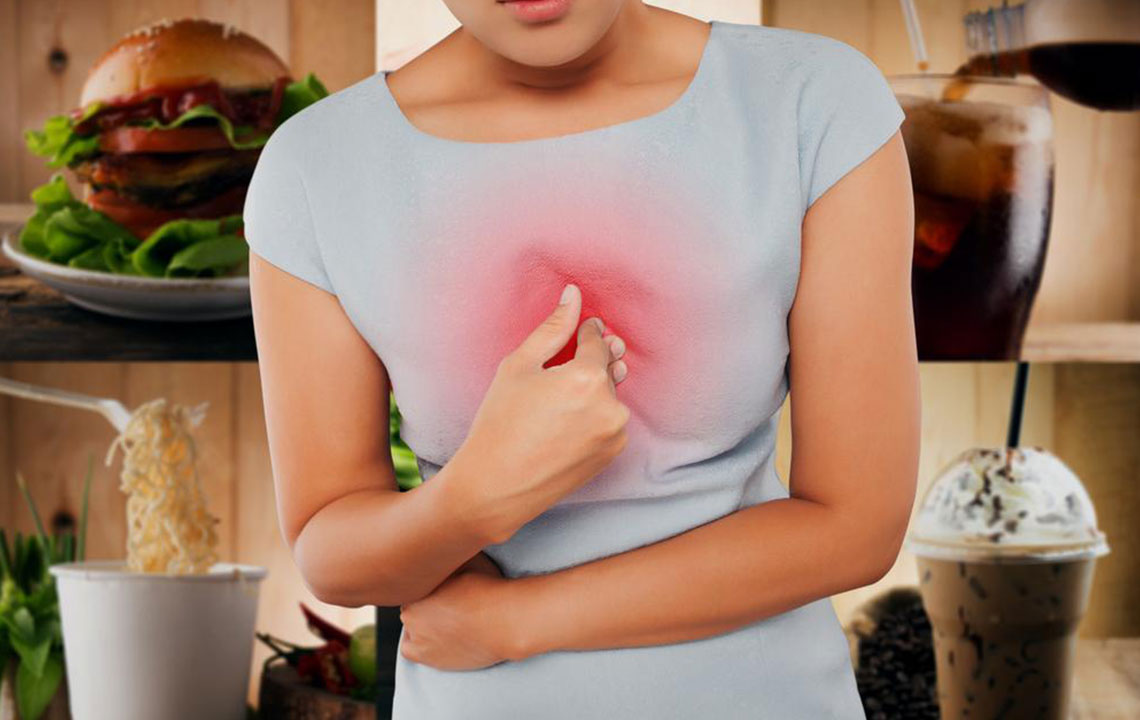
Comprehensive Guide to Alleviating Heartburn and Acid Reflux Naturally and Medically
This comprehensive guide offers proven strategies and medical advice to alleviate heartburn and acid reflux. From lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise to effective over-the-counter and prescription treatments, learn how to manage symptoms and prevent complications. Consulting healthcare professionals is recommended for persistent or severe cases, ensuring tailored treatment plans that safeguard your digestive health and overall well-being.

Comprehensive Strategies for Heartburn and Acid Reflux Relief
Experiencing discomfort after enjoying a substantial meal is a common issue for many people. These sensations often manifest as a burning feeling in the chest and upper abdomen, which can significantly impact daily comfort and quality of life. The primary cause of these symptoms is ascribed to acid reflux, a condition where stomach acids irritate the lining of the esophagus. Understanding the causes, triggers, and effective remedies—ranging from dietary modifications to medical treatments—can help individuals manage and prevent persistent heartburn effectively.
Understanding Heartburn and Acid Reflux
Heartburn, medically known as pyrosis, is characterized by a burning sensation that originates in the chest and can radiate towards the throat. The underlying mechanism involves the malfunctioning of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a ring-like muscle that functions as a barrier between the stomach and the esophagus. When this sphincter relaxes inappropriately or weakens, stomach contents, including acids, can escape upward, leading to irritation and the characteristic burning sensation.
What Causes Heartburn?
The root cause of heartburn is acid reflux, which occurs when the stomach’s acidic contents traverse the LES into the esophagus. Normally, the LES's tight closure prevents this backward flow. However, various factors can compromise its integrity, such as increased abdominal pressure, foods, medications, or underlying health conditions, leading to frequent reflux episodes.
Common Triggers and Contributing Factors
Several lifestyle and dietary factors are known to provoke or worsen acid reflux symptoms. Spicy foods, greasy and fatty meals, caffeine, alcohol, and citrus fruits are some of the most common triggers. Overeating or irregular meal times can also increase stomach acid production, heightening the risk of reflux. Additionally, habits like smoking and obesity significantly contribute to LES malfunction, making reflux more likely.
Persistent or frequent heartburn might indicate underlying health issues such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). These conditions involve more complex dysfunctions of the digestive system and require targeted management approaches, including lifestyle adjustments, medication, or even medical procedures.
Effective Lifestyle and Dietary Habits to Reduce Heartburn
Avoid Specific Foods and Drinks: Limiting or completely avoiding caffeine, citrus fruits, chocolates, carbonated beverages, alcohol, and high-fat or spicy foods can significantly diminish reflux episodes. These items tend to relax the LES or increase stomach acidity, exacerbating symptoms.
Maintain Regular Eating Habits: Consistently eating meals at scheduled times prevents extreme hunger, which can cause increased acid secretion. Skipping meals or eating irregularly can disturb digestive harmony and trigger reflux.
Eat Smaller, Frequent Meals: Dividing daily food intake into smaller portions consumed every two hours reduces the burden on the stomach and facilitates smoother digestion, minimizing the chance of reflux.
Choose Light Dinners and Post-Meal Activities: Opt for a lighter evening meal to lessen stomach pressure before bedtime. Taking a leisurely walk after eating can also promote digestion and reduce acid buildup.
Stay Physically Active: Regular exercise enhances overall digestive health and aids in maintaining a healthy weight, which is crucial for reducing reflux incidents.
Manage Body Weight: Losing excess weight decreases abdominal pressure, alleviating stress on the LES and reducing the frequency and severity of acid reflux episodes.
Wear Comfortable Clothing: Loose-fitting garments, especially around the waist, prevent unnecessary pressure on the stomach and lower esophageal sphincter, easing reflux.
Elevate Your Head During Sleep: Raising the head of your bed or using pillows to elevate the upper body can prevent acid from flowing back into the esophagus during night-time, improving sleep quality and reducing symptoms.
Immediate and Over-the-Counter Remedies
Baking Soda Solution: Dissolving a teaspoon of baking soda in water offers quick neutralization of stomach acid, providing relief from acute heartburn.
Antacid Medications: Over-the-counter options like Tums, Rolaids, or Maalox can rapidly alleviate symptoms by neutralizing acid in the stomach.
Milk of Magnesia: An effective antacid that can soothe heartburn and reduce acidity levels temporarily.
H2 Receptor Blockers: Medications such as Ranitidine (Zantac), famotidine, or other H2 antagonists work by decreasing acid production, offering longer-lasting relief. These should be used under medical supervision, especially for frequent symptoms.
Proton Pump Inhibitors: Powerful drugs like Omeprazole (Omez) significantly suppress gastric acid secretion. They are typically reserved for chronic GERD management and require a prescription from a healthcare professional.
Prokinetic Agents: Certain medications improve gastric motility and accelerate stomach emptying, proving beneficial for severe or persistent reflux, but they should only be taken under medical guidance.
When to See a Healthcare Professional
If you experience frequent heartburn that does not respond to lifestyle changes or over-the-counter medications, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider. Chronic acid reflux can damage the esophagus's lining, potentially leading to serious conditions such as esophagitis, Barrett’s esophagus, or even esophageal cancer. Diagnostics like endoscopy, pH monitoring, or biopsies may be necessary to identify the underlying issues and formulate an appropriate treatment plan.
Understanding your triggers and adopting healthy lifestyle habits are vital steps to managing heartburn effectively. Combining dietary adjustments, physical activity, weight management, and medical therapies ensures relief and helps prevent complications in the long term. Remember, persistent symptoms should never be ignored, and professional guidance is crucial for optimal care.