Comprehensive Strategies for Identifying and Managing Heartburn Effectively
This comprehensive guide offers detailed insights into recognizing, differentiating, and managing heartburn symptoms effectively. It emphasizes the importance of accurate diagnosis for appropriate treatment, highlights key signs such as burning sensation and chest discomfort, and explains how lifestyle changes and medical interventions can provide relief. The article also educates readers on distinguishing heartburn from serious conditions like heart attacks, promoting timely medical attention. Practical tips for daily management and prevention are included, making this resource essential for anyone seeking to better control their reflux symptoms.

Understanding the Key Symptoms of Heartburn and How to Manage Them
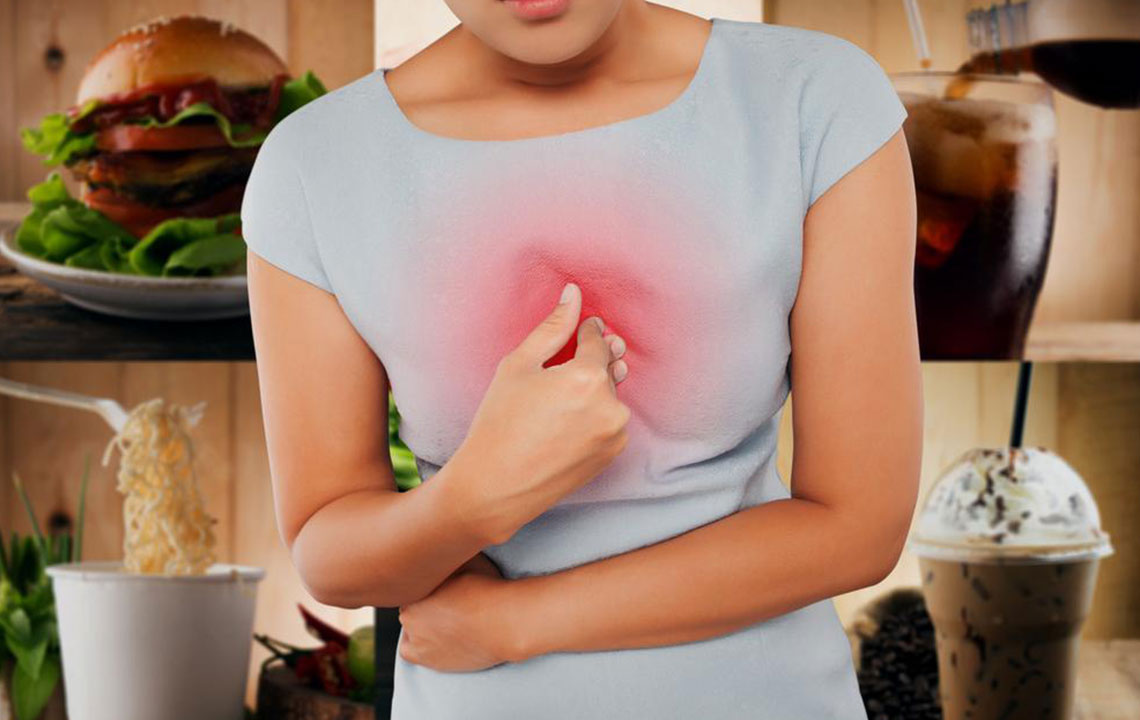
Heartburn is an extremely common condition that affects millions worldwide, characterized by a burning sensation in the chest area. This discomfort originates from acid reflux, a process where stomach acid flows backward into the esophagus, leading to a range of unpleasant symptoms. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for effective treatment and relief. In this article, we delve into the main signs of heartburn, how to differentiate it from other serious conditions such as heart attacks, and practical approaches to manage and prevent its occurrence. We aim to equip readers with comprehensive knowledge to handle heartburn efficiently and seek medical help when necessary.
What Is Heartburn and Why Does It Happen?
Heartburn arises due to the relaxation or weakening of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a circular muscle that normally acts as a valve to keep stomach contents from refluxing into the esophagus. When the LES fails, acid from the stomach escapes into the esophagus, irritating its lining and causing a burning sensation. This process can be triggered by various factors, including certain foods, lifestyle habits, medications, or underlying medical conditions.
While occasional heartburn is common and often manageable, persistent or severe symptoms warrant medical attention as they may indicate conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or other digestive disorders. Understanding the intricate mechanisms behind acid reflux can help individuals identify triggers and adopt effective management strategies.
Recognizing the physical signs of heartburn can enable timely intervention. These symptoms, although common, can sometimes be mistaken for other health issues, emphasizing the importance of accurate identification.
Burning Sensation: The hallmark symptom of heartburn, this burning feeling typically occurs behind the breastbone. It often arises after meals and can last from a few minutes to several hours. It may worsen when lying down or bending over, as these positions increase pressure on the stomach.
Chest Discomfort: Many individuals experience pain or discomfort in the chest area, which may feel like a tightness or pressure. This sensation can radiate to the neck, throat, or even the shoulders. It's important to differentiate this from cardiac pain, especially in at-risk populations.
Understanding that not all chest pain is heartburn is critical. Chest pain caused by heart attacks can mimic heartburn symptoms but requires immediate emergency care. Therefore, any unexplained or severe chest pain should prompt immediate medical evaluation.
Throat irritation is another common manifestation, characterized by a hot or salty sensation at the back of the throat. This can be accompanied by difficulty swallowing, a feeling of food being stuck, or a persistent sore throat. Some individuals might also experience a chronic cough or hoarseness, which can be symptoms of acid reflux affecting the upper airways.
Other accompanying signs include regurgitation of sour liquids or food, bitter taste, and halitosis. These symptoms can impact daily activities and sleep quality, underscoring the need for effective management.
If you experience symptoms such as persistent heartburn, difficulty swallowing, unexplained weight loss, or recurrent chest pain, it is imperative to seek medical advice. Diagnosis may involve endoscopy, pH monitoring, or other testing to determine the severity and underlying causes of reflux.
Distinguishing Heartburn from Heart Attack: Critical Differences
While chest discomfort is common to both heartburn and heart attacks, distinguishing between these two is vital for survival. Heart attacks are medical emergencies that require immediate intervention, whereas heartburn, although uncomfortable, is generally manageable with lifestyle changes and medications.
The typical signs of heartburn include:
A burning sensation beneath the sternum or ribs
Discomfort that may radiate to the neck, jaw, or shoulders but predominantly stays centered in the chest
Relief after taking antacids or other acid-reducing medications
In contrast, heart attack symptoms often involve:
Intense pressure, squeezing, or fullness in the chest that may escalate quickly
Pain radiating to the arms, back, neck, or jaw
Sudden onset of shortness of breath, dizziness, or cold sweats
Nausea, weakness, or lightheadedness
If chest pain persists for more than 10-15 minutes or is accompanied by symptoms like sweating, nausea, or radiating pain, seek emergency medical assistance immediately. Do not delay treatment, as early intervention can save lives.
Effective Strategies to Relieve and Prevent Heartburn
Managing heartburn involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, dietary adjustments, and over-the-counter remedies. Simple changes can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms.
Wear loose, comfortable clothing to avoid unnecessary pressure on your stomach, especially after meals.
Maintain an upright posture during and after eating to facilitate digestion and prevent acid reflux.
Elevate the head of your bed by approximately 6-8 inches to prevent acid from flowing back while sleeping.
Incorporate gentle stretches or yoga to improve overall digestion and reduce stress — a known trigger for reflux.
Avoid trigger foods such as spicy meals, fatty foods, caffeine, alcohol, and acidic drinks like citrus or tomato-based products.
Limit late-night meals and snacking to reduce the chances of nighttime reflux.
Stay hydrated and maintain a healthy weight, as obesity is a significant risk factor for acid reflux.
Home remedies can provide temporary relief. For instance, baking soda mixed with water acts as a natural antacid, neutralizing stomach acid quickly. However, such remedies should not replace medical treatment, particularly for chronic or severe symptoms.
Pregnant women experiencing frequent heartburn should consult their healthcare provider before starting any treatment to avoid harming the fetus. Safe and effective options, tailored for pregnancy, can help manage symptoms during this sensitive period.
In cases where lifestyle modifications and home remedies are ineffective, medical treatment involving proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 receptor blockers might be necessary. Always seek professional advice for persistent or worsening symptoms to prevent complications like esophageal erosion or Barrett’s esophagus.