Comprehensive Guide to Heartburn: Causes, Recognizing Symptoms, and Effective Relief Methods
This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, and effective relief methods for heartburn. Learn how dietary habits, lifestyle choices, and medical options can help manage this common discomfort. Discover tips for prevention and when to seek professional help to ensure optimal digestive health.

Comprehensive Guide to Heartburn: Causes, Recognizing Symptoms, and Effective Relief Methods
Heartburn is a widespread condition that affects millions of people worldwide, often occurring after large or spicy meals. This discomfort is more than just an inconvenience; understanding its root causes, common symptoms, and strategies for relief is key to managing it effectively. Whether you experience occasional discomfort or frequent episodes, this detailed guide aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to identify, prevent, and alleviate heartburn symptoms, improving your quality of life.
Unraveling the Causes of Heartburn
Heartburn primarily signals the presence of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a condition whereby stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that connects your mouth to your stomach, and when acid irritates its lining, the characteristic burning sensation occurs. Several factors contribute to this reflux, and understanding these can help in adjusting your habits and diet to reduce symptoms.
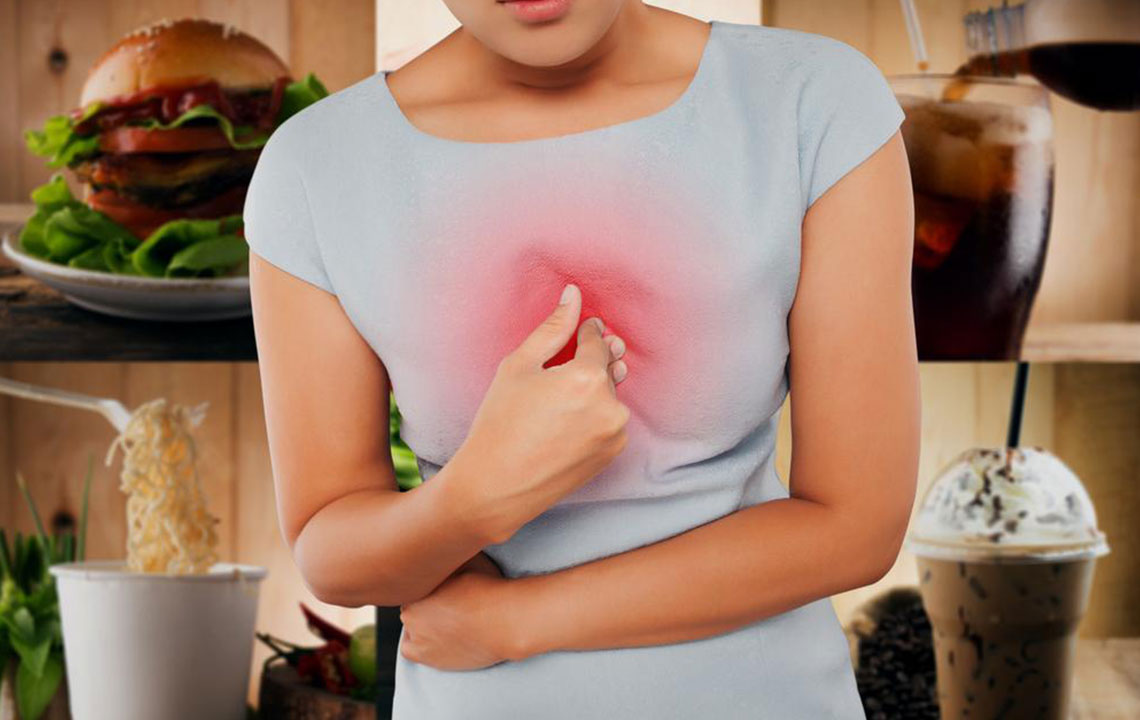
Diet plays a significant role in the onset of heartburn. Foods and beverages such as alcohol, high doses of caffeine, fizzy soft drinks, spicy dishes, and acidic foods like tomatoes and citrus are common culprits that relax the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) or increase acidity, thereby enhancing reflux risk. Smoking interferes with esophageal function and increases acid production, exacerbating symptoms, especially when combined with the consumption of fatty foods. During pregnancy, hormonal changes and increased abdominal pressure can also trigger frequent heartburn episodes, as the growing uterus presses against the stomach, pushing acid into the esophagus. Additionally, certain esophageal conditions, including esophageal motility disorders or hiatal hernia, can predispose individuals to frequent reflux and heartburn.
Identifying Heartburn Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of heartburn is crucial for timely management. The hallmark symptom is a burning sensation occurring behind the breastbone, often rising in the chest or throat. This sensation can vary from mild discomfort to severe pain and might occur suddenly or persist for hours. It typically worsens after meals, especially if the meal was rich, spicy, or fatty, and when lying down or bending over. Some individuals experience a sour or bitter taste in the mouth or throat, which is due to acid overflow.
Additional symptoms include persistent cough, hoarseness, a sensation of a lump in the throat, and difficulty swallowing. Over time, repeated acid exposure can lead to erosion of tooth enamel, esophageal inflammation, ulcers, or strictures. Importantly, heartburn can sometimes mimic more serious conditions, such as angina (heart attack), which necessitates prompt medical evaluation especially if symptoms are new, severe, or accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, or sweating.
Strategies for Managing and Relieving Heartburn
Long-term Lifestyle Modifications
Effective management of heartburn begins with lifestyle and dietary changes. Eating smaller, more frequent meals can prevent excessive stomach distension, which aggravates reflux. Chewing food slowly also promotes better digestion and reduces air swallowing, which can increase pressure on the stomach. Avoiding meals close to bedtime—ideally at least three hours before sleep—can significantly decrease nighttime symptoms.
It is recommended to limit or completely avoid alcohol intake and smoking, as both weaken the LES and increase acid production. Maintaining a healthy weight is essential, as excess abdominal fat exerts pressure on the stomach, pushing acid upward. Elevating the head of your bed by about 6 to 8 inches can help prevent acid reflux during sleep. Wearing loose-fitting clothes around the waist can also reduce pressure on the stomach.
Medicinal Relief and When to Seek Medical Advice
For immediate relief of symptoms, over-the-counter medications are the most common options. Antacids, such as Tums, Rolaids, or Maalox, work by neutralizing existing stomach acid and provide quick, short-term relief. H2 receptor blockers like ranitidine and famotidine decrease acid production, providing longer-lasting relief within 30 minutes of intake. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs), including omeprazole and esomeprazole, inhibit acid secretion more profoundly and are usually used for persistent or severe cases; however, they typically take about four days to reach full effect.
It is advisable to consult a healthcare provider if you experience frequent heartburn—more than twice a week—or if symptoms worsen despite lifestyle modifications. Persistent or severe symptoms might indicate underlying conditions that require diagnostic procedures such as endoscopy or further medical intervention to prevent complications like esophageal damage or Barrett's esophagus.
In summary, understanding the causes and symptoms of heartburn can empower individuals to take proactive steps towards prevention and relief. Simple lifestyle changes combined with appropriate medication use can significantly improve comfort and prevent long-term complications. Recognizing when to seek medical attention ensures that more serious conditions are not overlooked, fostering better digestive health and overall well-being.