The Ultimate Guide to Effectively Managing Heartburn and Acid Reflux
Explore comprehensive strategies for managing heartburn effectively. Learn about causes, symptoms, lifestyle adjustments, and medical options to prevent complications and improve digestive health. This detailed guide offers practical advice for both occasional and frequent heartburn sufferers, emphasizing early recognition and proactive treatment for better quality of life.

The Ultimate Guide to Effectively Managing Heartburn and Acid Reflux
Heartburn, also known as acid reflux, is a common discomfort experienced by millions worldwide. It occurs when stomach acids flow back into the esophagus, leading to a burning sensation in the chest, throat irritation, and sometimes more serious complications if left untreated. While intermittent heartburn can be managed with lifestyle adjustments and over-the-counter remedies, frequent episodes might signal underlying health issues like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management strategies is essential for anyone seeking relief and better digestive health.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the causes and symptoms of heartburn, explore effective lifestyle changes, and discuss medical treatments to alleviate persistent symptoms. Recognizing early signs and understanding risk factors are critical steps toward prevention and management. Heartburn is more than just a minor inconvenience—it can significantly impair quality of life, affecting sleep, eating habits, and even respiratory health. Therefore, adopting proactive measures and consulting healthcare professionals when necessary can help maintain a healthy digestive system.
Understanding Heartburn and Acid Reflux
Heartburn manifests as a burning sensation behind the chest or throat, often worsened after meals or when lying down. It can also cause a bitter or acidic taste in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, and persistent coughs. While occasional episodes are typical, frequent heartburn (more than twice a week) indicates a more serious issue that requires medical attention. Chronic acid reflux can damage esophageal tissue, lead to strictures, and even increase the risk of esophageal cancer if untreated.
Key Factors Contributing to Heartburn
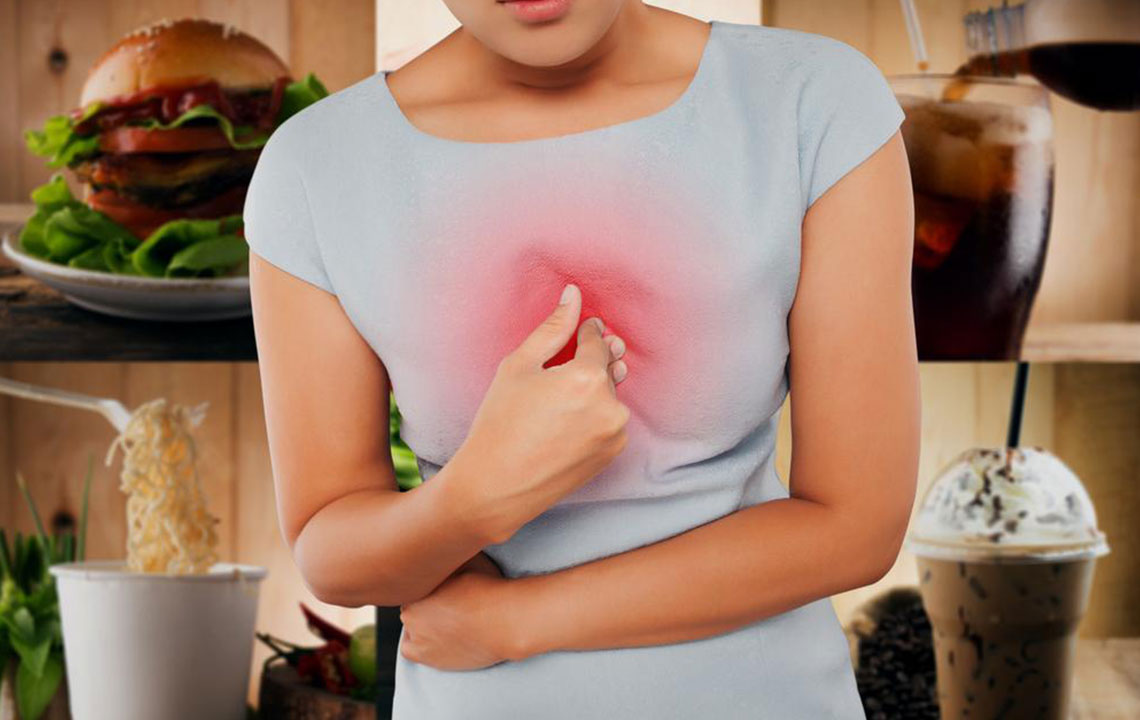
Dietary choices: Consuming large meals, spicy foods, onions, garlic, chocolate, citrus fruits, tomato-based products, and processed foods high in salt or artificial additives can trigger symptoms.
Beverages: Alcohol, caffeinated drinks like coffee and tea, and carbonated sodas increase stomach acid production and relax the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), facilitating acid reflux.
Eating habits: Eating close to bedtime or lying down immediately after meals often causes acid to flow back into the esophagus, leading to discomfort.
Lifestyle factors: Obesity puts pressure on the abdomen, increasing the likelihood of reflux. Smoking weakens the LES, and tight clothing around the waist can also contribute to symptoms.
Medical conditions and medications: Conditions such as pregnancy, hiatal hernia, and GERD, as well as certain medications including NSAIDs and muscle relaxants, can predispose individuals to heartburn.
Symptoms and Potential Complications
Recognizing the symptoms early is crucial for effective management. Common signs include a burning sensation in the chest (often after meals or when lying down), persistent sore throat, hoarseness, and regurgitation of acid. Additional signs may involve nausea, bloating, bad breath, and a sensation of a lump in the throat. Over time, repeated acid exposure can cause esophageal tissue damage, leading to complications such as esophageal strictures, Barrett’s esophagus, and increased cancer risk. Heartburn can also worsen respiratory conditions like asthma or cause chronic coughs and infections.
Practical Strategies for Managing Heartburn
Many people find relief through simple lifestyle changes and over-the-counter (OTC) remedies. These include:
Eating smaller, more frequent meals to reduce stomach load
Avoiding trigger foods and beverages around meal times
Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced diet and regular exercise
Lifting the head of the bed by 6–8 inches to prevent nighttime reflux
Avoiding lying down immediately after eating—wait at least 2-3 hours
Wearing loose-fitting clothing to reduce pressure around the abdomen
Using antacids, H2 blockers, or proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) as recommended by healthcare professionals
Beyond medication and diet, behavioral modifications such as quitting smoking, managing stress levels, and engaging in gentle activities like walking or swimming can significantly improve symptoms. In some cases, clinicians may recommend procedures or surgery for severe cases that do not respond to conservative treatments. Regular checkups and monitoring are essential to prevent progression and complications of chronic reflux.
In conclusion, understanding the root causes and early symptoms of heartburn enables effective management. Whether through lifestyle adjustments, medication, or medical intervention, individuals can regain control over their digestive health and improve their overall quality of life.