Comprehensive Guide to Heartburn: Causes, Prevention, and Relief Strategies
Discover comprehensive strategies to manage and prevent heartburn, including dietary modifications, lifestyle adjustments, and medical options. Learn how to identify triggers, improve digestion, and reduce symptoms effectively for lasting relief and better quality of life.
An In-Depth Look at Managing and Alleviating Heartburn Naturally
Have you ever experienced a persistent burning sensation or discomfort in your chest after indulging in indulgent, greasy, or spicy foods? If so, you might be suffering from a common digestive condition known as heartburn. This condition affects many people worldwide, ranging from occasional discomfort to chronic symptoms that significantly impact quality of life. Heartburn, medically called acid indigestion, presents as a burning sensation in the upper abdomen or chest area, often radiating to the neck, jaw, or arms. These discomforts can last anywhere from a few minutes to several hours, interfering with daily activities, sleep, and overall well-being.
Understanding the underlying causes and triggers of heartburn is essential to effectively prevent and manage this uncomfortable condition.
What is Heartburn?
Heartburn occurs when stomach acids reflux into the esophagus, the tube that connects your mouth to your stomach. The primary barrier preventing this reflux is the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a muscle ring that opens to allow food entry into the stomach and closes to prevent acid escape. When the LES weakens, relaxes excessively, or becomes dysfunctional, stomach acids can flow back into the esophagus, leading to the characteristic burning sensation known as heartburn.
Major Causes and Contributing Factors
The primary cause of heartburn is the malfunctioning of the LES. Several factors can contribute to this malfunction, including lifestyle choices, diet, and health conditions. Overeating, particularly large meals high in fat and spice, can stretch and relax the LES, increasing the risk of reflux. Additionally, habits like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, and pregnancy can weaken the LES and promote acid reflux.
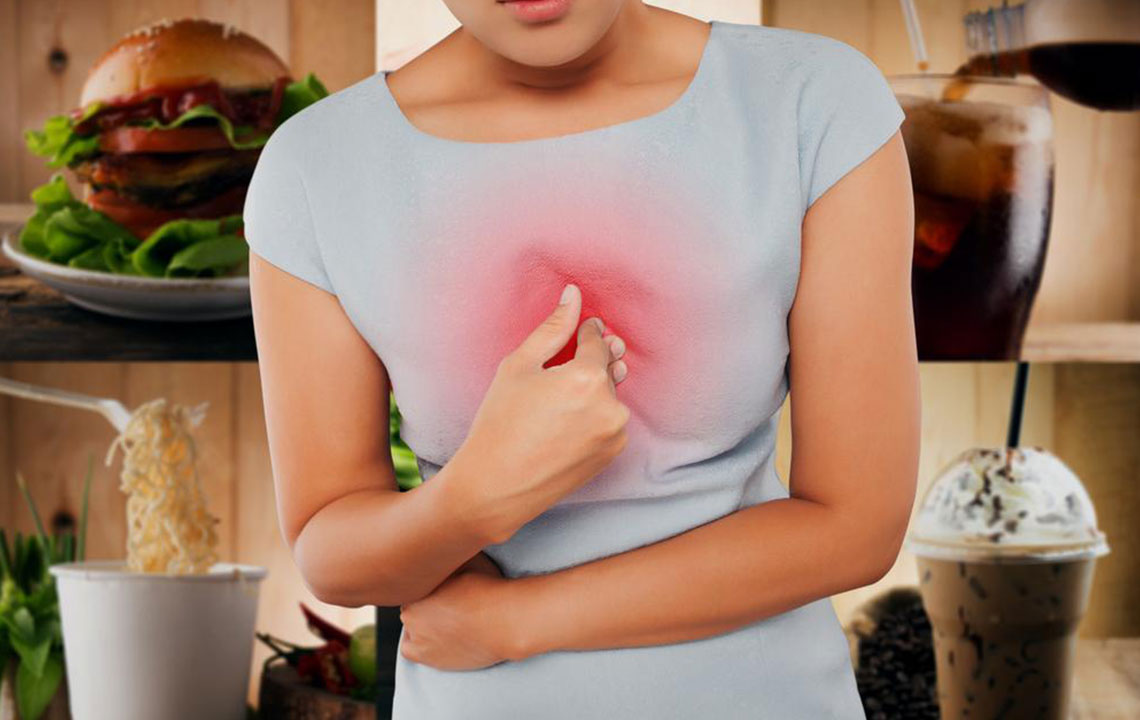
Dietary and Lifestyle Triggers
Certain foods and beverages are more likely to provoke heartburn symptoms. These include coffee, onions, alcohol, chocolate, fried foods, tomatoes, citrus fruits, peppermint, and carbonated drinks. Post-meal habits also influence reflux; lying down immediately after eating, wearing tight clothing, or engaging in vigorous activities can exacerbate symptoms. Understanding individual triggers is vital to developing an effective management plan.
Nutrition and Lifestyle Modifications for Heartburn Relief
Adopting dietary changes is a cornerstone of managing heartburn. Limiting or avoiding foods known to trigger reflux can significantly decrease symptoms. This includes reducing intake of caffeine, spicy dishes, fried foods, and acidic fruits. Incorporating smaller, more frequent meals instead of large portions helps reduce stomach pressure. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day and eating slowly can also improve digestion and lessen reflux episodes.
Additional Lifestyle Strategies
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on the stomach and LES, decreasing the likelihood of reflux. Wearing loose-fitting clothing prevents unnecessary constriction around the abdomen. Quitting smoking is critical, as nicotine relaxes the LES and increases stomach acid production. If you're taking medications such as NSAIDs (pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs), consult your healthcare provider for alternatives, as these can worsen reflux symptoms. Physical activity is beneficial but should be approached cautiously; high-impact workouts may trigger reflux episodes, while low-impact exercises can promote overall digestive health.
Managing Nighttime Heartburn Effectively
Nighttime heartburn can severely disrupt sleep and lead to more severe complications if untreated. To prevent nocturnal reflux, have your last meal at least two to three hours before bedtime, and avoid foods and beverages that trigger symptoms in the evening. Elevating the head of your bed using blocks or foam wedges to create an incline helps prevent stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus during sleep. Sleeping on your left side can also reduce reflux episodes, as this position minimizes pressure on the stomach.
Exercise Tips for Optimal Heartburn Prevention
Regular physical activity supports weight management and overall digestive health, thereby reducing heartburn risk. Engaging in moderate, low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling is preferred. Avoid activities involving intense abdominal strain, such as crunches or inverted yoga poses, especially if you experience frequent reflux symptoms. Consistent exercise, combined with dietary modifications, enhances your ability to manage and prevent heartburn effectively.
When to Seek Professional Medical Advice
If lifestyle modifications and dietary changes do not alleviate your symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional. Persistent heartburn may indicate underlying conditions requiring treatment with medications like antacids, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), or H2 receptor blockers. In rare cases where reflux is severe or chronic, surgical interventions—such as laparoscopic repair of the LES—may be recommended to provide lasting relief.
Conclusion
Managing heartburn effectively involves understanding its causes, identifying personal triggers, and adopting comprehensive lifestyle changes. From dietary adjustments and weight management to positioning techniques and medical treatments, multiple strategies can help you significantly reduce or eliminate discomfort. Early intervention and proactive management are key to preventing potential complications and maintaining a high quality of life.