Comprehensive Guide to Managing Blood Glucose Levels Effectively
This comprehensive guide offers in-depth strategies for managing blood glucose levels effectively, emphasizing the importance of regular monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and medical consultation. It covers normal ranges, diagnostic criteria, factors influencing blood sugar, and practical tips to prevent complications. Designed for individuals with diabetes or those seeking better metabolic health, this article aims to empower readers with knowledge for better disease management and improved quality of life.

Comprehensive Strategies for Effective Blood Glucose Management
Maintaining proper blood glucose levels is a cornerstone of managing diabetes and ensuring overall health. Fluctuations in blood sugar can result from various factors, including diet, physical activity, stress, infections, and medication adherence. Effective regulation of blood glucose not only helps in preventing acute symptoms but also significantly reduces the risk of long-term complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and kidney issues.
In the United States, blood glucose is typically measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl). Long-term control of blood sugar is assessed through Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) tests, which provide an average of blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. Keeping these parameters within normal ranges is crucial for people with diabetes and for those aiming to maintain overall metabolic health.
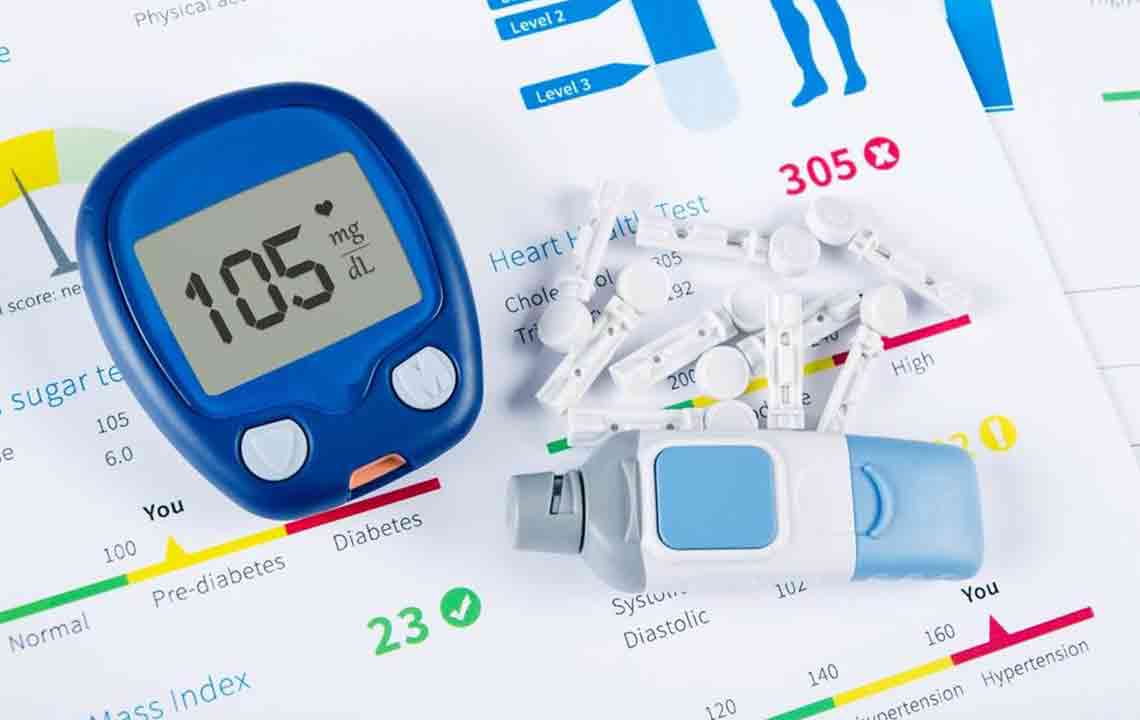
Understanding Normal Blood Sugar Levels
For individuals without diabetes, normal blood glucose levels are as follows:
Fasting blood sugar (measured after an overnight fast): less than 100 mg/dl
Pre-meal levels (before eating): 70–99 mg/dl
Post-meal blood sugar (about two hours after a meal): under 140 mg/dl
Hemoglobin A1c: below 5.7%
Maintaining these ranges is vital for optimal health. Slight deviations may indicate prediabetes or the need for lifestyle adjustments.
Criteria for Diabetes Diagnosis
Diabetes is diagnosed based on specific blood glucose thresholds:
Two separate fasting blood tests showing glucose over 126 mg/dl
Random blood glucose test exceeding 200 mg/dl
Oral glucose tolerance test result over 200 mg/dl
Hemoglobin A1c of 6.5% or higher
If you fall into these ranges, it is essential to seek medical advice and start appropriate management strategies.
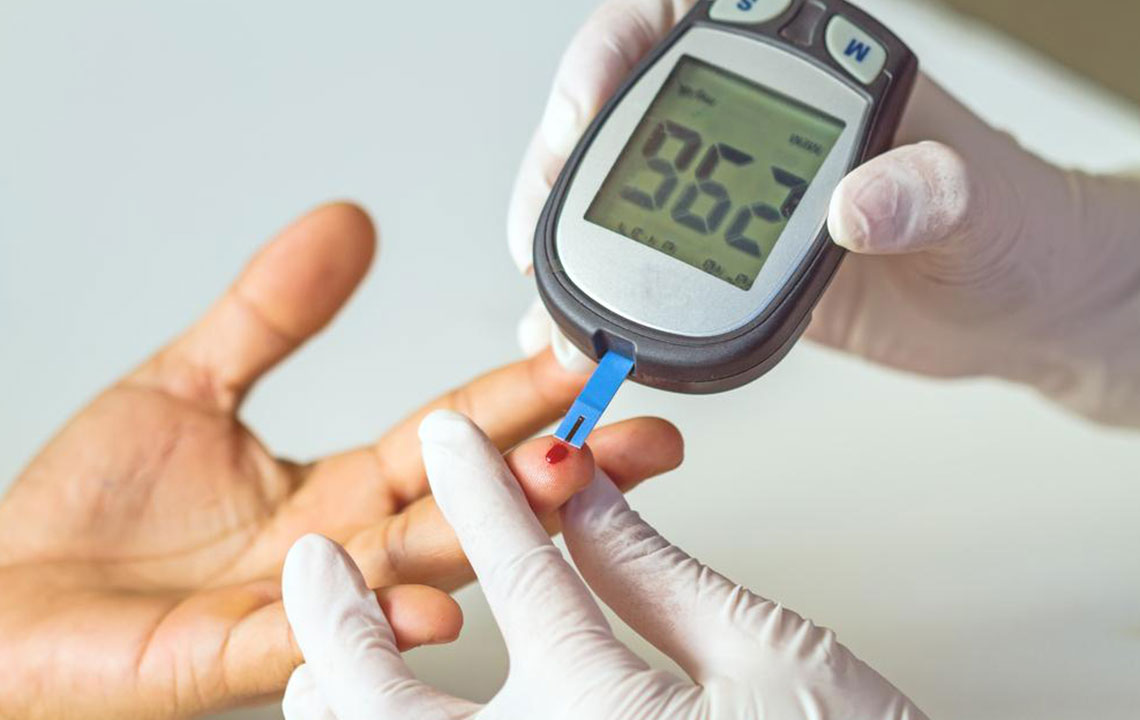
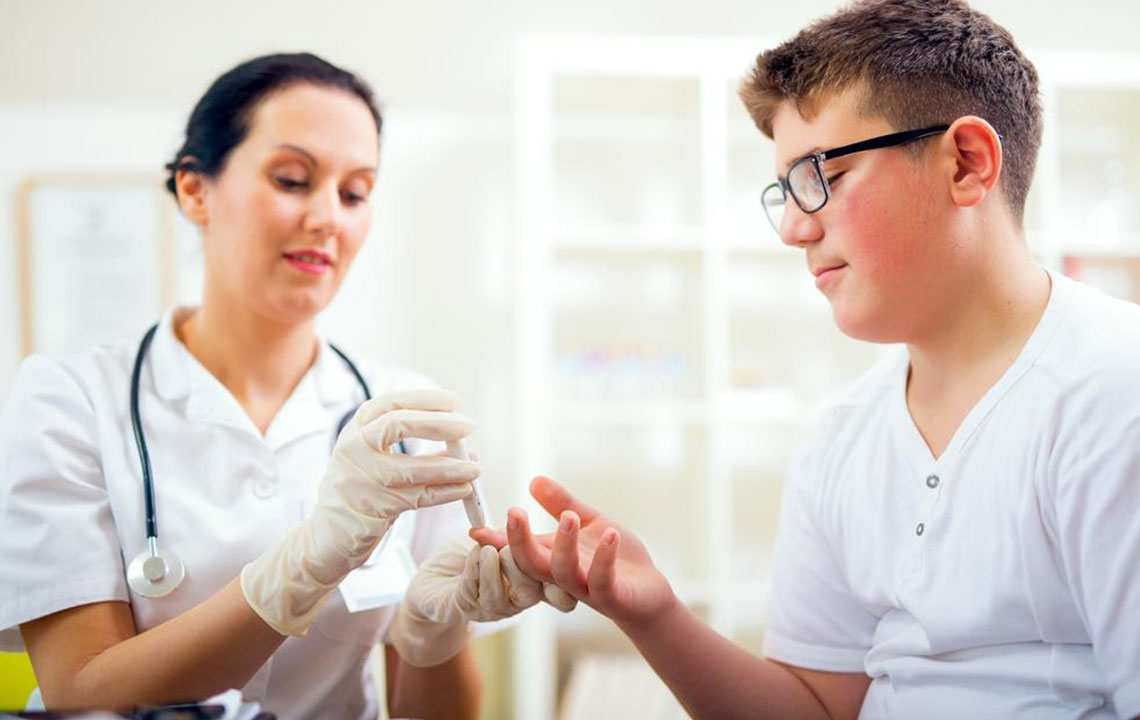
Monitoring Blood Glucose: Importance and Methods
Regular blood sugar monitoring is a fundamental component of diabetes management. It allows individuals to understand how different factors influence their levels, such as meals, activities, medications, and stress. Monitoring post-meal and post-activity levels provides insight into how effectively the body processes glucose. Using glucometers or continuous glucose monitoring systems can help track fluctuations accurately.
Key Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can cause rises or drops in blood glucose, including:
Missed or improperly taken medications
Infections or illnesses
High carbohydrate or sugar intake
Physical inactivity or sedentary lifestyle
High stress levels and emotional strain
Symptoms of blood sugar imbalance may include headaches, increased thirst, blurred vision, fatigue, unexplained weight changes, and anxiety. Recognizing these signs early can prompt timely intervention.
Strategies to Stabilize Blood Glucose Levels
Effective blood glucose management involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication adherence, and professional guidance. Key strategies include:
Consistent blood sugar testing, especially before and after meals or physical activity
Adhering to prescribed medication regimens
Maintaining proper hydration by drinking plenty of water
Engaging in regular physical activity tailored to individual capacity and health status
Eating a balanced diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, healthy fats, and controlled carbohydrate intake
Monitoring dietary patterns to avoid excessive sugar and carbohydrate consumption
Managing stress through relaxation techniques, meditation, or counseling
Additional Tips for Preventing Complications
Managing blood sugar is not just about immediate control but also about preventing long-term damage. This can be achieved by:
Regularly checking for ketones if blood sugar levels are consistently high, especially in type 1 diabetes
Staying well-hydrated to facilitate kidney function and toxin elimination
Following personalized dietary advice from healthcare professionals
Maintaining a healthy weight to improve insulin sensitivity
Scheduling routine check-ups to monitor organ health and prevent complications
Educating oneself about diabetes management and being proactive about health
Ultimately, effective blood glucose regulation relies on continuous effort, lifestyle discipline, and professional support. Patience and perseverance play significant roles in achieving optimal health outcomes. Combining these strategies with personalized medical care ensures that individuals living with diabetes can lead healthy, active lives with minimized risks.