Comprehensive Guide to Blood Sugar Management Strategies for Diabetes Control
This comprehensive guide provides detailed strategies to effectively manage blood glucose levels in diabetes. It emphasizes regular monitoring, carbohydrate control, physical activity, and collaborative healthcare. Implementing these practices can help prevent complications and improve quality of life with ongoing commitment and support.
Comprehensive Guide to Blood Sugar Management Strategies for Diabetes Control
Managing diabetes effectively hinges on maintaining stable blood glucose levels, which plays a critical role in overall health and quality of life. Proper blood sugar control can significantly reduce the risk of serious complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision impairment. While managing diabetes presents challenges, a structured approach combining lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and medical guidance can make a profound difference. This comprehensive guide provides detailed strategies to help you take charge of your blood glucose levels and improve your health outcomes.
Importance of Regular Blood Glucose Monitoring
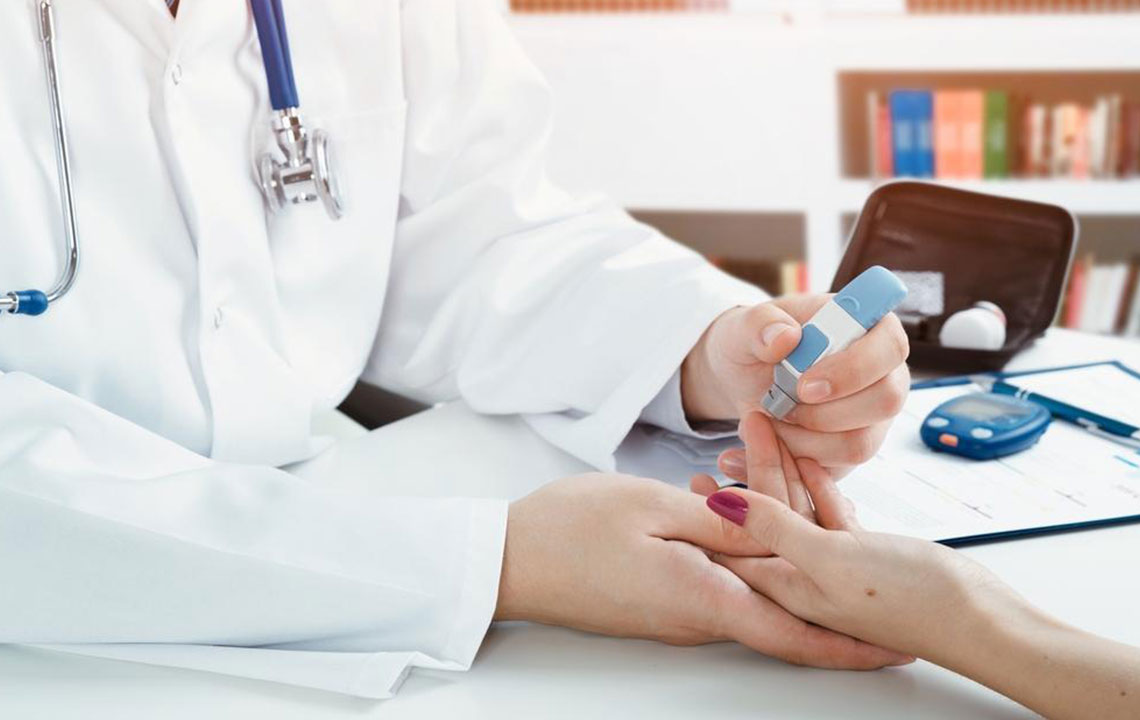
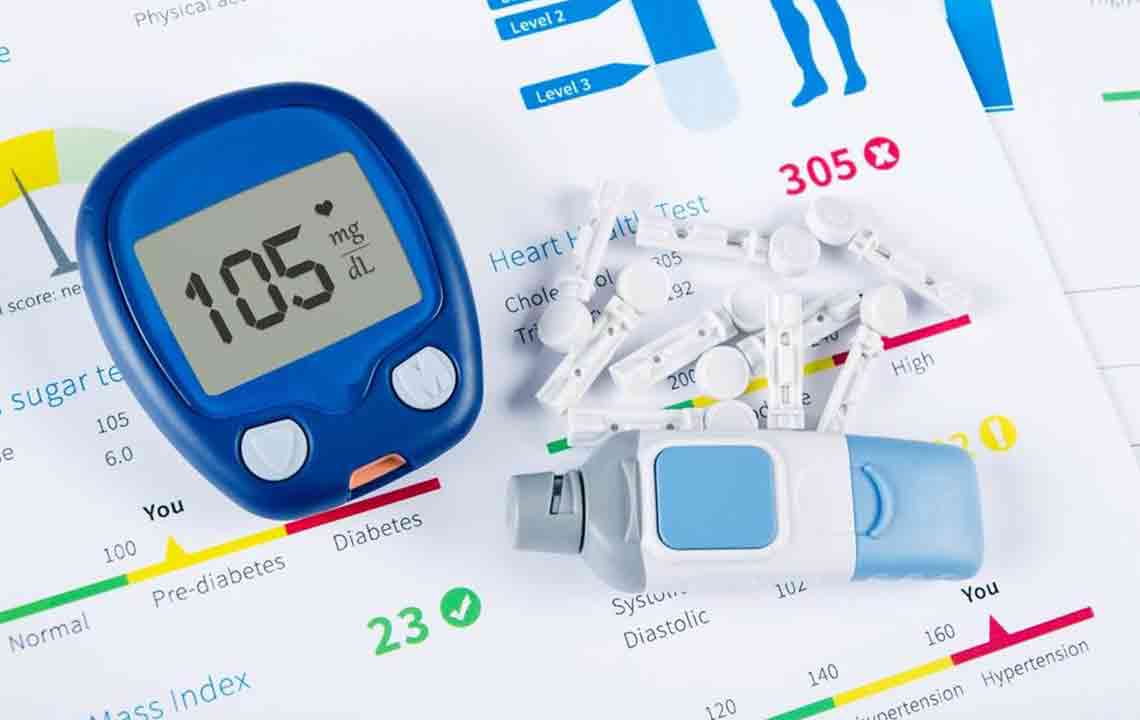
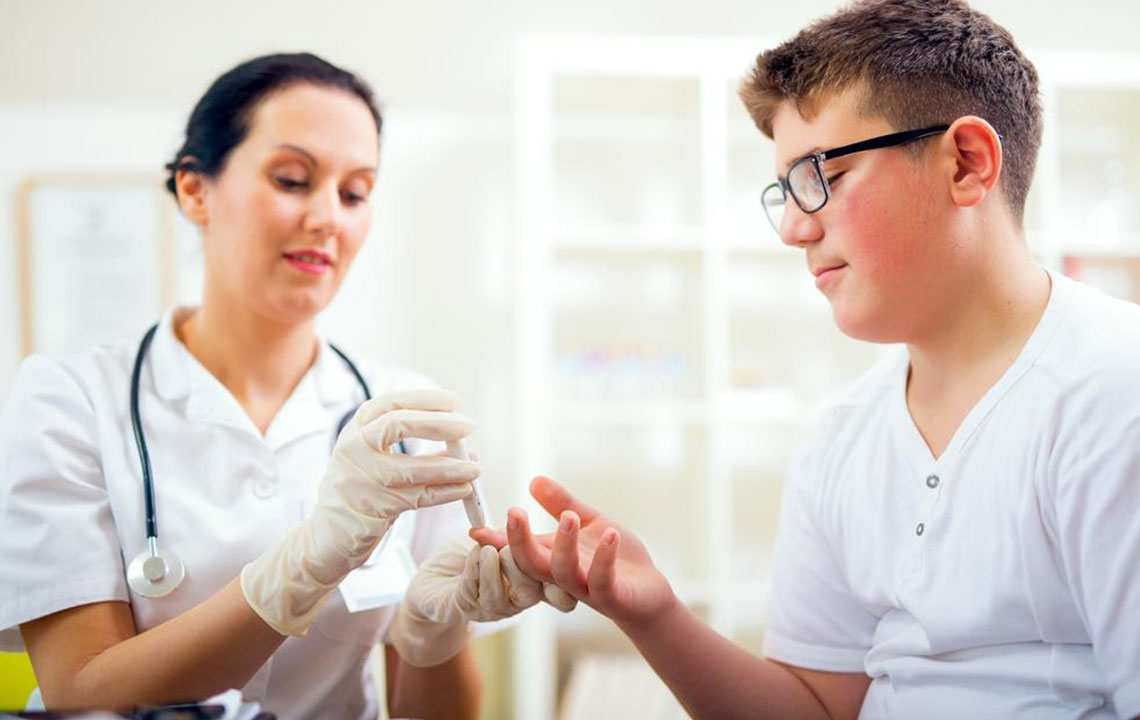
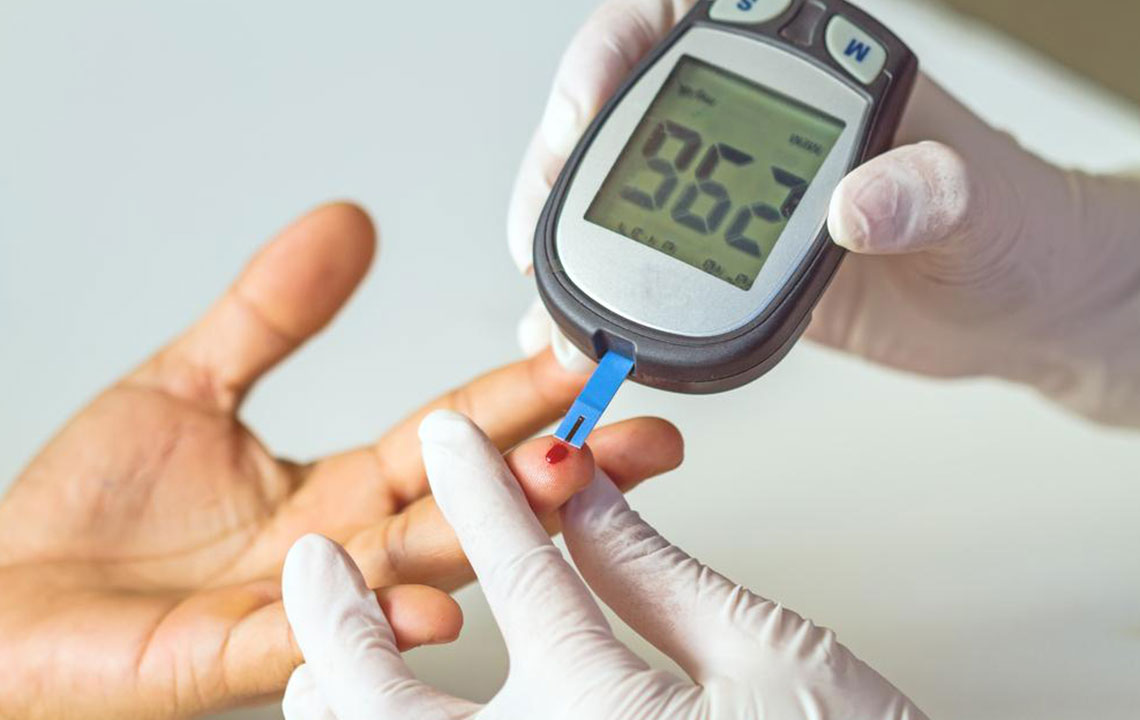
One of the fundamental aspects of diabetes management is consistent blood sugar testing. This involves measuring your glucose levels at different times of the day to understand how your body responds to various foods, activities, and medications. Healthcare providers may recommend specific testing schedules, such as fasting blood glucose tests in the morning or post-meal measurements to assess how effectively your body is handling carbohydrates. Additionally, home testing kits enable you to perform quick checks without prior notice, providing real-time data that can inform immediate lifestyle adjustments.
Regular monitoring acts like a control panel for your health. It allows you to identify patterns in your blood sugar fluctuations, helping you to make well-informed decisions about diet, activity, and medication adherence. Think of it as managing a complex system where constant feedback is necessary to optimize performance. The insights gained through monitoring empower you to take proactive steps to prevent hypo- or hyperglycemia, ultimately leading to better long-term health management.
Managing Carbohydrate Intake Effectively
Carbohydrates are the primary dietary factor influencing blood glucose levels. It is essential to understand how to regulate carbohydrate consumption to prevent spikes. Typically, women should aim for about 40–45 grams of carbs per meal, while men may need around 45–60 grams, depending on individual health goals and activity levels. For context, small servings of rice or pasta contain approximately 45 grams of carbs. Combining carbohydrates with proteins such as lean meats, eggs, nuts, or with high-fiber foods like vegetables, legumes, and whole grains helps slow digestion and glucose absorption into the bloodstream. This strategy minimizes rapid blood sugar spikes and promotes more stable glucose levels.
Including fiber-rich foods like sweet potatoes, whole wheat bread, beans, pumpkins, and gourds improves vascular health and enhances insulin sensitivity. Limiting added sugars and processed foods is crucial; many "sugar-free" labeled products may still contain high-carb additives that could adversely affect your blood sugar control. Preparing meals that emphasize whole, unprocessed ingredients can lead to better health outcomes and increased energy levels.
Incorporation of Physical Activity in Diabetes Management
Engaging in regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to lower blood glucose levels naturally. Exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, allowing your body to utilize glucose more effectively. Aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly — such as brisk walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing — provides significant benefits. Breaking this into manageable 30-minute sessions makes it more achievable and sustainable. It's important to consult your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen to ensure safety, especially if you have other health conditions.
Beyond glucose regulation, physical activity releases endorphins that improve mood and reduce stress, which can positively influence blood sugar levels. Incorporating movement into your daily routine, whether through structured workouts or active leisure activities, can help maintain a healthy weight, improve cardiovascular health, and boost overall well-being.
Monitoring Blood Pressure and Lipid Profiles
Effective diabetes management extends beyond blood sugar levels. Controlling blood pressure and lipid levels—cholesterol and triglycerides—is equally crucial in reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications. Regular blood pressure measurements should be taken during medical visits, and routine lipid panels can be performed every five years or more frequently if advised by your healthcare provider. The HbA1c test, which offers an average blood glucose reading over two to three months, is recommended at least twice yearly to assess long-term control.
Maintaining a heart-healthy diet, engaging in physical activity, and adhering to prescribed medications are vital components of managing these parameters. Routine monitoring and timely adjustments in treatment plans help prevent emergencies like hypertensive crises or lipid abnormalities that can exacerbate diabetes-related health issues.
Collaborative Care and Education for Long-term Success
Diabetes management is most effective when approached collaboratively. Working closely with healthcare professionals, including endocrinologists, dietitians, and primary care providers, ensures personalized treatment plans that accommodate your specific needs. Support systems such as family, friends, or diabetes education groups provide emotional encouragement and practical advice, reinforcing your commitment to lifestyle changes.
Participating in diabetes education programs helps enhance your understanding of the condition, medication management, dietary choices, and the importance of regular screenings. Peer support networks offer motivation, shared experiences, and accountability, making it easier to stay on track. Remember, managing diabetes is a continuous process that requires dedication, education, and a proactive attitude.
Adopting these strategies can lead to better blood glucose control, prevention of complications, and an improved quality of life. With informed decisions and ongoing support, managing diabetes becomes an achievable goal that can significantly impact your overall health and well-being.