Comprehensive Guide to Managing Blood Sugar with Effective Exercise Routines
Discover how effective, enjoyable exercise routines can help manage blood sugar levels. Learn practical tips on monitoring glucose, choosing suitable activities, and integrating workouts into your daily life for improved diabetes control and overall wellness.
Comprehensive Guide to Managing Blood Sugar with Effective Exercise Routines
Contrary to common misconceptions, exercise is beneficial for individuals of all ages, including seniors and those with limited energy levels. Engaging in physical activity is one of the most effective ways to regulate blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and enhance overall health. Many think that exercise requires intense effort, but even moderate activities can significantly contribute to better blood glucose control. This comprehensive guide explores various workout strategies tailored for blood sugar management, highlighting the importance of choosing enjoyable activities, monitoring blood glucose levels, and integrating exercise into daily routines for optimal health outcomes.
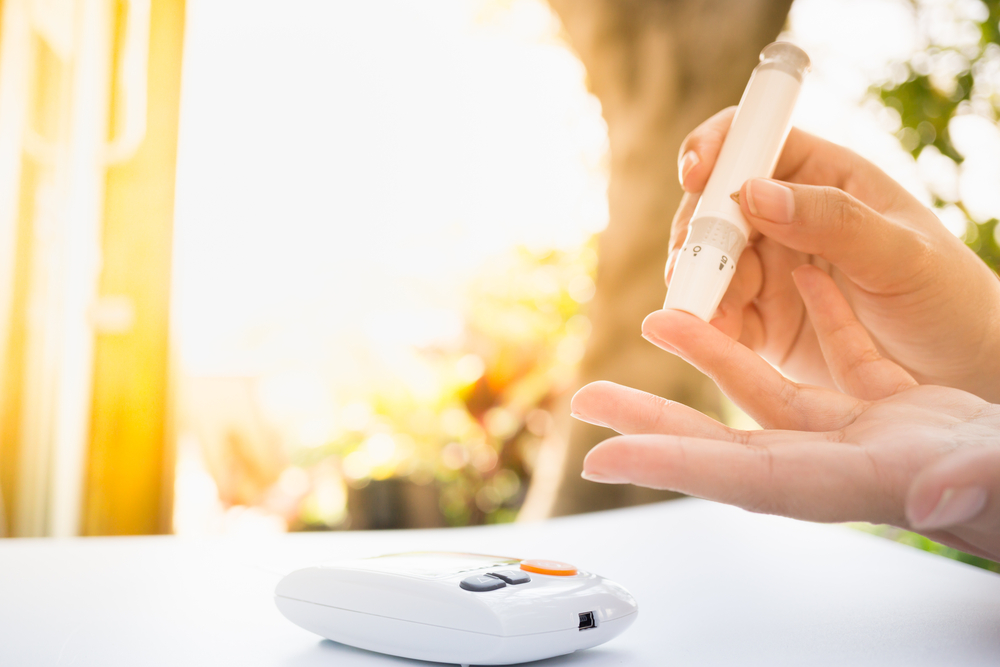
For effective blood sugar regulation, it is crucial to monitor your blood glucose levels before and after physical activity. This helps you understand how different exercises impact your blood sugar and allows you to make necessary adjustments. Always consult with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized exercise plan that takes into account your age, health status, and fitness level. A professional's guidance ensures that your chosen activities are safe and effective.
Engaging in activities you genuinely enjoy not only makes exercise more sustainable but also enhances the mental health benefits associated with physical activity. Popular options include dancing, brisk walking (both indoors and outdoors), swimming, water aerobics, tennis, and gardening. These activities are not only enjoyable but are also excellent for lowering blood sugar levels and improving the body’s insulin response. Incorporating a variety of these exercises into your routine can help prevent boredom and maintain motivation.
During moderate-intensity exercises such as walking, your heart rate elevates, and your breathing becomes deeper and more rhythmic. This physiological response prompts your muscles to consume more glucose, which in turn helps lower blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity can provide sustained benefits that last several hours, especially when performed post-meal. This is because muscles actively use blood glucose during and after exercise, reducing the amount circulating in your bloodstream.
Planning workouts around meal times can maximize blood sugar benefits. For instance, taking your dog for a walk, joining a yoga session, or playing a friendly game of tennis after eating can be very effective. Before starting any exercise, it’s essential to check your blood sugar levels. If your readings are below 100 mg/dL, consult your healthcare provider for snack recommendations to prevent low blood sugar. Carrying quick-acting carbohydrate sources like glucose tablets or a small snack is advisable in case your blood sugar drops unexpectedly. Hydration is equally important; drink plenty of water before, during, and after exercise to stay well-hydrated and support metabolic processes.
To monitor progress and refine your exercise plan, keep a detailed record of your workout durations and blood sugar levels before and after physical activity. Tracking this data enables you to identify patterns and make informed adjustments to optimize blood sugar control. Over time, consistent exercise can lead to improved glycemic stability, higher energy levels, and better overall health. Remember, the key is to start gradually, listen to your body, and stay committed to a routine that brings you joy and health benefits.